Abstract
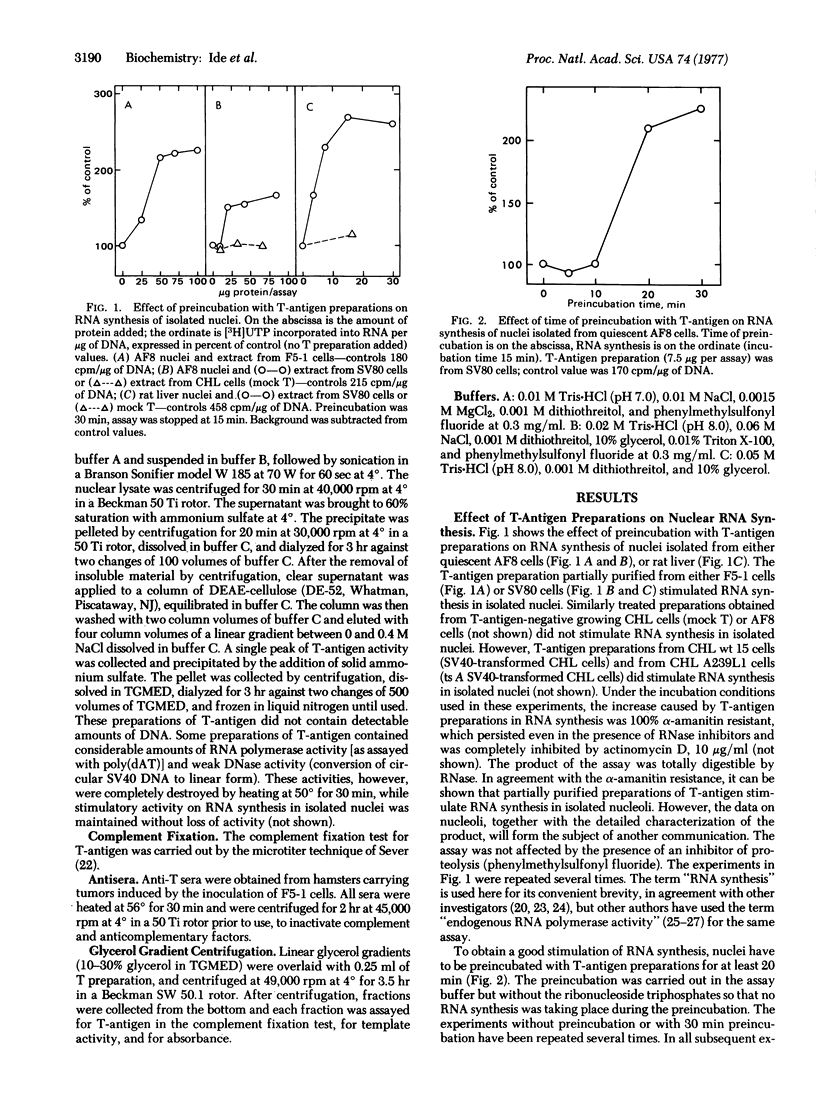
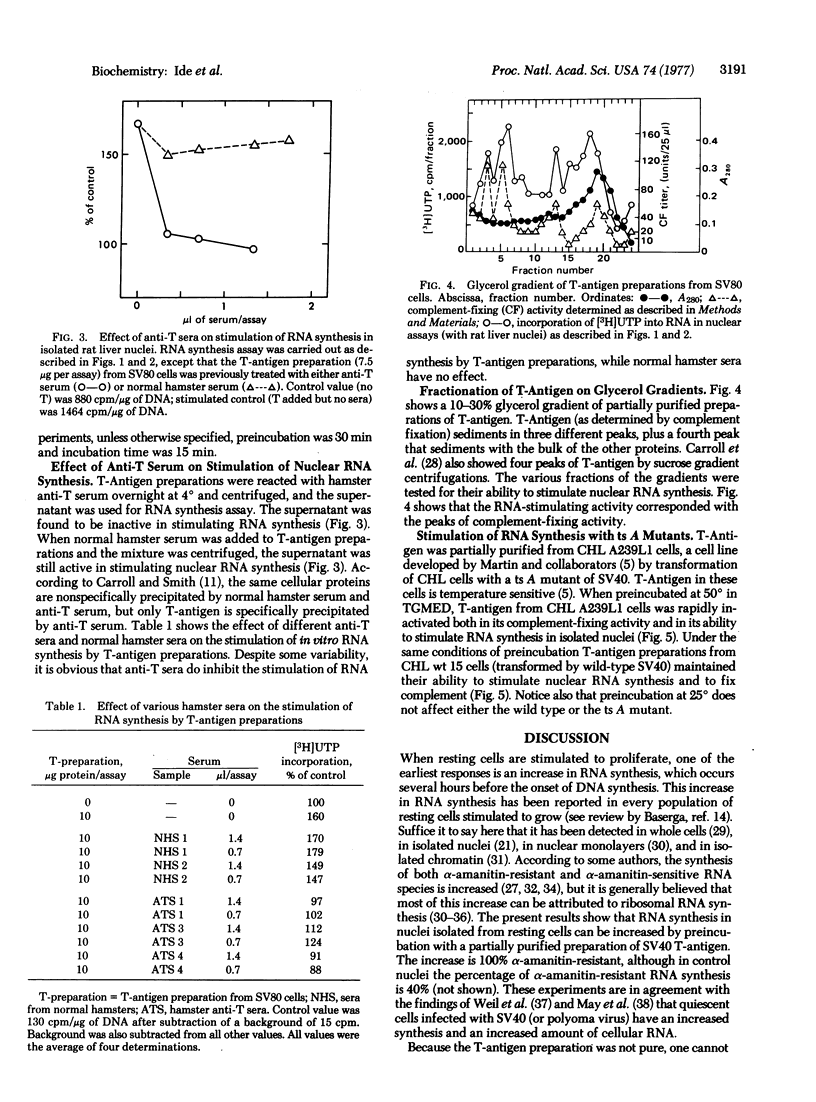
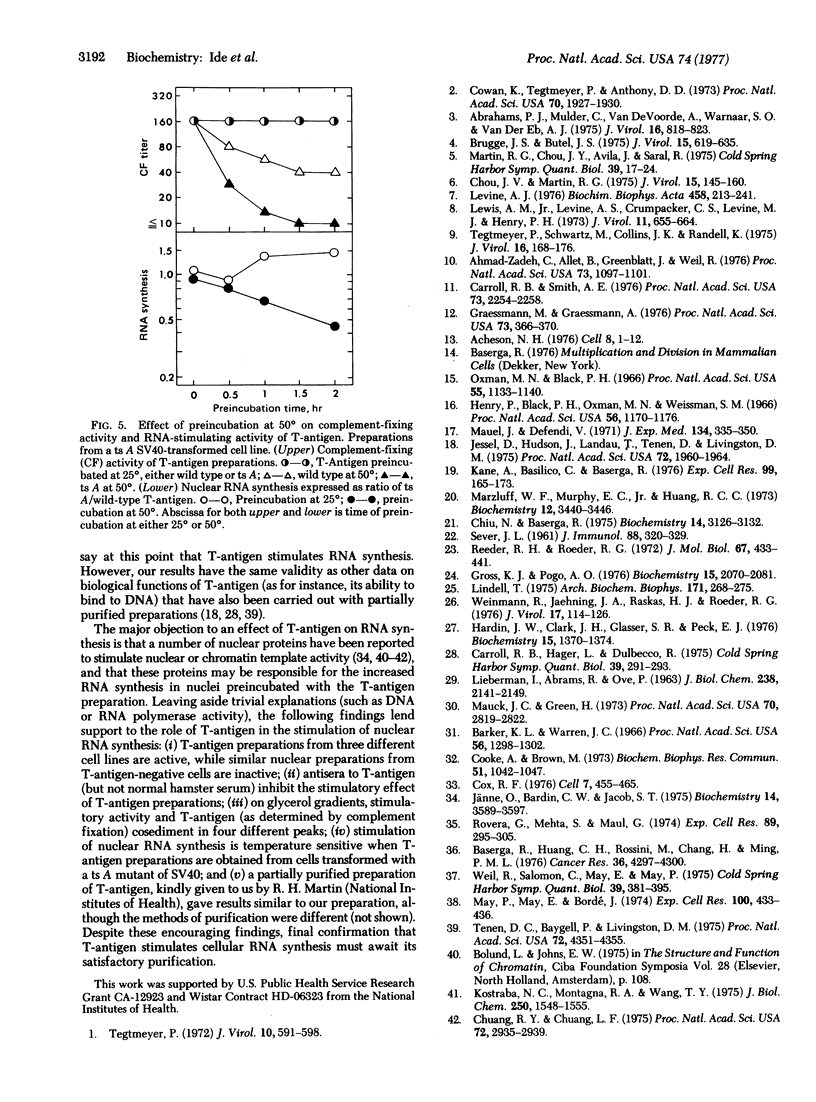
T-Antigen was partially purified from nuclei of cells transformed by simian virus 40 (SV 40). When nuclei isolated from either rat liver or quiescent hamster cells were preincubated with T-antigen preparations, there was a marked stimulation of RNA synthesis in an in vitro assay, up to 150% above control levels. The stimulation of RNA synthesis was inhibited by hamster antiserum against T-antigen but not by normal hamster serum. When the T-antigen preparations were fractionated on glycerol gradients, the fractions containing complement-fixing activity with antiserum to T-antigen also had the highest stimulatory activity on nuclear RNA synthesis. T-Antigen was also partially purified from nuclei of cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive A mutant of SV40. When preincubated up to 2 hr at 50 degrees, the T-antigen preparation from these temperature-sensitive A mutants was rapidly inactivated, in terms of both complement-fixing activity and ability to stimulate RNA synthesis in isolated rat liver nuclei. Under the same conditions of preincubation, T-antigen preparations from cells transformed by wild-type SV40 maintained their complement-fixing activity and ability to stimulate RNA synthesis. These results suggest that the biological action of T-antigen may be exerted at the level of transcription.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Van De Voorde A., Warnaar S. O., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of primary rat kidney cells by fragments of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.818-823.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Transcription during productive infection with polyoma virus and Simian virus 40. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad-Zadeh C., Allet B., Greenblatt J., Weil R. Two forms of simian-virus-40-specific T-antigen in abortive and lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker K. L., Warren J. C. Template capacity of uterine chromatin: control by estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Huang C. H., Rossini M., Chang H., Ming P. M. The role of nuclei and nucleoli in the control of cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4297–4300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Dissociation and DNA binding of SV40 T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):291–293. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Smith A. E. Monomer molecular weight of T antigen from simian virus 40-infected and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2254–2258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu N., Baserga R. Changes in template activity and structure of nuclei from WI-38 cells in the prereplicative phase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3126–3132. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. DNA infectivity and the induction of host DNA synthesis with temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):145–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.145-150.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang R. Y., Chuang L. F. Increased frequency of initiation of RNA synthesis due to a protein factor from chicken myeloblastosis nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2935–2939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A., Brown M. Stimulation of the activities of solubilized pig lymphocyte RNA polymerases by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):1042–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K., Tegtmeyer P., Anthony D. D. Relationship of replication and transcription of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1927–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Quantitation of elongating form A and B RNA polymerases in chick oviduct nuclei and effects of estradiol. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K. J., Pogo A. O. Control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in eukaryotes. 2. The effect of protein synthesis on the activities of nuclear and total DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in yeast. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2070–2081. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. W., Clark J. H., Glasser S. R., Peck E. J., Jr RNA polymerase activity and uterine growth: Differential stimulation by estradiol, estriol, and nafoxidine. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 6;15(7):1370–1374. doi: 10.1021/bi00652a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P., Black P. H., Oxman M. N., Weissman S. M. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in mouse cell line 3T3 by Simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1170–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessel D., Hudson J., Landau T., Tenen D., Livingston D. M. Interaction of partially purified simian virus 40 T antigen with circular viral DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1960–1964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänne O., Bardin C. W., Jacob S. T. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases I and II from kidney. Effect of polyamines on the in vitro transcription of DNA and chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3589–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane G., Basilico C., Basterga R. Transcriptional activity and chromatin structural changes in a temperature-sensitive mutant of BHK cells blocked in early G1. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostraba N. C., Montagna R. A., Wang T. Y. Study of the loosely bound non-histone chromatin proteins. Stimulation of deoxyribonucleic acid-templated ribonucleic acid synthesis by a specific deoxyribonucleic acid-binding phosphoprotein fraction. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1548–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., ABRAMS R., OVE P. Changes in the metabolism of ribonucleic acid preceding the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid in mammalian cells cultured from the animal. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2141–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. SV40 and adenovirus early functions involved in DNA replication and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 12;458(3):213–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Samaha R. J., Henry P. H. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. V. Isolation of additional hybrids which differ in their simian virus 40-specific biological properties. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.655-664.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J. Inhibition of eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerase release from isolated nuclei and nucleoli by phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y., Avila J., Saral R. The semiautonomous replicon: a molecular model for the oncogenicity of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J. C., Green H. Regulation of RNA synthesis in fibroblasts during transition from resting to growing state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2819–2822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauel J., Defendi V. Infection and transformation of mouse peritoneal macrophages by simian virus 40. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):335–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Bordé J. Stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis in mouse-kidney cell cultures infected with SV40 virus. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Black P. H. Inhibition of SV40 T antigen formation by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1133–1140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roeder R. G. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Mehta S., Maul G. Ghost monolayers in the study of the modulation of transcription in cultures of CV1 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Dec;89(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90793-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Baygell P., Livingston D. M. Thermolabile T (tumor) antigen from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4351–4355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Jaehning J. A., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Viral RNA synthesis and levels of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases during replication of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.114-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


