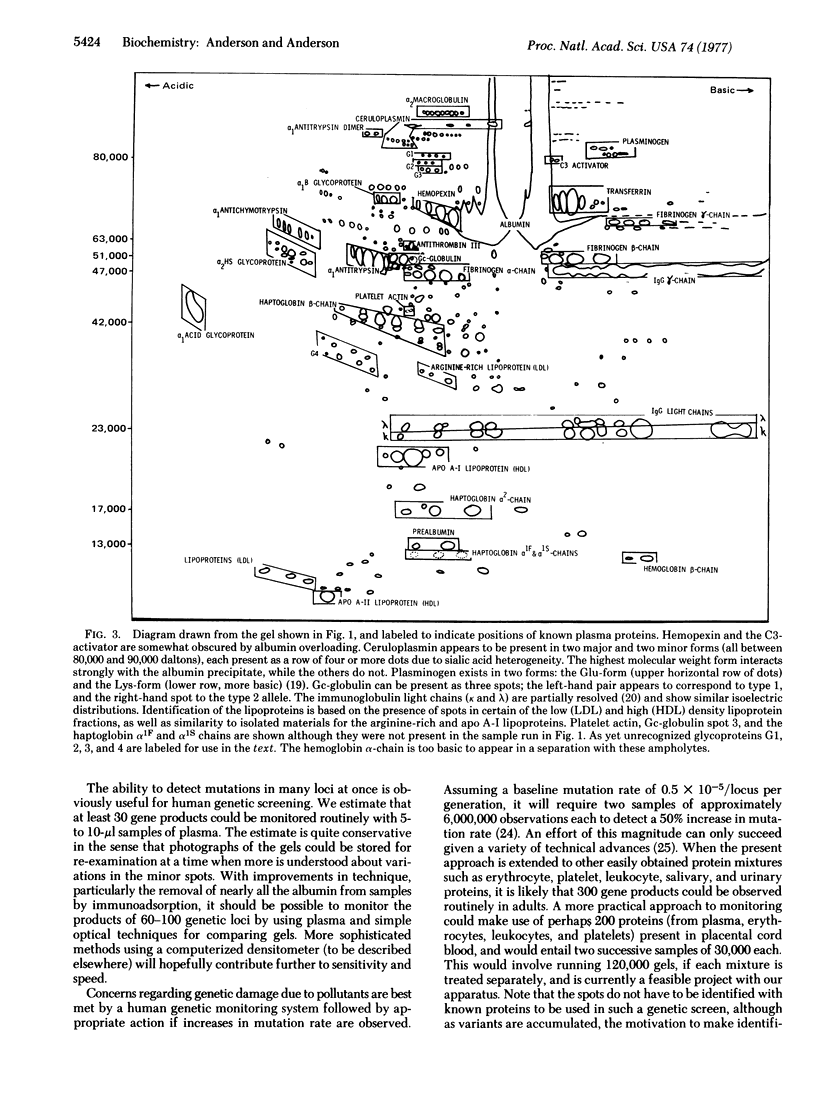
Abstract
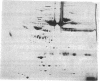
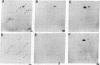
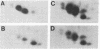
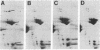
The two-dimensional electrophoretic technique of O'Farrell has been adapted to the analysis of human plasma proteins, and 30 polypeptides have been identified in the pattern produced. Genetic variants involving charge (isoelectric point) or size (molecular weight in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate) changes should be routinely detectable in at least 20 proteins at once, facilitating studies of human mutation rates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G., Latner A. L. Isoelectric focusing of serum proteins in acrylamide gels followed by electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Apr;24(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman T., Smith J. Human serum protein fractionation by gel filtration. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):869–873. doi: 10.1042/bj1180869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iborra F., Buhler J. M. Protein subunit mapping. A sensitive high resolution method. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klose J. Protein mapping by combined isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis of mouse tissues. A novel approach to testing for induced point mutations in mammals. Humangenetik. 1975;26(3):231–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00281458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. 2-dimensional resolution of plasma proteins by combination of polyacrylamide disc and gradient gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1969 Mar 15;221(5185):1056–1057. doi: 10.1038/2211056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoproteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V. The detection of increased mutation rates in human populations. Perspect Biol Med. 1971;14(4):522–537. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1971.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYMOND S., WEINTRAUB L. Acrylamide gel as a supporting medium for zone electrophoresis. Science. 1959 Sep 18;130(3377):711–711. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3377.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Boreisha I. G., Arzadon L., Summaria L. Physical and chemical properties of the NH2-terminal glutamic acid and lysine forms of human plasminogen and their derived plasmins with an NH2-terminal lysine heavy (A) chain. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4044–4047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Simons K., Ehnholm C. Immunological purification and chemical characterization of the group-specific proteins (Gc) from human serum. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):45–48. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G. A. Two-dimensional gel analysis of soluble proteins. Charaterization of guinea pig exocrine pancreatic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5375–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., O'Farrell P. H., Friedrich U., Coffino P. Mutations causing charge alterations in regulatory subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase of cultured S49 lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiselius A. Electrophoresis of serum globulin. I. Biochem J. 1937 Feb;31(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0310313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virella G., Coelho I. M. Unexpected mobility of human lambda chains in sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunochemistry. 1974 Mar;11(3):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]