Abstract
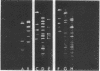
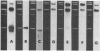
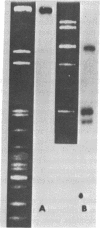
The closed-circular DNA molecules of 85 × 106 daltons from Zea mays chloroplasts were isolated, digested with the restriction endonucleases Sal I, Bam I, and EcoRI, and the resulting fragments sized by agarose gel electrophoresis. A map of maize chloroplast DNA showing the relative location of all the Sal I recognition sequences and many of the Bam I and EcoRI recognition sites was determined. A DNA sequence representing approximately 15% of the Zea mays chloroplast genome is repeated. The two copies of this sequence are in an inverted orientation with respect to one another and are separated by a nonhomologous sequence representing approximately 10% of the genome length. The inverted repeats contain the genes for chloroplast ribosomal RNAs.
Keywords: chloroplast rRNAs, Sal I, Bam I, EcoRI, hybridization
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelberg E. A., Bergquist P. The stabilization of episomal integration by genetic inversion: a general hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2061–2065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allet B., Solem R. Separation and analysis of promoter sites in bacteriophage lambda DNA by specific endonucleases. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Thomas C. A., Jr Molecular cloning of DNA fragments produced by restriction endonucleases Sa1I and BamI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1537–1541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Smith M. G. The chromosome of bacteriophage T5. I. Analysis of the single-stranded DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. DNA nucleotide sequence restricted by the RI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Bohnert H. J., Kowallik K. V., Schmitt J. M. Size, conformation and purity of chloroplast DNA of some higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 20;378(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Chan R. K., Tye B. K., Botstein D. Mutagenesis by insertion of a drug-resistance element carrying an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Tewari K. K. Denaturation mapping studies on the circular chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from pea leaves. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4888–4895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. The molecular size and conformation of the chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):372–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Cohen S. N. Site specific recA--independent recombination between bacterial plasmids: involvement of palindromes at the recombinational loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1373–1377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton J. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Specific fragments of phi X174 deoxyribonucleic acid produced by a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease Z. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.42-50.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne K., Cohen S. N. Occurrence of insertion sequence (IS) regions on plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid as direct and inverted nucleotide sequence duplications. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):776–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.776-781.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Manning J. E., Davidson N. Inverted repeat sequences in the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos A. C., Bogorad L. Proteins of cytoplasmic, chloroplast, and mitochondrial ribosomes of some plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):492–502. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. A., Thomas C. A., Jr Palindromes in chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 25;84(1):115–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Isolation of a sequence-specific endonuclease (BamI) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]