Abstract
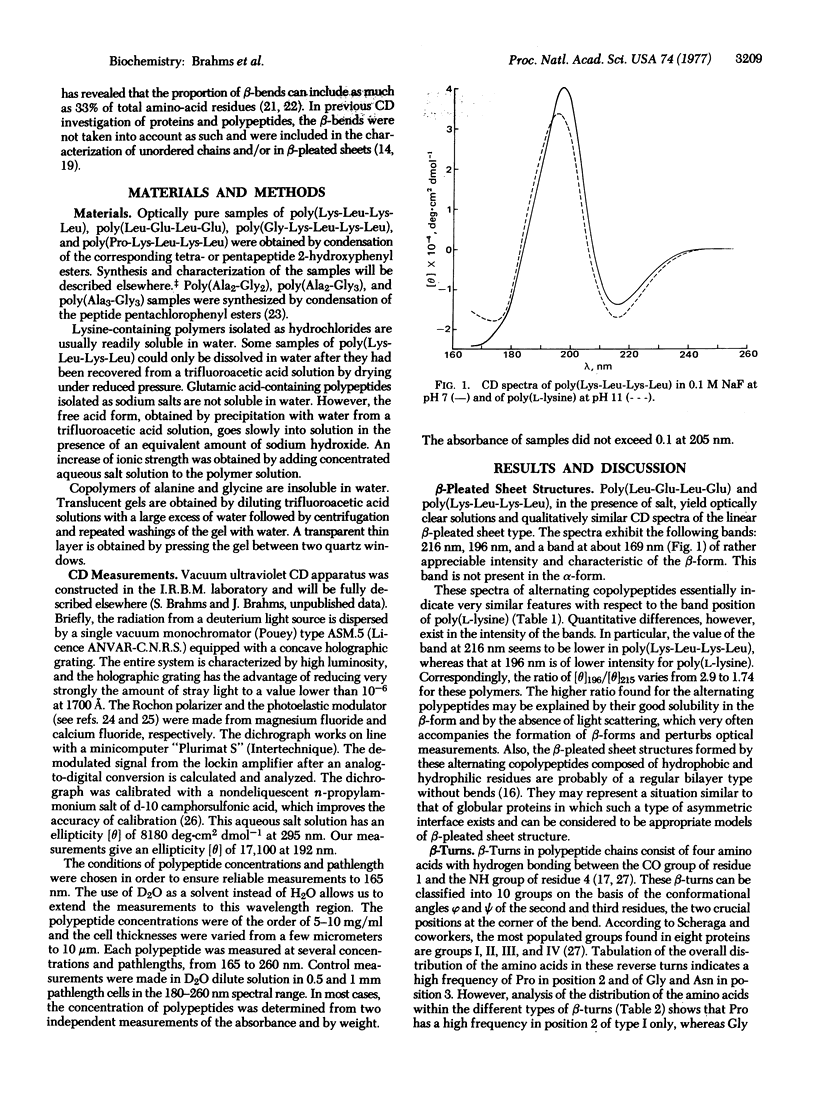
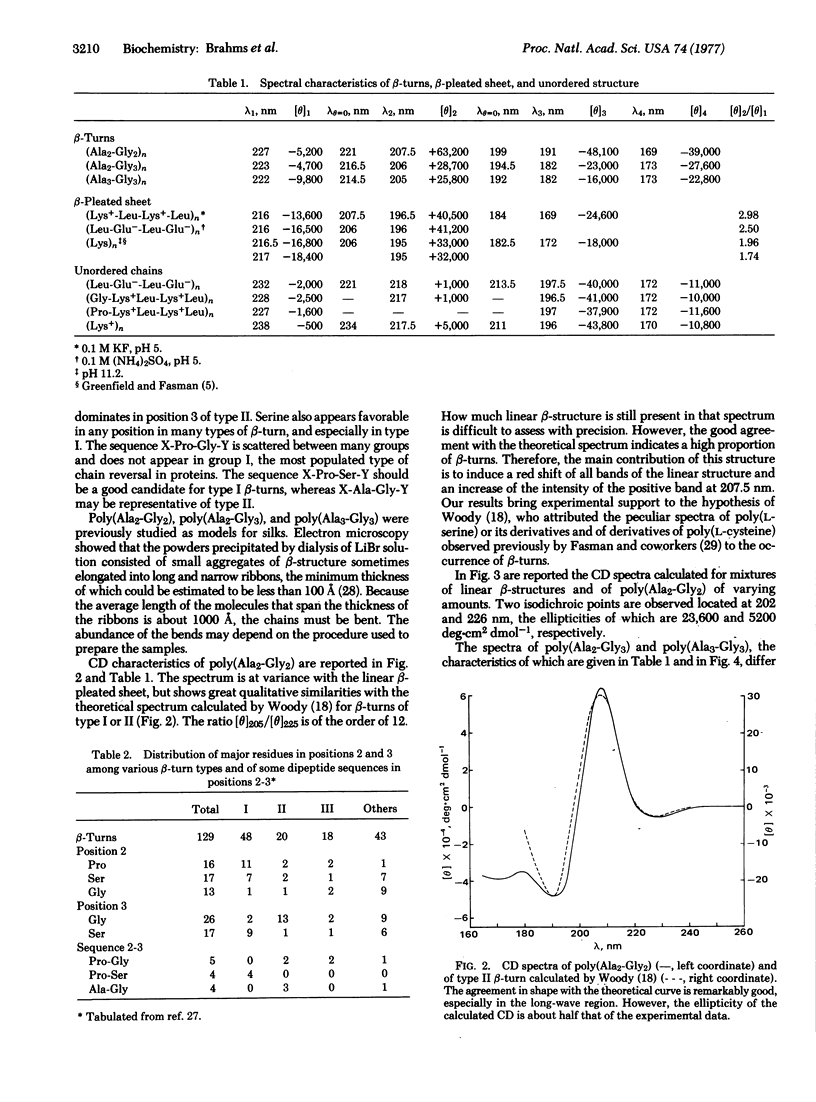
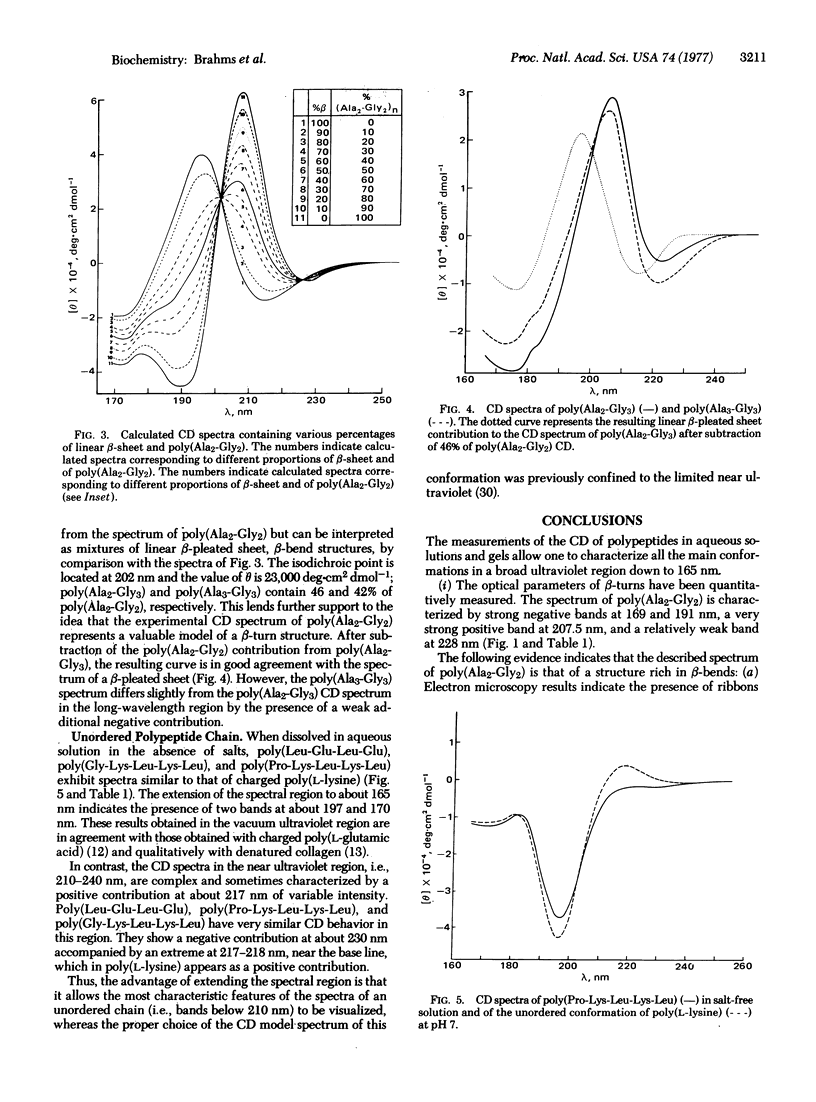
Different conformations of polypeptides were characterized by measurements of the circular dichroism (CD) extended into the vacuum ultraviolet region. (i) The linear β-pleated sheet structure was characterized in a broad ultraviolet region down to 165 nm by examination of copolypeptides composed of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino-acid residues, e.g., poly(Lys-Leu-Lys-Leu). A short-wavelength intense band was found at about 169 nm, which is characteristic of β-pleated sheet conformation. (ii) The β-turns were experimentally measured using poly(Ala2-Gly2) in a broad spectral region down to 165 nm with accuracy. The observed CD spectrum is in excellent qualitative agreement with the theoretical curve calculated by Woody for the β-turns of type II and/or I of Venkatachalam. The similarity in shape between the theoretical curve and the observed CD spectra suggests a dominance of β-turn segments in the poly(Ala2-Gly2) structure. The presence of β-turns in poly(Ala2-Gly2) is also in agreement with the characterization of this polypeptide by solid state methods (electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction). The CD spectrum of β-turns is characterized by a very intense band at 207.5 nm and strong negative bands at 191 and 169 nm. Copolypeptides such as poly(Ala2-Gly3) and poly(Ala3-Gly3) yielded a similar type of CD spectrum, analysis of which indicates that a large fraction of their residues is contained in β-turn regions. (iii) The CD spectrum of the unordered chain of these alternating copolypeptides in salt-free solution is observed in the vacuum ultraviolet region.
Keywords: polypeptide conformation, β-pleated sheets, reverse turns, protein structure
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Isenberg I. On the analysis of circular dichroic spectra of proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):629–634. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcerski J. S., Pysh E. S., Bonora G. M., Toniolo C. Vacuum ultraviolet circular dichroism of beta-forming alkyl oligopeptides. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Jun 9;98(12):3470–3473. doi: 10.1021/ja00428a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack A., Orgel L. E. Beta structures of alternating polypeptides and their possible prebiotic significance. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):383–387. doi: 10.1038/256383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack A., Spach G. Synthesis and conformations of periodic copolypeptides of L-alanine and Glycine. Biopolymers. 1972 Mar;11(3):563–586. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Conformation of twisted beta-pleated sheets in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. L., Lipscomb W. N., Schellman C. G. The reverse turn as a polypeptide conformation in globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):538–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D., Potter J. The optical rotatory dispersion of two beta structures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZWARTH G., DOTY P. THE ULTRAVIOLET CIRCULAR DICHROISM OF POLYPEPTIDES. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jan 20;87:218–228. doi: 10.1021/ja01080a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka E., Yang J. T. Optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism of the beta-form of silk fibroin in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1175–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Sprecher C., Johnson W. C., Jr Circular dichroism of collagen, gelatin, and poly(proline) II in the vacuum ultraviolet. Biopolymers. 1976 Mar;15(3):513–521. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Jr, Tinoco I., Jr Circular dichroism of polypeptide solutions in the vacuum ultraviolet. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 14;94(12):4389–4392. doi: 10.1021/ja00767a084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Fasman G. D. The beta conformation of polypeptides of valine, isoleucine, and threonine in solution and solid-state: optical and infrared studies. Biopolymers. 1975 Mar;14(3):605–631. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. N., Momany F. A., Scheraga H. A. Folding of polypeptide chains in proteins: a proposed mechanism for folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2293–2297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz B., Brack A., Spach G. Beta structure of periodic copolypeptides of L-alanine and glycine. Their relevance to the structure of silks. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 5;87(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison V., Schellman J. Optical activity of polypeptides and proteins. Biopolymers. 1972;11(5):1041–1076. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quadrifoglio F., Urry D. W. Ultraviolet rotatory properties of polypeptides in solution. II. Poly-L-serine. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 May 22;90(11):2760–2765. doi: 10.1021/ja01013a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Doty P. The optical rotatory properties of the beta-configuration in polypeptides and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):981–989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany M. L., Krimm S. Effect of temperature on the circular dichroism spectra of polypeptides in the extended state. Biopolymers. 1972;11(11):2309–2316. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townend R., Kumosinski T. F., Timasheff S. N., Fasman G. D., Davidson B. The circular dichroism of the beta structure of poly-L-lysine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Apr 19;23(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Long M. M., Ohnishi T., Jacobs M. Circular dichroism and absorption of the polytetrapeptide of elastin: a polymer model for the beta-turn. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1427–1433. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam C. M. Stereochemical criteria for polypeptides and proteins. V. Conformation of a system of three linked peptide units. Biopolymers. 1968 Oct;6(10):1425–1436. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360061006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


