Abstract
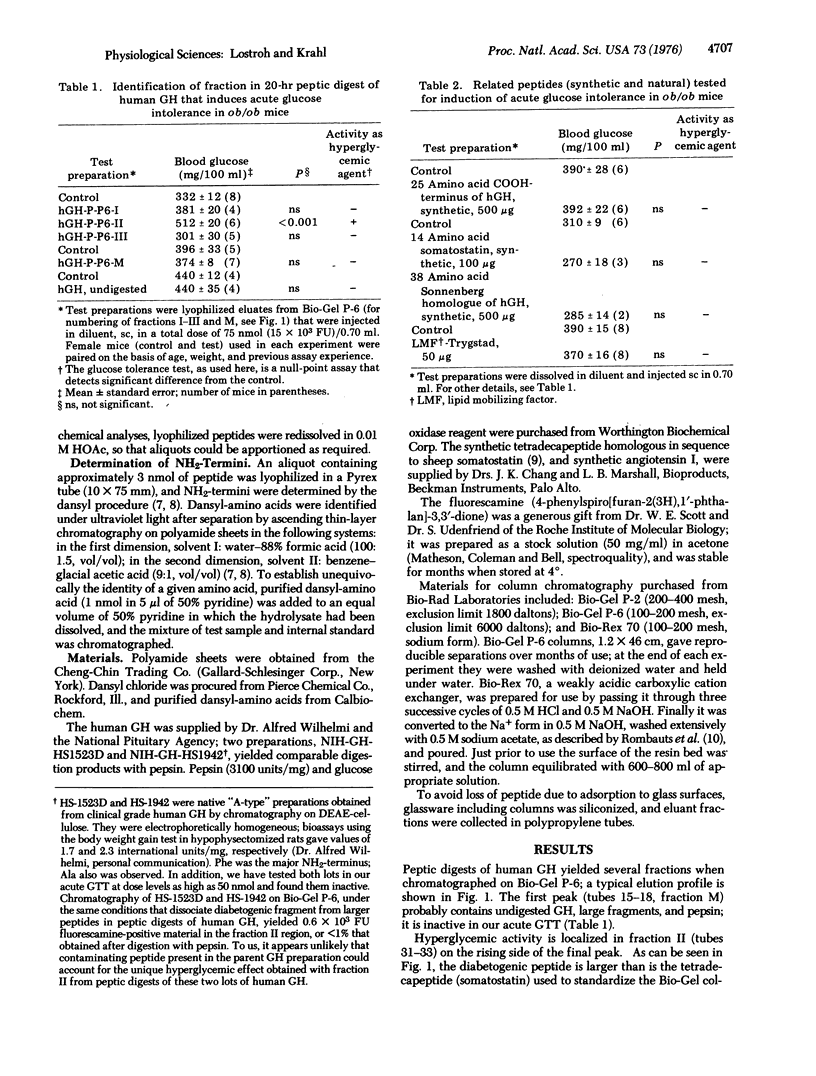
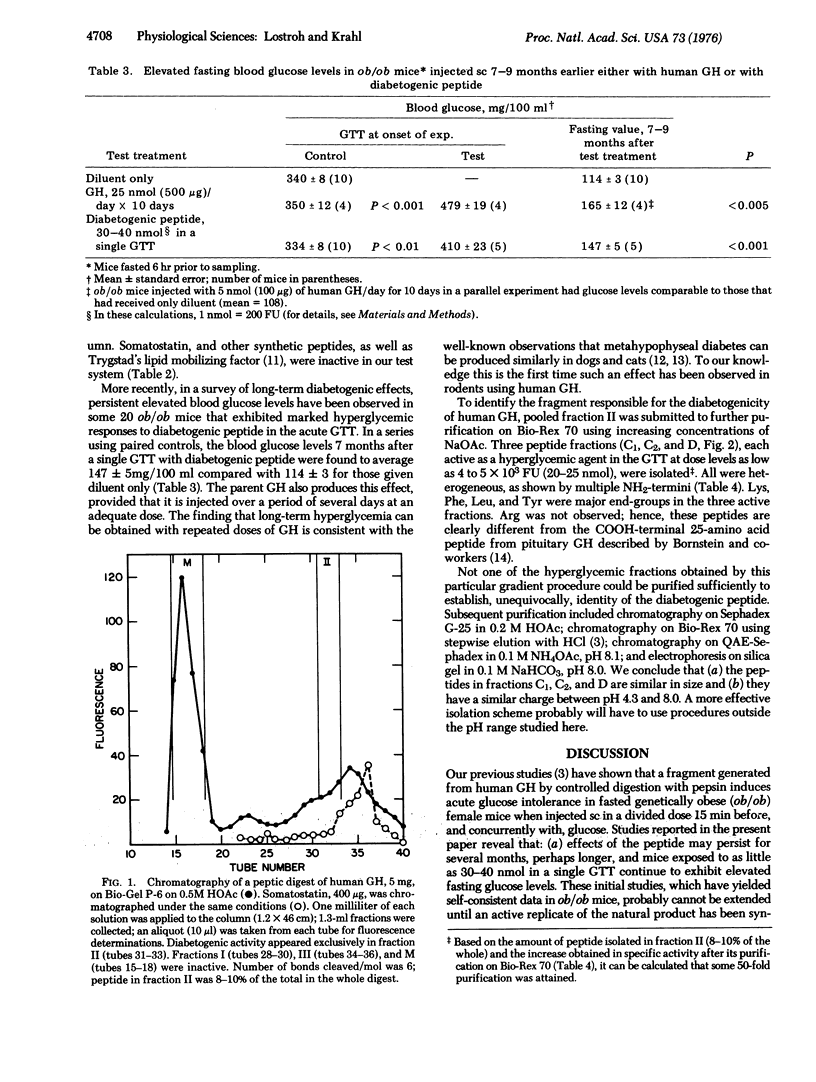
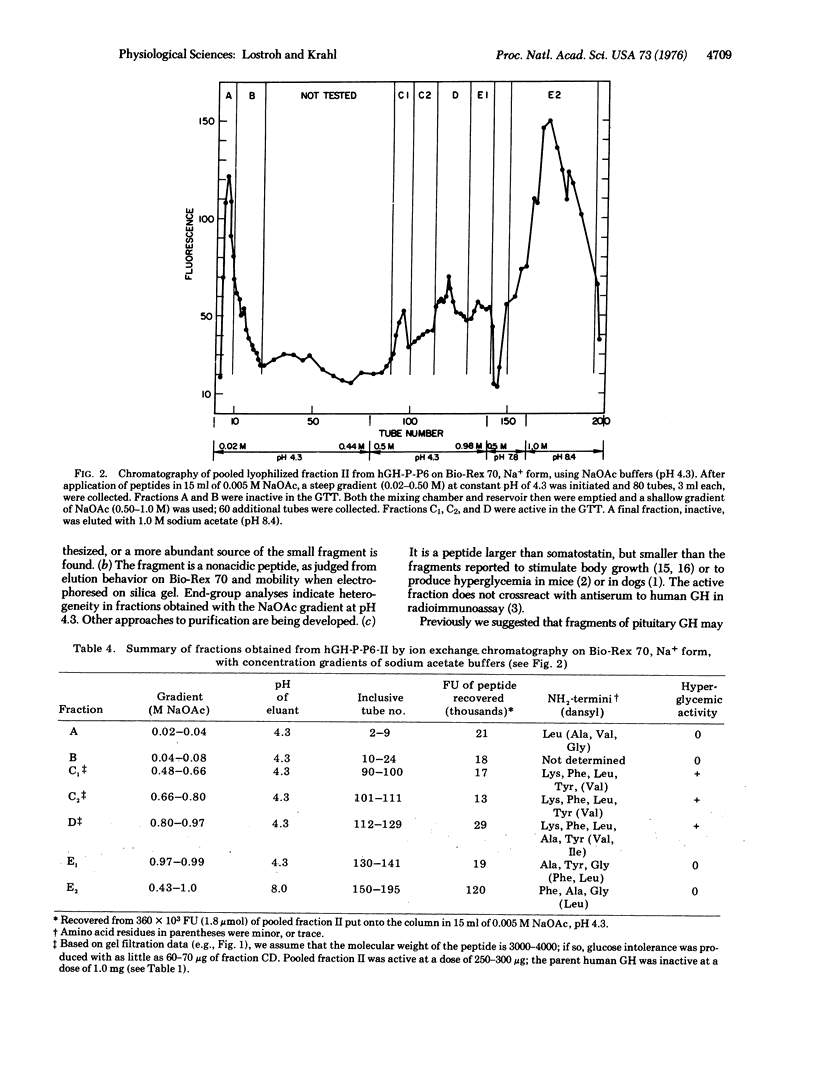
Studies in female ob/ob mice demonstrated diabetogenic properties of human growth hormone (somatotropin) and of a fragment generated therefrom by controlled digestion with pepsin; both the fragment and parent growth hormone produce long-term effects on carbohydrate metabolism; in acute glucose tolerance tests, only the fragment is active. Two nonacidic diabetogenic fractions have been separated from inactive fractions by chromatography on Bio-Gel P-6 followed by ion exchange chromatography at pH 4.3 and gel filtration on Bio-Gel P-2 and/or Sephadex G25; these active fractions exhibited multiple NH2-terminal (Lys, Phe, Leu, and Tyr). Fraction CD has these characteristics: (i) It induces glucose intolerance in fasting female ob/ob mice when injected subcutaneously in a divided dose, 15 min before and concurrently with glucose; mice injected with sufficient peptide exhibit elevated fasting glucose levels as long as 7 months after a single glucose tolerance test. (ii) It is a peptide smaller than that reported to stimulate body growth, but larger than somatostatin. This peptide, as reported earlier, does not crossreact with antiserum to human growth hormone in radioimmunoassay.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bornstein J., Armstrong J. M., Ng F., Paddle B. M., Misconi L. Structure and synthesis of biologically active peptides derived from pituitary growth hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Guillemin R. Primary structure of somatostatin, a hypothalamic peptide that inhibits the secretion of pituitary growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):684–688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL J., CHAIKOF L., DAVIDSON I. W. Metahypophyseal diabetes produced by growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1954 Jan;54(1):48–58. doi: 10.1210/endo-54-1-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M., Przybylski R. J., Rosenberg D. M. Insulin resistance in genetically obese, hyperglycemic mice. Endocrinology. 1971 May;88(5):1230–1238. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-5-1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETTERER B., RANDLE P. J., YOUNG F. G. The pituitary growth hormone and metabolic processes. Ergeb Physiol. 1957;49:127–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahl M. E. Insulin action at the molecular level. Facts and speculations. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):695–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Pence S. J., Singh R. N., VanderLaan W. P. Enhancement of the growth promoting activity of human growth hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 17;67(2):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90857-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lostroh A. J., Krahl M. E. A hyperglycemic peptide from pituitary growth hormone: preparation with pepsin and assay in ob-ob mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1244–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reagan C. R., Mills J. B., Kostyo J. L., Wilhelmi A. E. Biological properties of plasmin digests of S-carbamidomethylated human growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1684–1686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombauts W. A., Schroeder W. A., Morrison M. Bovine lactoperoxidase. Partial characterization of the further purified protein. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):2965–2977. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trygstad O., Foss I. The lipid-mobilizing effect of some pituitary gland preparations. IV. Subdivision of a human growth hormone preparation into a somatotrophic and an adipokinetic-hyperglycaemic agent. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1968 Jun;58(2):295–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


