Abstract
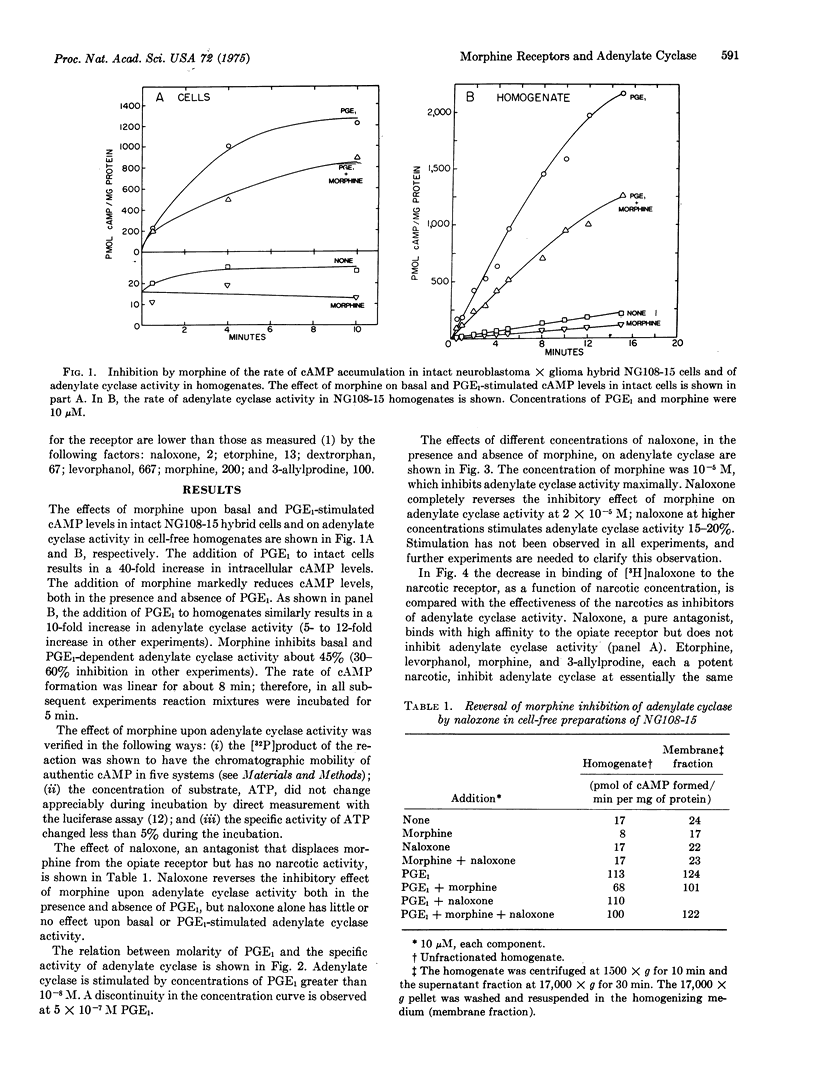
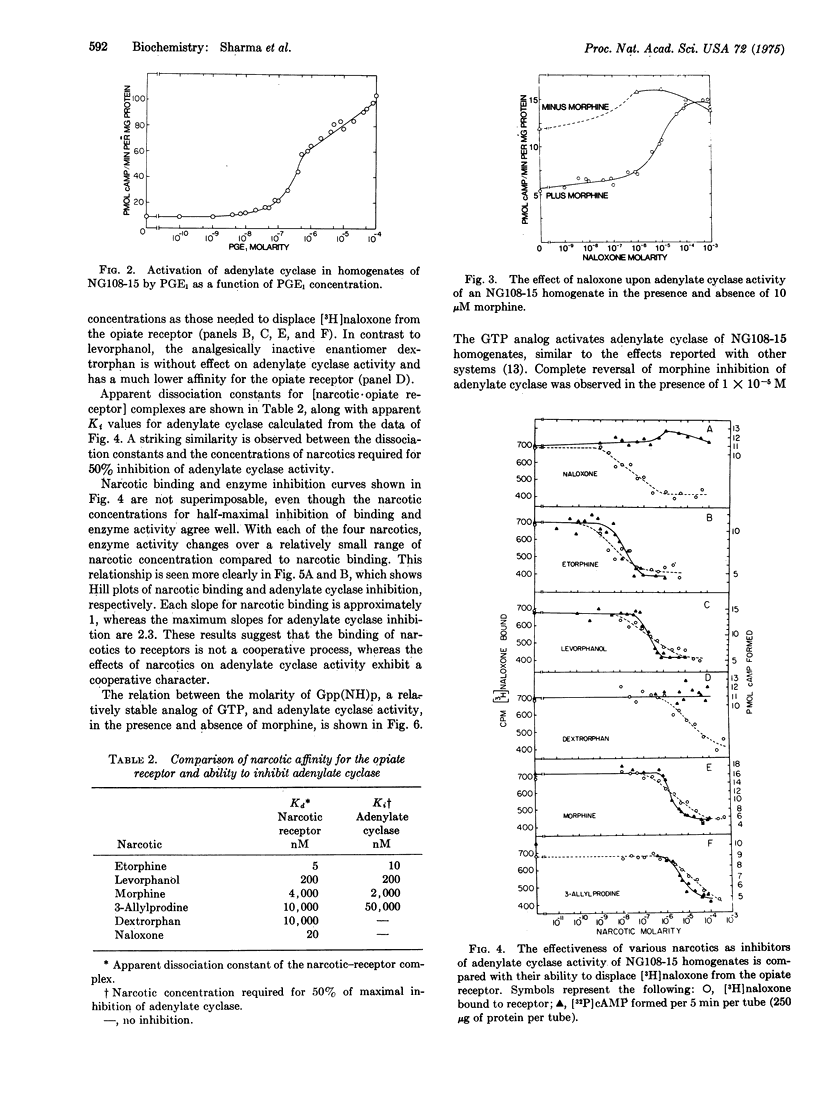
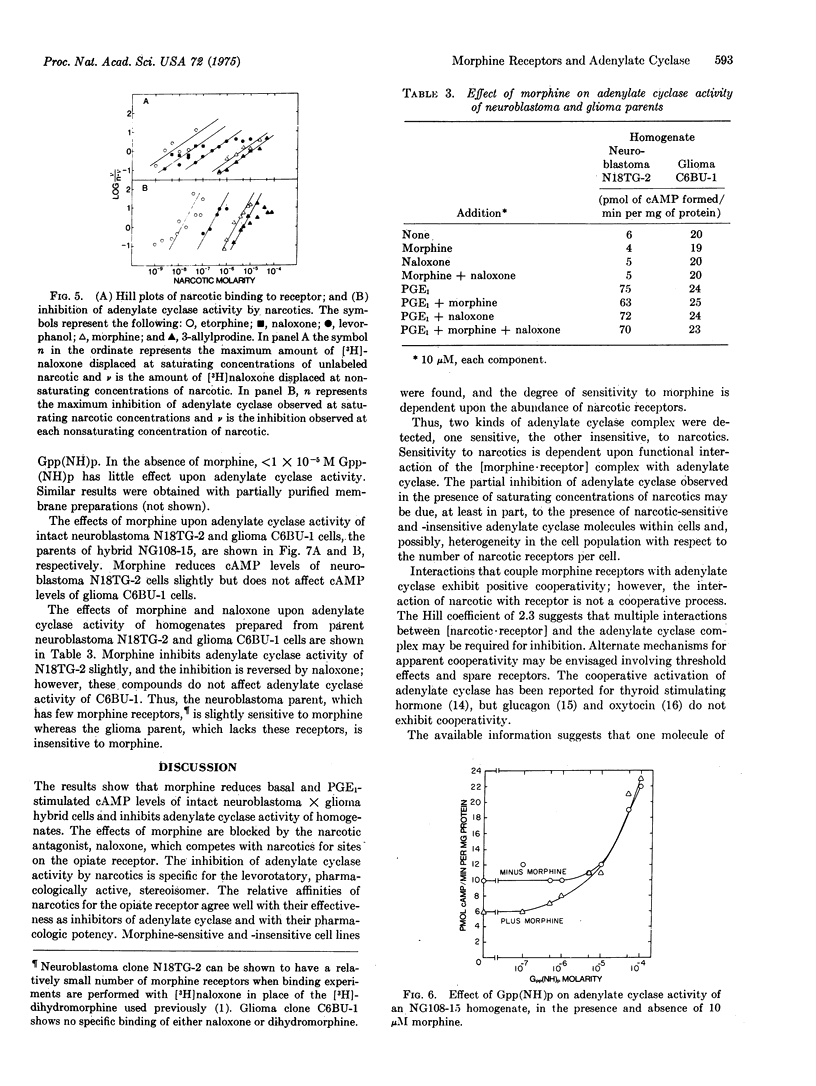
Morphine inhibits adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1) activity of neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cells. The inhibition is stereospecific and is reversed by the antagonist, naloxone. The relative affinities of narcotics for the opiate receptor agree well with their effectiveness as inhibitors of adenylate cyclase. Morphine-sensitive and -insensitive cell lines were found, and the degree of sensitivity was shown to be dependent upon the abundance of narcotic receptors. Thus, morphine receptors are functionally coupled to adenylate cyclase. A molecular mechanism for narcotic addiction and tolerance is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Hamprecht B., Kemper W. High activity of choline acetyltransferase induced in neuroblastoma x glia hybrid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benda P., Lightbody J., Sato G., Levine L., Sweet W. Differentiated rat glial cell strain in tissue culture. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):370–371. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Rodbell M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. 1. Properties and the effects of adrenocorticotropin and fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3468–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Roy C., Jard S. Oxytocin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in frog bladder epithelial cells. Role of calcium, nucleotides, and other factors in hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7073–7081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeynaems J. M., Pochet R., Dumont J. E. Stimulation by thyrotropin of horse thyroid plasma membranes adenylate cyclase: evidence of cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 20;58(2):446–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Hypothesis: Inhibition of E prostaglandin-sensitive adenyl cyclase as the mechanism of morphine analgesia. Prostaglandins. 1974 Sep 10;7(5):361–376. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Morphine-like drugs inhibit the stimulation of E prostaglandins of cyclic AMP formation by rat brain homogenate. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):24–27. doi: 10.1038/248024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos A., Najjar V. A. The activation of adenylate cyclase. II. The postulated presence of (A) adenylate cyclase in a phospho (inhibited) form (B) a dephospho (activated) form with a cyclic adenylate stimulated membrane protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):794–799. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Tao P., Kiefer H. C. Kinetic evidence for the presence of two prostaglandin receptor sites regulating the activity of intestinal adenylate cyclase sensitive to Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1317–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. A neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cell line with morphine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3474–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klofat W., Picciolo G., Chappelle E. W., Freese E. Production of adenosine triphosphate in normal cells and sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3270–3276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Salomon Y., Lin M. C., Harwood J. P., Schramm M., Wolff J., Rodbell M. 5'-Guanylylimidodiphosphate, a potent activator of adenylate cyclase systems in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3087–3090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J., Glazer D., Nirenberg M. Genetic dissection of neural properties using somatic cell hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):225–231. doi: 10.1038/newbio235225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y. Evidence for interdependent action of glucagon and nucleotides on the hepatic adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Drummond G. I., Sulakhe P. V. Adenylate cyclase in skeletal muscle. Kinetic properties and hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2949–2958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I. Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic (3H) Etorphine to rat-brain homogenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1947–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Stereospecific interaction between narcotic analgesics and a synaptic plasm a membrane fraction of rat cerebral cortex. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1973;32(3):317–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1973.tb01477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haën C. Adenylate cyclase. A new kinetic analysis of the effects of hormones and fluoride ion. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2756–2762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


