Abstract
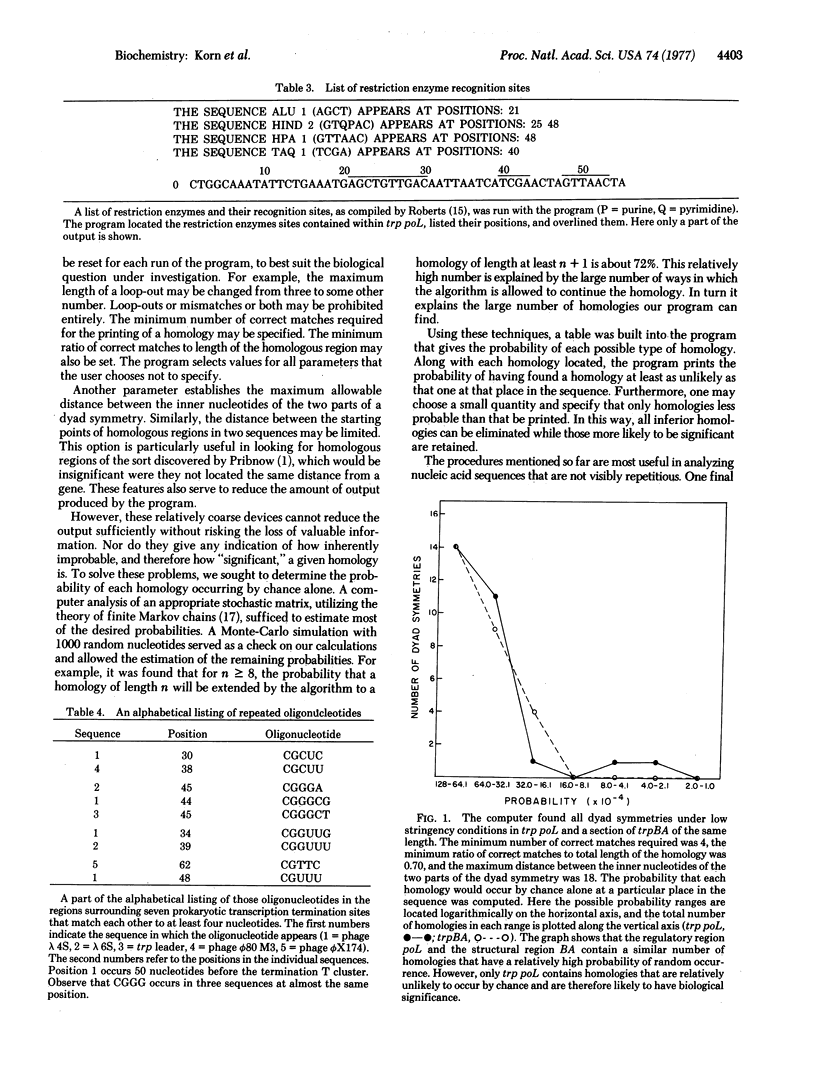
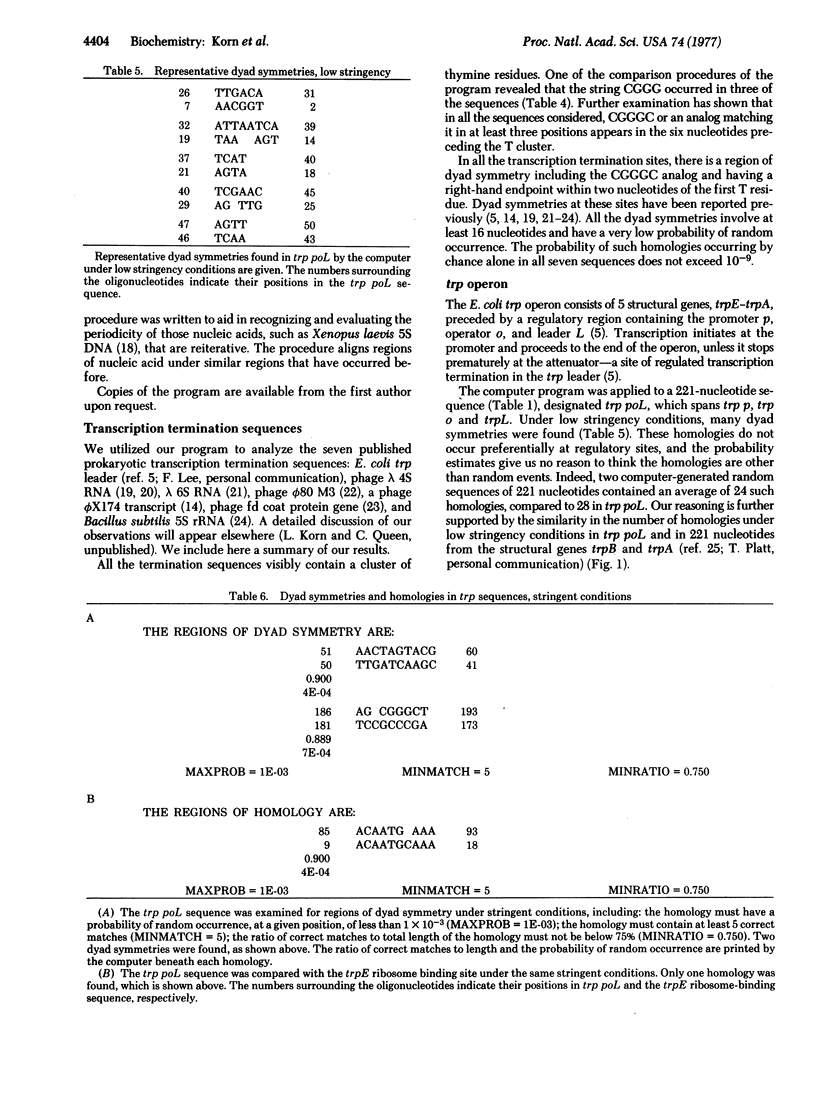
We describe a computer program designed to facilitate the analysis of nucleic acid sequences. The program can search several nucleic acid sequences for oligonucleotides common to all of them. It can examine a DNA or RNA sequence for two kinds of homologous regions--repetitions and dyad symmetries. The homologies need not be perfect: mismatches and "looping out" of nucleotides are allowed. The program also finds (A+T)- and (G+C)-rich regions, locates restriction enzyme recognition sites, determines the distribution of di- and trinucleotides, and performs various other functions. We include two representative applications of the program. All published prokaryotic transcription termination sequences (June 1977) were found to share the following features: (i) a string of at least five T residues, (ii) the sequence CGGGC or a close analog immediately preceding the T cluster, (iii) a region of strong dyad symmetry preceding the Ts and including the CGGGC sequence. A sequence of 221 nucleotides consisting of the Escherichia coli trp promoter, operator, and leader was found to contain two strong dyad symmetries. These homologies both occur at known regulatory sites; no comparable homologies occur in regions without regulatory significance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett G. N., Schweingruber M. E., Brown K. D., Squires C., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of region preceding trp mRNA initiation site and its role in promoter and operator function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2351–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K., Korn L., Lee F., Platt T., Squires C. L., Squires C., Yanofsky C. New features of the regulation of the tryptophan operon. Science. 1975 Jul 4;189(4196):22–26. doi: 10.1126/science.1094538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Considerations regarding the regulation of gene transcription and messenger translation. J Mol Evol. 1971;1(1):185–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M., Radding C. M. Nucleotide sequence of a ribonucleic acid transcribed in vitro from lambda phage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5120–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieczenik G., Barrell B. G., Gefter M. L. Bacteriophage phi 80-induced low molecular weight RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., McMahon J. E. Method for predicting RNA secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2017–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Squires C., Yanofsky C. Ribosome-protected regions in the leader-trpE sequence of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Yanofsky C. An intercistronic region and ribosome-binding site in bacterial messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. DNA base sequence of the po promoter region of phage lamdba. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):117–121. doi: 10.1038/265117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Nucleotide sequence of 5 S ribosomal RNA precursor from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3480–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Okamoto T., Takanami M. Studies on bacteriophage fd DNA. IV. The sequence of messenger RNA for the major coat protein gene. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):487–507. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


