Abstract
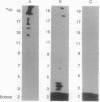
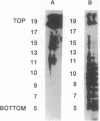
The neu protooncogene (also known as c-erbB2, NGL, and HER2) encodes a 185-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that resembles the receptor for epidermal growth factor. The p185 gene and protein were originally identified in the brain and are thought to play a critical role in neurogenesis. Aberrant c-erbB2 protein overexpression also occurs in several human adenocarcinomas. A ligand for p185, neu-activating factor (NAF), specifically binds to neu receptor and increases the p185c-neu tyrosine phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo in a dose-dependent manner. We now show that NAF specifically binds to purified p185 expressed in baculovirus. Direct binding analysis showed that NAF binds with high affinity (Kd = 1.3 nM). We have investigated changes in the structure and association state of baculovirus-produced neu holoreceptor that are induced by ligand binding. In this study, we used sucrose gradients to show that purified p185c-neu exists mainly in the monomeric form at low concentrations, whereas at higher concentrations p185c-neu exists as dimers or multimers. At low concentrations, but in the presence of ligand, p185c-neu sediments as a dimeric or multimeric form. Monomer-oligomer interconversion is absolutely ligand dependent at low receptor concentrations. The high molecular weight form of the receptor is enzymatically more active, as a consequence of ligand-driven activation of the receptor kinase. Oncogenic p185neu receptors sediment predominantly as high molecular weight forms and have constitutively active kinases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishayee S., Majumdar S., Khire J., Das M. Ligand-induced dimerization of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Monomer-dimer interconversion occurs independent of receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11699–11705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Blundell T. L., Lapatto R., McDonald N. Q., Murray-Rust J. Nerve growth factor revisited. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Feb;18(2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90052-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F. Mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation and high-affinity binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7709–7712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Koland J. G., Cerione R. A. Visualization of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor aggregation in plasma membranes by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Correlation of receptor activation with aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8699–8707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobashi K., Davis J. G., Mikami Y., Freeman J. K., Hamuro J., Greene M. I. Characterization of a neu/c-erbB-2 protein-specific activating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elberg G., Kelly P. A., Djiane J., Binder L., Gertler A. Mitogenic and binding properties of monoclonal antibodies to the prolactin receptor in Nb2 rat lymphoma cells. Selective enhancement by anti-mouse IgG. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14770–14776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger B. O., Stephens J. E., Staros J. V. High-yield trapping of EGF-induced receptor dimers by chemical cross-linking. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):71–75. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2783412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., Berlot C. H., Bothwell M. A. Affinity labeling and partial purification of nerve growth factor receptors from rat pheochromocytoma and human melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6819–6823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R. W., Henzel W. J., Lee J., Park J. W., Yansura D., Abadi N., Raab H., Lewis G. D. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Purification and characterization of the neu/erb B2 ligand-growth factor from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11508–11512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikari N., Yoshino H., Moses A. C., Flier J. S. Evidence that receptor aggregation may play a role in transmembrane signaling through the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Sep;2(9):831–837. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-9-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koland J. G., Cerione R. A. Growth factor control of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase activity via an intramolecular mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2230–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu R., Colomer R., Zugmaier G., Sarup J., Shepard M., Slamon D., Lippman M. E. Direct interaction of a ligand for the erbB2 oncogene product with the EGF receptor and p185erbB2. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1552–1555. doi: 10.1126/science.2218496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Bacus S. S., Koski R. A., Lu H. S., Wen D., Ogden S. G., Levy R. B., Yarden Y. Isolation of the neu/HER-2 stimulatory ligand: a 44 kd glycoprotein that induces differentiation of mammary tumor cells. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Ben-Levy R., Tzahar E., Liu N., Wen D., Yarden Y. Cell-type specific interaction of Neu differentiation factor (NDF/heregulin) with Neu/HER-2 suggests complex ligand-receptor relationships. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Stern D. F., Vaidyanathan L., Decker S. J., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):513–516. doi: 10.1038/312513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M. J., Gullick W. J. A sequence motif in the transmembrane region of growth factor receptors with tyrosine kinase activity mediates dimerization. Protein Eng. 1990 Mar;3(4):245–248. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.4.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Kokai Y., Wada T., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. Linkage of tyrosine kinase activity with transforming ability of the p185neu oncoprotein. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries C., Escobedo J. A., Ueno H., Houck K., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1312256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]