Abstract
Apolipoprotein C-II (apoC-II) is a small protein found associated with the plasma lipoproteins. It serves a unique function in the activation of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase (triacylglycerol acyl-hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.3). ApoC-II contains a single arginine residue, permitting tryptic cleavage into two peptides after succinylation of the native protein. The succinylated amino-terminal peptide, approximately 50 residues, did not activate lipoprotein lipase. The succinylated carboxyl-terminal peptide, about 29 residues, had significant cofactor activity. Relative to native apoC-II, the maximal activation observed with the succinylated carboxyl-terminal peptide was 50% lower and the concentration required for half-maximal activity was approximately 10 times higher. Mixtures of the carboxyl- and amino-terminal peptides had no more activity than the carboxyl-terminal peptide alone. Localization of functional properties to the carboxyl region is a feature also common to apolipoproteins C-III, A-II, and A-I.
Full text
PDF

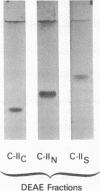
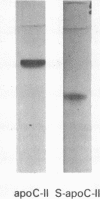
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Scanu A. M. Isoelectric fractionation and characterization of polypeptides from human serum very low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Ehnholm C., Steinberg D., Brown W. V. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2220–2227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further characterization of apolipoproteins from the human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6588–6594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further separation of the apoproteins of the human plasma very low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 31;200(3):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Scanu A. M., Reman F. Effect of phospholipids on lipoprotein lipase activation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Grossberg A. L., Pressman D. The effects of complete modification of amino groups on the antibody activity of antihapten antibodies. Reversible inactivation with maleic anhydride. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1941–1950. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Shore V. G., Shore B., Bier D. M. Role of specific glycopeptides of human serum lipoproteins in the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):595–600. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Shulman R. S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Fractionation of the C-apoproteins from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4941–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H. Coupling of glycosaminoglycans to agarose beads (sepharose 4B). Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1240677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Baker H. N., David J. S., Gotto A. M. Isolation of a helical, lipid-binding fragment from the human plasma high density lipoprotein, apoLP GLN-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1444–1451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90501-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr, Lux S. E., John K. M., Fleischer S. Human plasma high density lipoprotein. Interaction of the cyanogen bromide fragments from apolipoprotein glutamine II (A-II) with phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8449–8456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Sparrow J. T., Segrest J. P., Pownall H. J., Smith L. C., Hoff H. F., Gotto A. M., Jr The interaction of apolipoprotein-serine with phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5314–5320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN E. D. Clearing factor, a heparin-activated lipoprotein lipase. II. Substrate specificity and activation of coconut oil. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jul;215(1):15–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further observations on the activation and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):403–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Selective measurement of two lipase activities in postheparin plasma from normal subjects and patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1107–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI107855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Herbert P., Lux S. E., Fredrickson D. S. A specific apoprotein activator for lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Small P. A., Jr Electrophoretic heterogeneity of polypeptide chains of specific antibodies. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. Serum high-density lipoprotein: effect of change in structure on activity of chicken adipose tissue lipase. Science. 1966 Aug 5;153(3736):640–641. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3736.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B. Heterogeneity of human plasma very low density lipoproteins. Separation of species differing in protein components. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):502–507. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]