Abstract
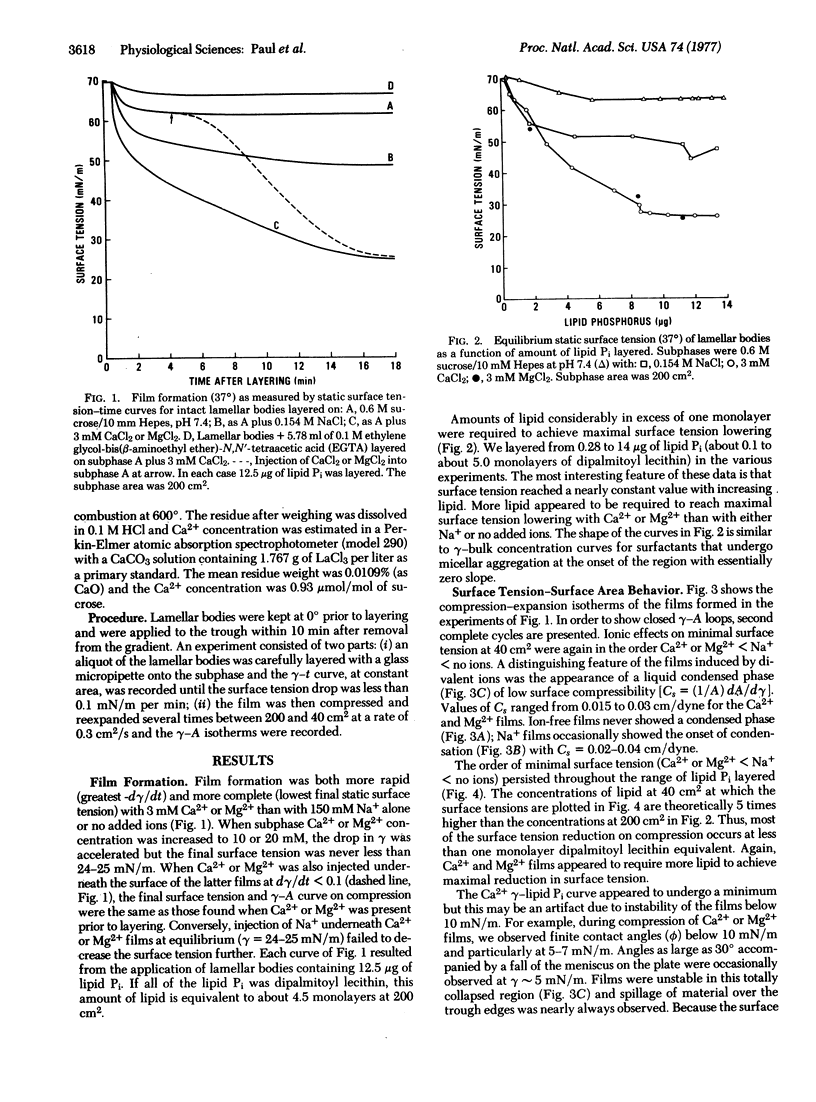
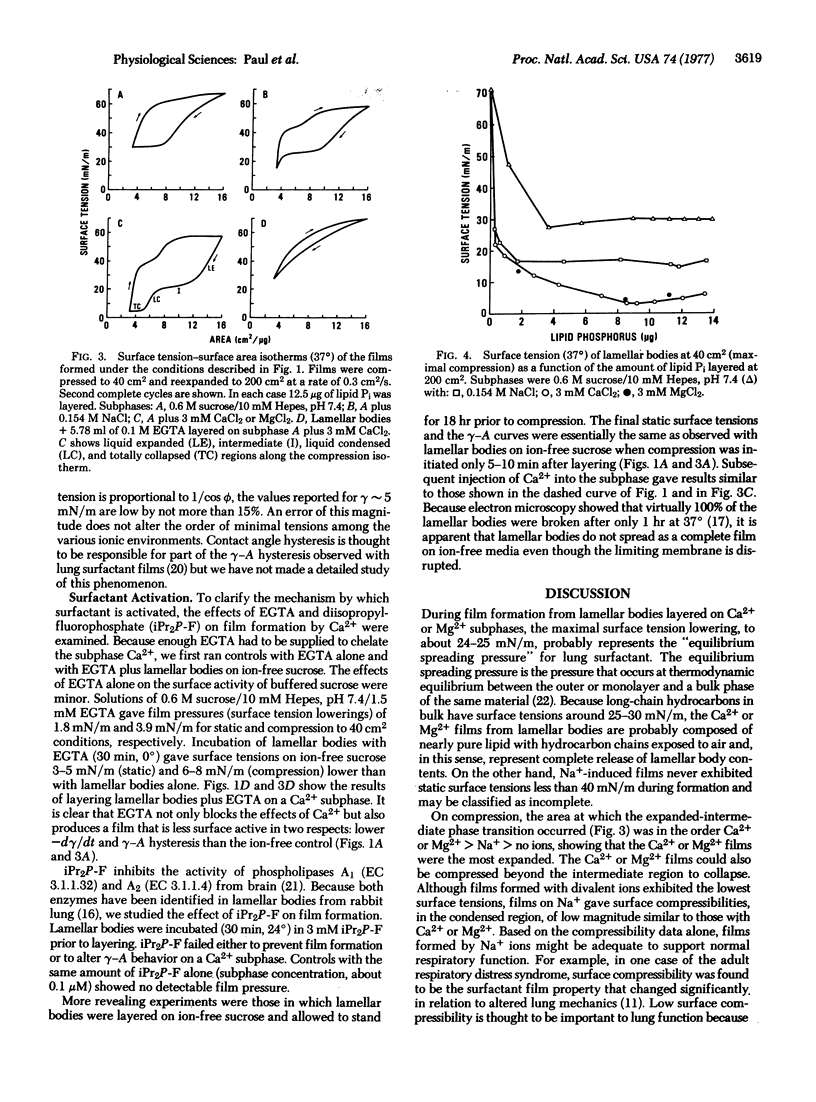
Lamellar bodies, an intracellular source of lung alveolar surfactant, were isolated from rat lung homogenates and studied in the Langmuir-Adams surface balance. By layering intact lamellar bodies on the surface of a more dense sucrose subphase, we studied the factors affecting film formation from surface tension-vs-time data and determined surface tension-surface area isotherms by compression and expansion of the resulting films. We found that films with properties representative of the alveolar surfactant are formed in the presence of Ca2+ or Mg2+ alone, or either plus Na+; that film formation is incomplete with Na+ alone or on ion-free subphases; and that Ca2+-induced film formation is blocked by chelation with EGTA but is unaffected by diisopropylfluorophosphate. The results suggest that divalent cations induce film formation by interactions at sites within the lamellar bodies and may be responsible for the binding of membrane lipids to membrane proteins in lung surfactant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSCH K., SCHAEFER K., AVERY M. E. GRANULAR PNEUMOCYTES: ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF THEIR EXOCRINIC FUNCTION. Science. 1964 Sep 18;145(3638):1318–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3638.1318-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENTS J. A., HUSTEAD R. F., JOHNSON R. P., GRIBETZ I. Pulmonary surface tension and alveolar stability. J Appl Physiol. 1961 May;16:444–450. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENTS J. A. Surface tension of lung extracts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):170–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. F., Webster G. R. The differentiation of phospholipase A1 and A2 in rat and human nervous tissues. J Neurochem. 1970 Nov;17(11):1543–1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J., Reiss O. K. Isolation and characterization of lamellar bodies and tubular myelin from rat lung homogenates. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):152–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Gluck L. Phosphatidylglycerol in lung surfactant. III. Possible modifier of surfactant function. J Lipid Res. 1976 May;17(3):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Miyai K., Wagner R. M. Isolated lamellar bodies from rat lung: correlated ultrastructural and biochemical studies. Lab Invest. 1976 Jul;35(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath M. F., Jacobson W. Phospholipases A1 and A2 in lamellar inclusion bodies of the alveolar epithelium of rabbit lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;441(3):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills B. A., Ng Y. L. Proceedings: Significance of the contact angle in studies of lung surfactant. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):52P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa Y., Motoyama E. K., Cook C. D. The ultrastructure of the lungs of lambs. The relation of osmiophilic inclusions and alveolar lining layer to fetal maturation and experimentally produced respiratory distress. Am J Pathol. 1965 Nov;47(5):877–903. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Clements J. A. Surface active materials from dog lung. II. Composition and physiological correlations. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):715–726. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd Cytochemistry of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1968 Nov;53(5):809–833. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTLE R. E. Properties, function and origin of the alveolar lining layer. Nature. 1955 Jun 25;175(4469):1125–1126. doi: 10.1038/1751125b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Reiss O. K., Paul G. W., Silvers G. W., Elkins N. D. Characteristics of pulmonary surfactant in adult respiratory distress syndrome associated with trauma and shock. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):531–536. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. C., Chapman D. Monolayer characteristics of saturated 1,2,-diacyl phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) and phosphatidylethanolamines at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenrath R., Zimmermann I. Blood plasma contamination of the lung alveolar surfactant obtained by various sampling techniques. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):238–248. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenrath R., Zimmermann I. Surface tension properties of lung alveolar surfactant obtained by alveolar micropuncture. Respir Physiol. 1973 Dec;19(3):369–393. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. J., Paul G. W., Vatter A. E., Filley G. F. Morphological and physical basis for lung surfactant action. Respir Physiol. 1976 Sep;27(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(76)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch S., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Direct determination of surface tension in the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4698–4702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin S P. A morphologic and cytochemical study on the great alveolar cell. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Dec;14(12):884–897. doi: 10.1177/14.12.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia E. Isolation and identification of pulmonary lamellar bodies from guinea pigs. Prep Biochem. 1973;3(1):19–30. doi: 10.1080/00327487308061486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Kistler G. S., Töndury G. A stereologic electron microscope study of "tubular myelin figures" in alveolar fluids of rat lungs. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;69:418–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00406293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


