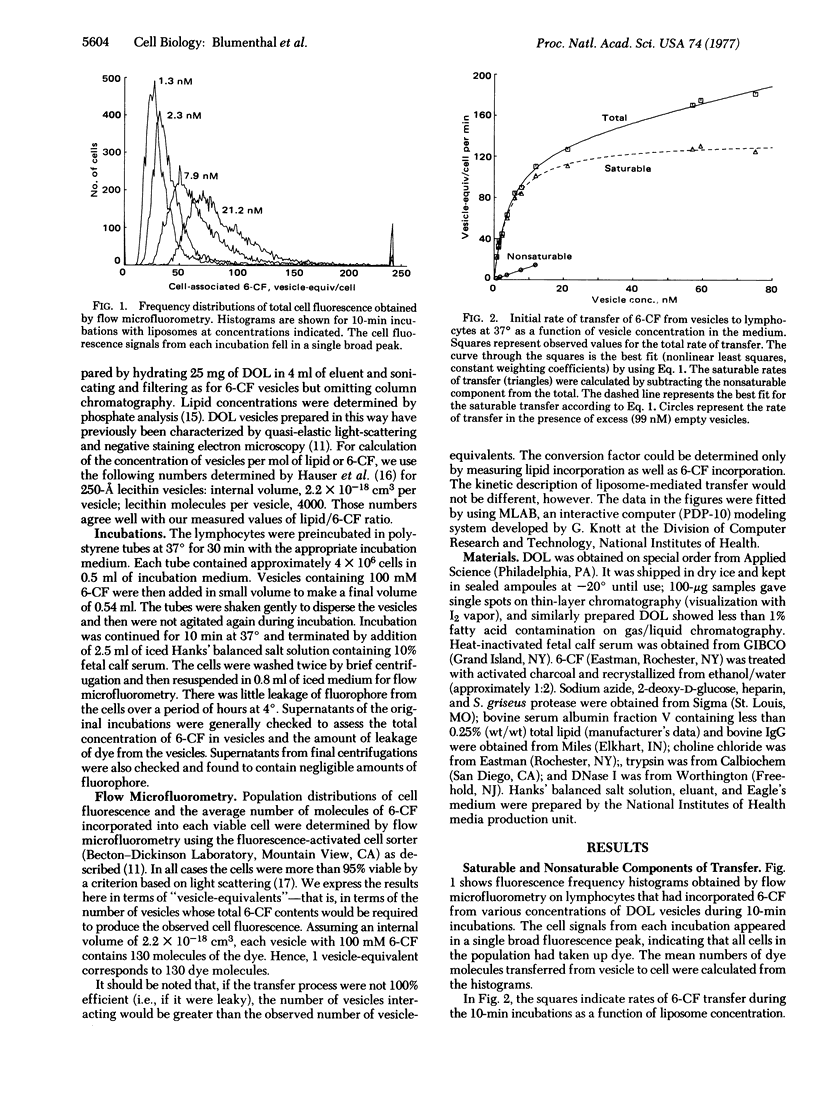
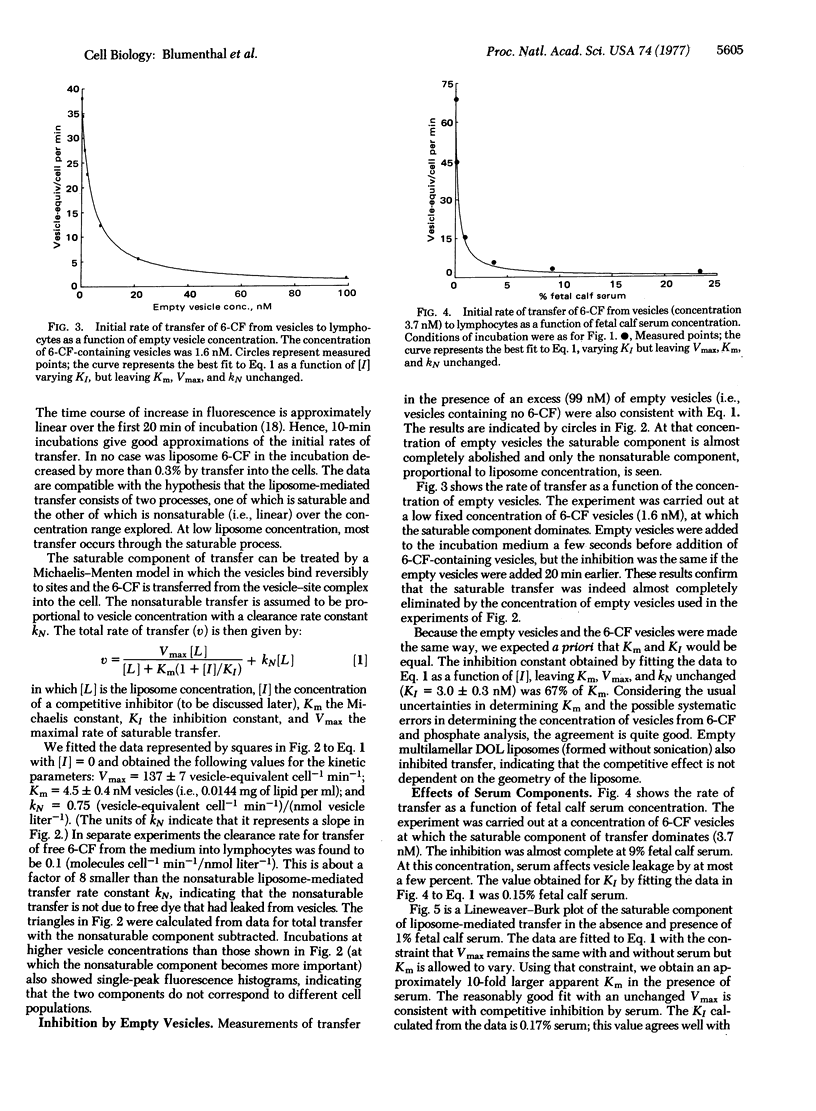
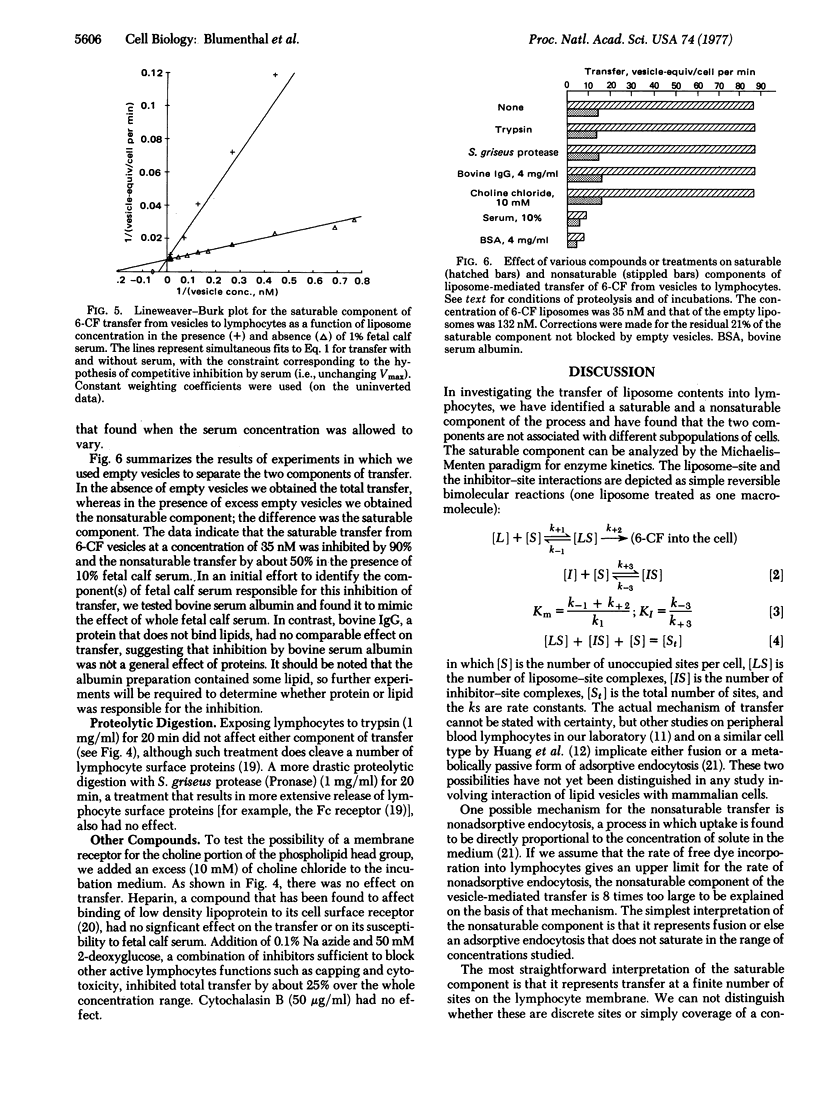
Abstract
The water-soluble dye 6-carboxyfluorescein was trapped in the internal aqueous compartments of small sonicated dioleoyl lecithin vesicles and used to assess the kinetics of transfer of vesicle contents to human lymphocytes. By using flow microfluorometry, the initial rate of dye transfer to the cells was measured as a function of the concentration of vesicles in the external medium. The rate of transfer consists of at least two components, one of which saturates at high vesicle concentration and the other of which does not saturate in the range of concentrations explored. The saturable component was competitively inhibited by vesicles not containing dye. Both the saturable and nonsaturable components of transfer were inhibited by fetal calf serum or bovine serum albumin but neither component was affected by bovine IgG, choline chloride, or heparin. Pretreatment of the lymphocytes with trypsin or Pronase had no effect on either component. The saturable component can be interpreted in terms of a two-step process in which vesicles bind reversely to sites on the cell surface, and dye is then transferred into the cell from the vesicle-site complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Mechanisms of cell fusion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):194–195. doi: 10.1038/253194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzri S., Korn E. D. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cells. Endocytosis and fusion as alternate mechanisms for the uptake of lipid-soluble and water-soluble molecules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):621–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Studies of the human lymphocyte receptor for heat-aggregated or antigen-complexed immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. W., McConnell H. M. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with viable Acholeplasma laidlawii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1238–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G. The carrier potential of liposomes in biology and medicine (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 30;295(14):765–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609302951406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Oldani D., Phillips M. C. Mechanism of ion escape from phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine single bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4507–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohrmann H. P., Novikovs L., Graw R. G., Jr Cellular interactions in the proliferative response of human T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens and allogeneic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1553–1567. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee W. E., Goff C. W., Schoknecht J., Smith M. D., Cherian K. The interaction of cationic liposomes containing entrapped horseradish peroxidase with cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):492–504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. J., MacDonald R. C. Lipid vesicle-cell interactions. III. Introduction of a new antigenic determinant into erythrocyte membranes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):515–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Huang L. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells. II. Studies of mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):49–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Takeichi M. Adhesion of phospholipid vesicles to Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Role of cell surface proteins. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):531–546. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Allison A. C. Membrane fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):421–465. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D. Lipid vesicles as carriers for introducing materials into cultured cells: influence of vesicle lipid composition on mechanism(s) of vesicle incorporation into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Heath T. D., Colley C. M., Ryman B. E. New aspects of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):259–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. N., Yoshikami S., Henkart P., Blumenthal R., Hagins W. A. Liposome-cell interaction: transfer and intracellular release of a trapped fluorescent marker. Science. 1977 Feb 4;195(4277):489–492. doi: 10.1126/science.835007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zborowski J., Roerdink F., Scherphof G. Leakage of sucrose from phosphatidylcholine liposomes induced by interaction with serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


