Abstract
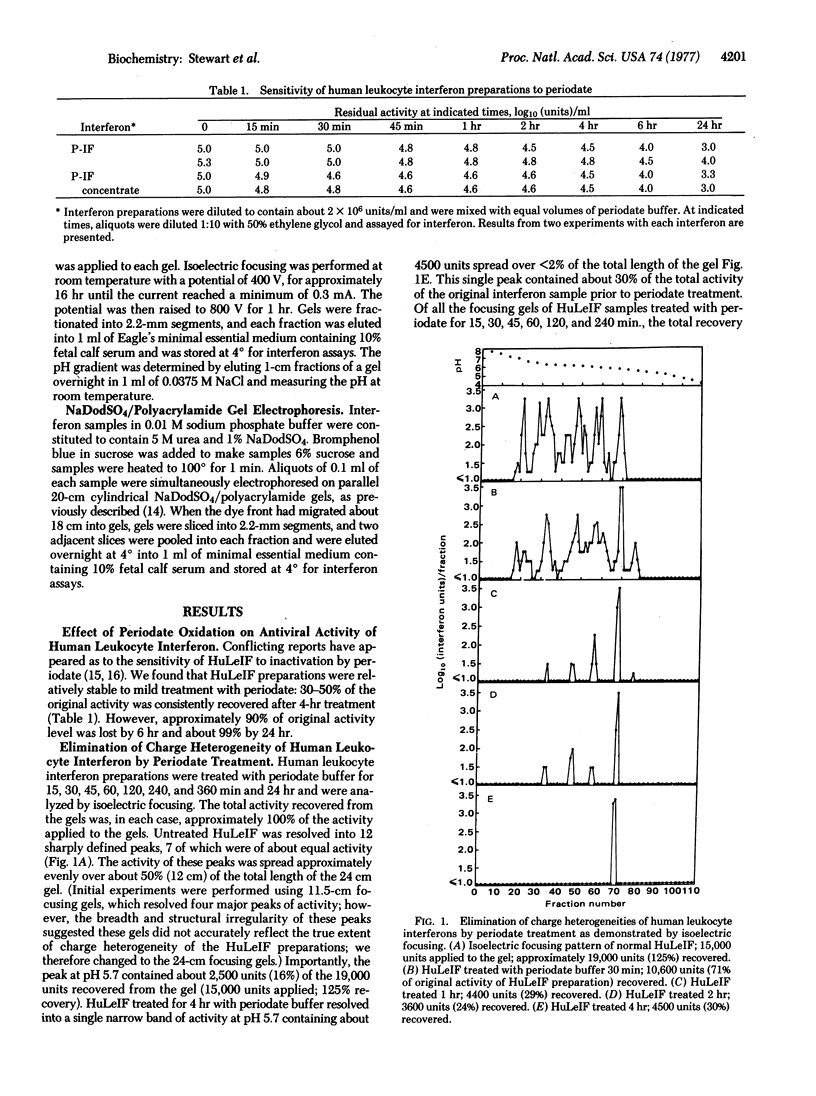
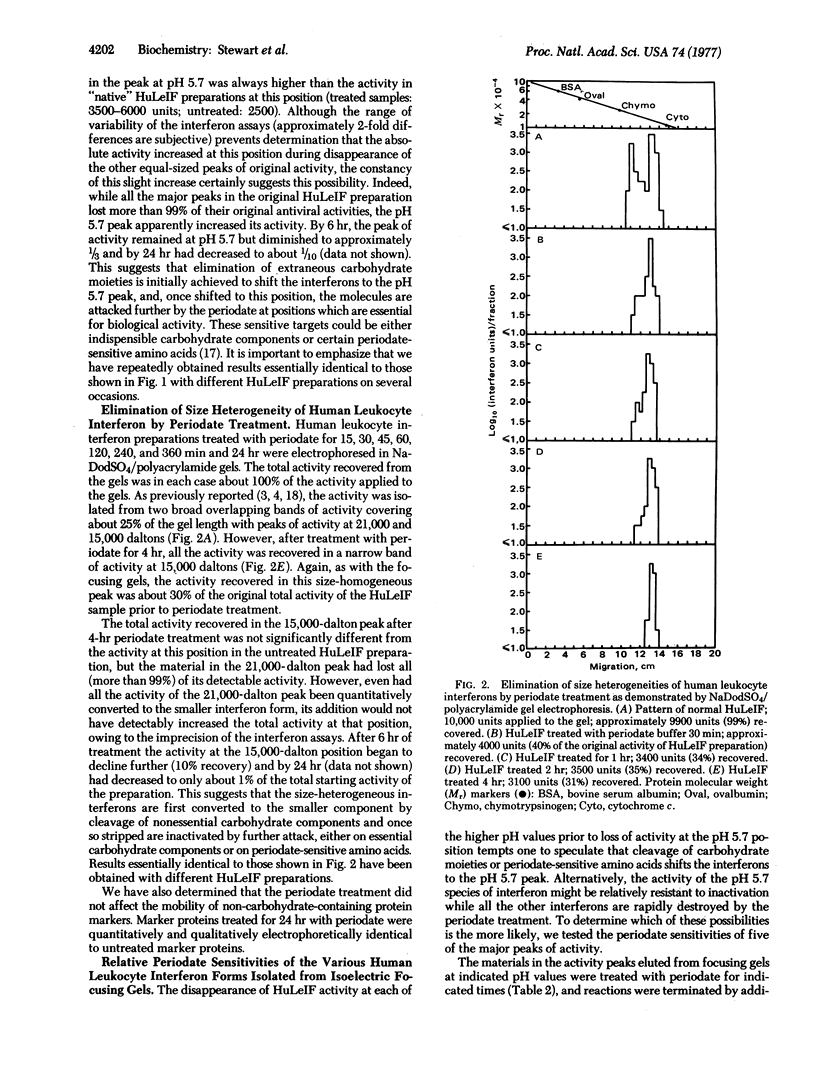
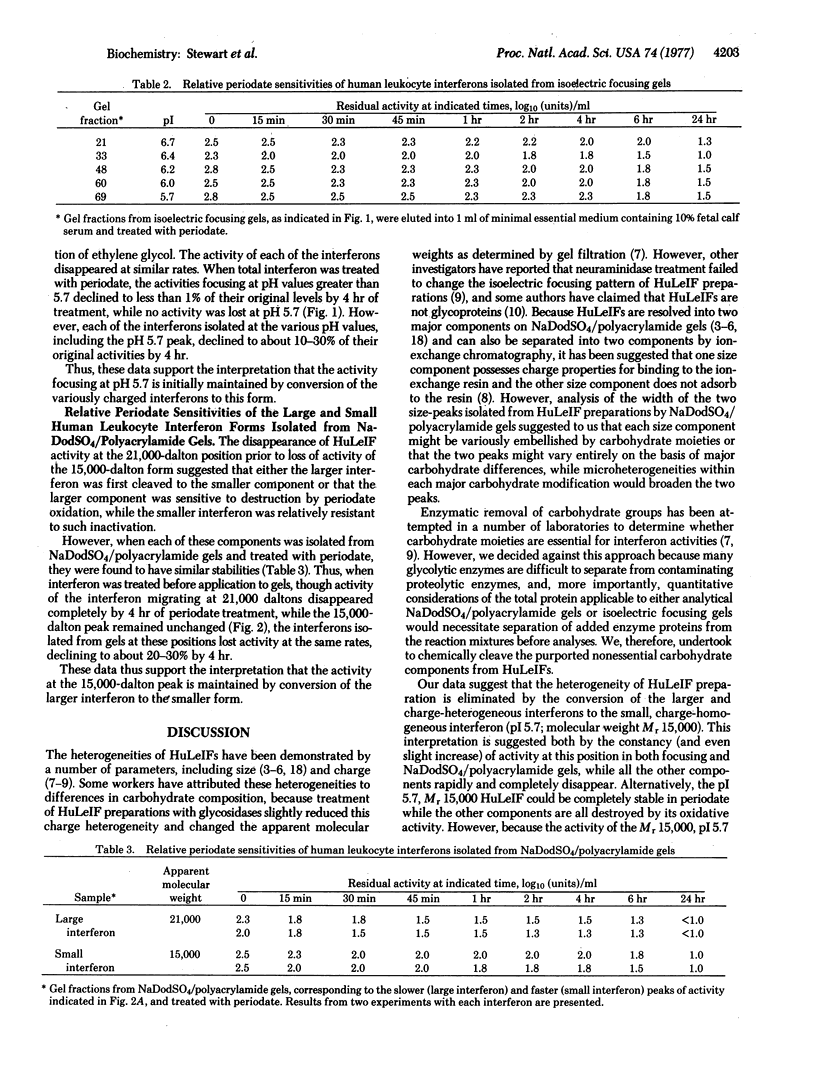
Human leukocyte interferon (HuLeIF) preparations contain distinct molecular forms of interferon exhibiting significant heterogeneties in sizes when analyzed by electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate (NaDodSO4)/polyacrylamide gels, migrating in two broad bands of activity with peaks at about 21,000 and 15,000 daltons. HuLeIFs exhibit extensive charge heterogeneities when analyzed by isoelectric focusing, resolving into several major peaks of approximately equal activity distributed from pH 5.7 to 7.0. When HuLeIF preparations are treated with 0.01 M sodium periodate buffer, pH 4.5, at 4°, both the size and charge heterogeneities rapidly disappear: periodate-treated HuLeIF migrates as a single, narrow band at 15,000 daltons in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels and focuses as a single, narrow band at pH 5.7. Quantitative considerations suggest that either the larger, heterogeneously charged HuLeIFs are converted to the smaller, size- and charge-homogeneous interferon by extensive chemical deglycosylation, or, alternatively, the smaller, 15,000 dalton, pH 5.7 interferon is much more stable to periodate treatment than are the other interferon forms. However, the activity of each of the variously charged forms of HuLeIF isolated from focusing gels exhibited the same stability as the pH 5.7 component; similarly, the activity of each of the size-forms of HuLeIF isolated from NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels exhibited the same stability as the 15,000-dalton interferon.
Keywords: sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, isoelectric focusing, deglycosylation
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bose S., Gurari-Rotman D., Ruegg U. T., Corley L., Anfinsen C. B. Apparent dispensability of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon for antiviral activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1659–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesario T. C., Schryer P. J., Tilles J. G. Relationship between the physicochemical nature of human interferon, the cell induced, and the inducing agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):291–298. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. K., Jankowski W. J., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Nature of the molecular heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):425–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.425-434.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Binding of human fibroblast interferon to concanavalin A-agarose. Involvement of carbohydrate recognition and hydrophobic interaction. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):704–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Stewart W. E., 2nd Molecular modification of interferon: attainment of human interferon in a conformation active on cat cells but inactive on human cells. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy V. G., Billiau A., Joniau M., De Somer P. Stabilisation of mouse and human interferons by acid pH against inactivation due to shaking and guanidine hydrochloride. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 May;146(1):249–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy V. G., Braude I. A., De Clercq E., Billiau A., De Somer P. Purification of interferon by adsorption chromatography on controlled pore glass. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):517–521. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Pollard R. B., Lutwick L. I., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on hepatitis B virus infection in patients with chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 2;295(10):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609022951001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Brouty-boye D., Tovey M. Pronounced antiviral activity of human interferon on bovine and porcine cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):543–545. doi: 10.1038/251543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Bandu M. T. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. II. Studies with herpes simplex, Moloney sarcoma, vesicular stomatitis, Newcastle disease, and influenza viruses. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Yamazaki S., Vilcek J. Altered molecular species of human interferon produced in the presence of inhibitors of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4425–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Interferon: purification and initial characterization from human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):520–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Pyhälä L., Törmä E., Cantell K. No evidence for a carbohydrate moiety affecting the clearance of circulating human leukocyte interferon in rabbits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):305–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucker K., Dalton B. J., Törmä E. T., Ogburn C. A. Biological properties of human leukocyte interferon components. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):341–351. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., McInnes J., Weiss D., Havell E. A., Vilcek J. De novo cell-free synthesis of human interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:697–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb22005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Pitha P. M. Molecular weight study of human fibroblast interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R. Recent developments in chemical modification and sequential degradation of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:261–308. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart II W. E., De Somer P., Edy V. G., Paucker K., Berg K., Ogburn C. A. Distinct molecular species of human interferons: requirements for stabilzation and reactivation of human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):327–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Desmyter J. Molecular heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon: two populations differing in molecular weights, requirements for renaturation, and cross-species antiviral activity. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd Distinct molecular species of interferons. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M., Le Goff S. Identification of the cell multiplication inhibitory factors in interferon preparations as interferons. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):300–302. doi: 10.1038/262300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


