Abstract
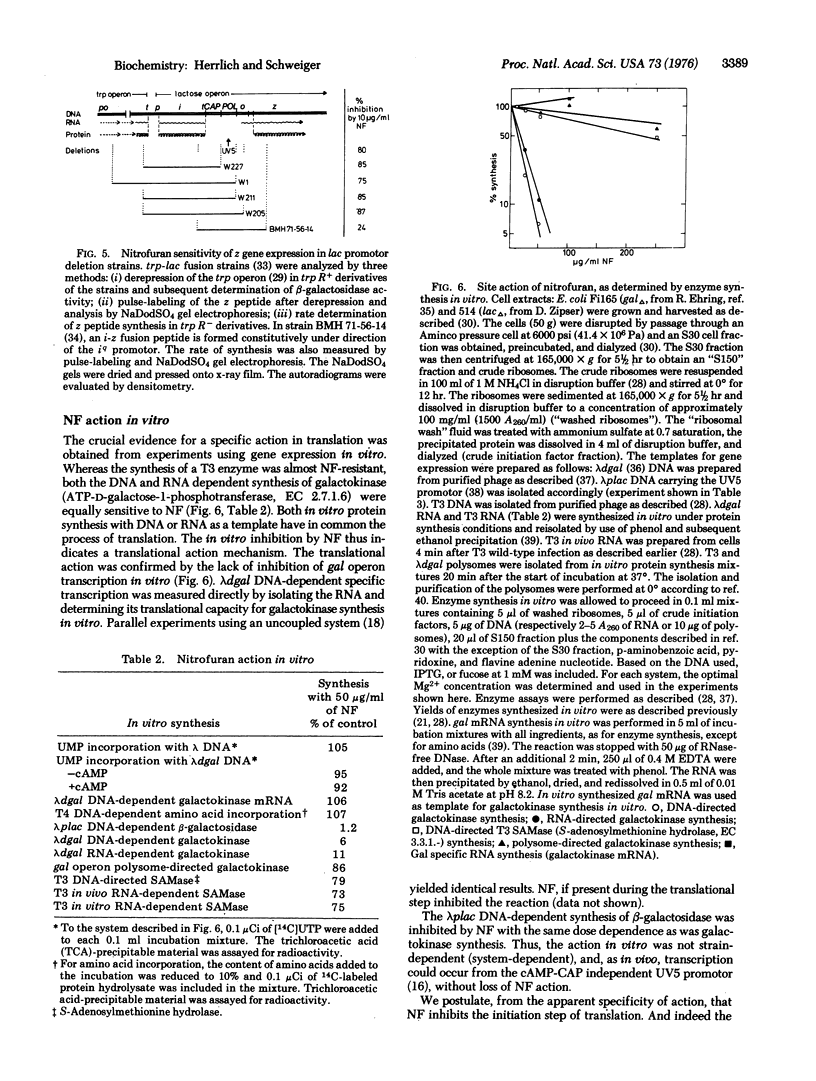
Nitrofurans, a class of antibacterial drugs in extensive use, interferes with gene expression in a highly specific manner. While in the low dose range (0.5-25 mug/ml), 5-nitro-2-furfurylidene-1-aminohydantoin has no effect on transcription, it inhibits specifically the expression of one class of genes in translation. The specific inhibition concerns the inducible genes. The inhibition of messenger RNA expression occurs at the initiation step. The action of nitrofurans, thus, indicates heterogeneity in the population of mRNA molecules and in the translational machinery and suggests the possibility of selective translational control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arditti R. R., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The nature of mutants in the lac promoter region. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE A. F., GOTS J. S. Nitrofurans as electron acceptors for certain respiratory enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;39(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer D. L. The Mode of Action of Nitrofuran Compounds: II. Application of Physicochemical Methods to the Study of Action against Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1947 Aug;54(2):119–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiethen L., Starlinger P. Mutations in the galactose-operator. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(4):322–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00267769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. I., Gibson F. Preliminary studies on the isolation and metabolism of an intermediate in aromatic biosynthesis: chorismic acid. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):248–256. doi: 10.1042/bj0900248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. Loci for radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli strain Bs-1. Genetics. 1967 Feb;55(2):193–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. F., SIMSON E. A study of radiosensitive and radioresistant mutants of Escherichia coli strain B. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jan;24:1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R., Rothman-Denes L. B. Protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:397–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Pai S. H., Schweigher M. Translational control induced by bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1088–1092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ippen K., Miller J. H., Scaife J., Beckwith J. New controlling element in the Lac operon of E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):825–827. doi: 10.1038/217825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis G., Saedler H., Venkov P., Starlinger P. Two insertions in the galactose operon having different sizes but homologous DNA sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1969 Aug 15;104(4):371–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00334236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Reckendorf H. K. The nitrofurans. Prog Med Chem. 1967;5:320–381. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Kania J. Lac repressor can be fused to beta-galactosidase. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):561–563. doi: 10.1038/249561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouwels P. H., Stevens W. F. Expression of the trp operon in phi80trp transducing phages. Orientation of transcription and an artificial high-efficiency promotor in phage lambda h +phi80 pt5-2AB. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 18;120(1):55–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00332984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röschenthaler R., Kindler P., Herrlich P., Igbokwe J. The action of nitrofurantoin: inhibition of growth of Escherichia coli K 12 and of IPTG-induced beta-galaotosidase synthesis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(2):203–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher G., Ehring R. Effect of different conformations of galactose messenger RNA on gene expression and messenger half-life in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;136(1):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00275447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Herrlich P. DNA-directed enzyme synthesis in vitro. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;65:59–132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65875-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Herrlich P., Millette R. L. Gene expression in vitro from deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6707–6712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J., Machattie L., Eron L., Ihler G., Ippen K., Beckwith J. Isolation of pure lac operon DNA. Nature. 1969 Nov 22;224(5221):768–774. doi: 10.1038/224768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstone A. E., Arditti R. R., Magasanik B. Catabolite-insensitive revertants of lac promoter mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):773–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Wallace B. J., Herzog E. L., Davis B. D. Properties of initiation-free polysomes of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):609–615. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazima Y., Kada T., Murakami A. Mutagenicity of nitrofuran derivatives, including furylfuramide, a food preservative. Mutat Res. 1975;32(1):55–80. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(75)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetekam W., Staack K., Ehring R. DNA-dependent in vitro synthesis of enzymes of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(1):14–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00266928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiessbach H., Brot N. The role of protein factors in the biosynthesis of proteins. Cell. 1974 Jul;2(3):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]