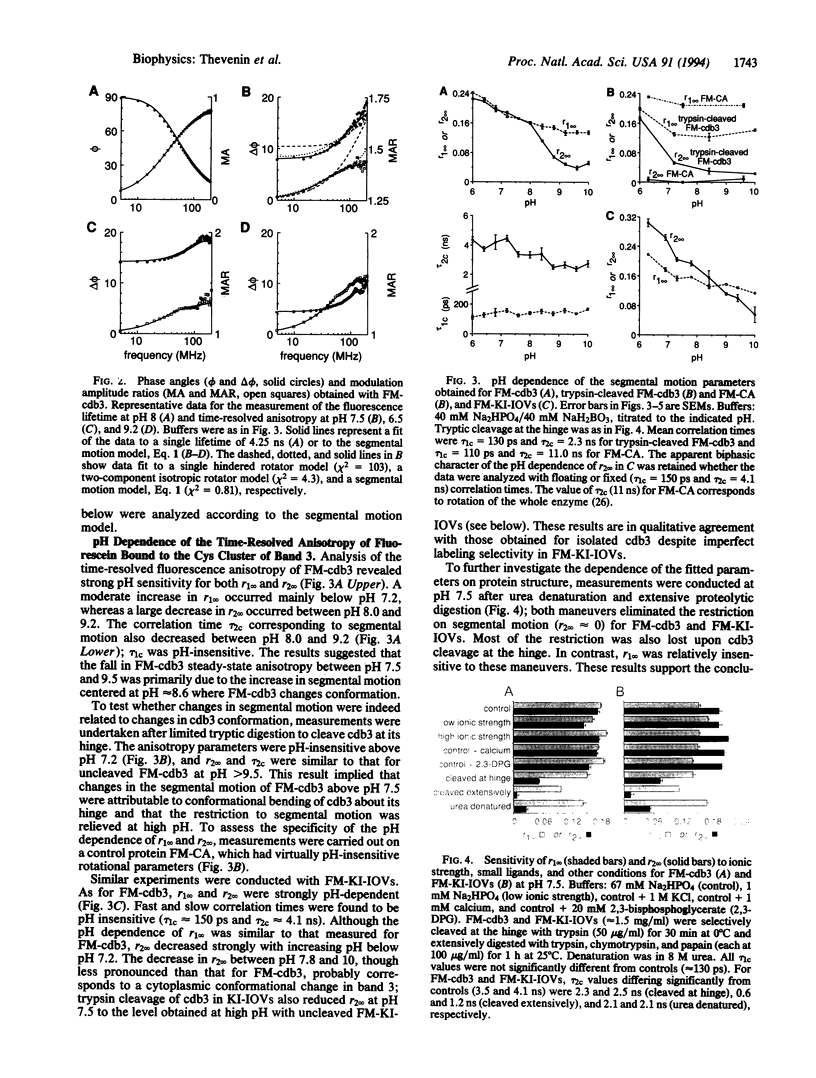
Abstract
Interactions between the erythrocyte membrane and its skeleton are mediated primarily by binding of cytoskeletal components to a conformationally sensitive structure, the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 (cdb3). To examine the nanosecond segmental motions of cdb3, band 3 was labeled selectively by fluorescein maleimide at Cys-201 near the proposed hinge in cdb3 about which pH-dependent conformational changes occur. Time-resolved anisotropy of labeled cdb3 in isolated form and in stripped erythrocyte membranes was measured by parallel-acquisition frequency-domain microfluorimetry. Samples had a single-component fluorescein lifetime of approximately 4 ns. Multifrequency phase and modulation data (5-200 MHz) fitted well to a segmental motion model containing two correlation times (tau 1c and tau 2c) and two limiting anisotropies (r1infinity and r2infinity). Measurements in protease-cleaved and denatured samples indicated that tau 1c (100-150 ps) corresponded to rapid rotation of bound fluorescein and tau 2c (2-5 ns) corresponded to segmental motion of cdb3. Both motions were hindered as quantified by nonzero r1infinity and r2infinity. The strong pH dependence of segmental motion correlated with that of cdb3 conformation measured by intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence. Significant changes in cdb3 segmental motion occurred upon interactions with the small ligands 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate and calcium and several glycolytic enzymes known to bind to the N terminus of band 3. These time-resolved fluorescence measurements of the nanosecond segmental dynamics of a labeled membrane protein provide evidence for the sensitivity of cdb3 conformation to ligand binding and suggest long-range structural communication through cdb3.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appell K. C., Low P. S. Partial structural characterization of the cytoplasmic domain of the erythrocyte membrane protein, band 3. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11104–11111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. Proteins involved in membrane--cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes: spectrin, ankyrin, and band 3. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci E., Steiner R. F. Anisotropy decay of fluorescence as an experimental approach to protein dynamics. Biophys Chem. 1988 Jul 15;30(3):199–224. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)85017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursaux E., Hilly M., Bluze A., Poyart C. Organic phosphates modulate anion self-exchange across the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 7;777(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90427-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calafut T. M., Dix J. A., Verkman A. S. Fluorescence depolarization of cis- and trans-parinaric acids in artificial and red cell membranes resolved by a double hindered rotational model. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5051–5058. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. R., Reithmeier R. A. Analysis of the oligomeric state of Band 3, the anion transport protein of the human erythrocyte membrane, by size exclusion high performance liquid chromatography. Oligomeric stability and origin of heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15726–15737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charuk J. H., Pirraglia C. A., Reithmeier R. A. Interaction of ruthenium red with Ca2(+)-binding proteins. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jul;188(1):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90539-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Lux S. E., Bennett V. Mapping the ankyrin-binding site of the human erythrocyte anion exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9665–9672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducis I., Kandrach A., Racker E. Stimulation of 32Pi transport into human erythrocyte ghosts and reconstituted vesicles by Mg2+ and hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8544–8550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Verkman A. S. Low viscosity in the aqueous domain of cell cytoplasm measured by picosecond polarization microfluorimetry. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):719–725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Krebs K. E., Whitfield C. F., Riederer B. M., Zagon I. S. Spectrin and related molecules. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):171–234. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Structure and function of the red blood cell anion transport protein. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:397–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipari G., Szabo A. Effect of librational motion on fluorescence depolarization and nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules and membranes. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):489–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85109-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo C. R., Willardson B. M., Low P. S. Localization of the protein 4.1-binding site on the cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte membrane band 3. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9540–9546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S. Structure and function of the cytoplasmic domain of band 3: center of erythrocyte membrane-peripheral protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 22;864(2):145–167. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Westfall M. A., Allen D. P., Appell K. C. Characterization of the reversible conformational equilibrium of the cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte membrane band 3. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13070–13076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Willardson B. M., Mohandas N., Rossi M., Shohet S. Contribution of the band 3-ankyrin interaction to erythrocyte membrane mechanical stability. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1581–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 1. Comparison of ghosts and intact cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3527–3538. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson R. A., Sawyer W. H., Tilley L. Rotational diffusion of the erythrocyte integral membrane protein band 3: effect of hemichrome binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):512–518. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Winardi R., Knowles D., Leung A., Parra M., George E., Conboy J., Chasis J. Molecular basis for membrane rigidity of hereditary ovalocytosis. A novel mechanism involving the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):686–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI115636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama R., Lombardo C. R., Workman R. F., Low P. S. Regulation of linkages between the erythrocyte membrane and its skeleton by 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10990–10996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Cassoly R. Kinetics of p-mercuribenzoate binding to sulfhydryl groups on the isolated cytoplasmic fragment of band 3 protein. Effect of hemoglobin binding on the conformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1399–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Cordes K. A., Gaines E. D. Light-scattering measurements of hemoglobin binding to the erythrocyte membrane. Evidence for transmembrane effects related to a disulfonic stilbene binding to band 3. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1447–1454. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Cordes K. A. The isolated cytoplasmic domain of band 3 binds calcium at physiological salt concentration and neutral PH. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):975–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91514-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield A. E., Tanner M. J., Pinder J. C., Clough B., Bayley P. M., Nash G. B., Dluzewski A. R., Reardon D. M., Cox T. M., Wilson R. J. Basis of unique red cell membrane properties in hereditary ovalocytosis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):949–958. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90254-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thevenin B. J., Low P. S. Kinetics and regulation of the ankyrin-band 3 interaction of the human red blood cell membrane. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16166–16172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thevenin B. J., Willardson B. M., Low P. S. The redox state of cysteines 201 and 317 of the erythrocyte anion exchanger is critical for ankyrin binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15886–15892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S., Armijo M., Fushimi K. Construction and evaluation of a frequency-domain epifluorescence microscope for lifetime and anisotropy decay measurements in subcellular domains. Biophys Chem. 1991 Apr;40(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(91)85036-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willardson B. M., Thevenin B. J., Harrison M. L., Kuster W. M., Benson M. D., Low P. S. Localization of the ankyrin-binding site on erythrocyte membrane protein, band 3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15893–15899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J., Epstein H. F., Stryer L. Segmental flexibility in an antibody molecule. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]