Abstract
Pyran covalently linked to cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose has been shown to be an effective affinity matrix for several viral DNA polymerases. Differential salt elution of viral compared with cellular polymerases, as well as substrate elution, suggests the affinity nature for the matrix. Unlike some other affinity systems described, pyran-Sepharose is totally resistant to nuclease digestion and is stable at 4 degrees for several months. DNA polymerases isolated from several viruses by detergent treatment were recovered in good yield. Analysis of iodinated proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis revealed that the DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus found in crude preparations of the virus could be purified nearly to homogeneity by a single passage through the column. These results suggest that pyran-Sepharose is an effective affinity column that is potentially adaptable as part of a general purification procedure for viral DNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF
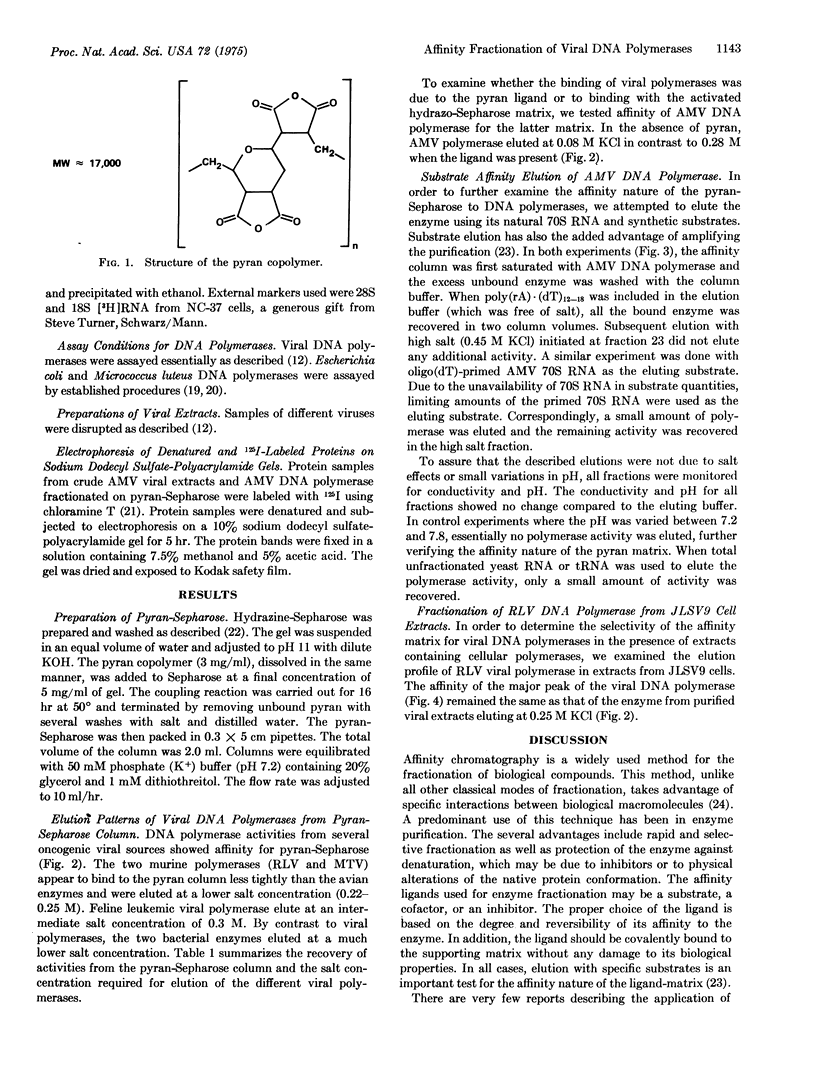
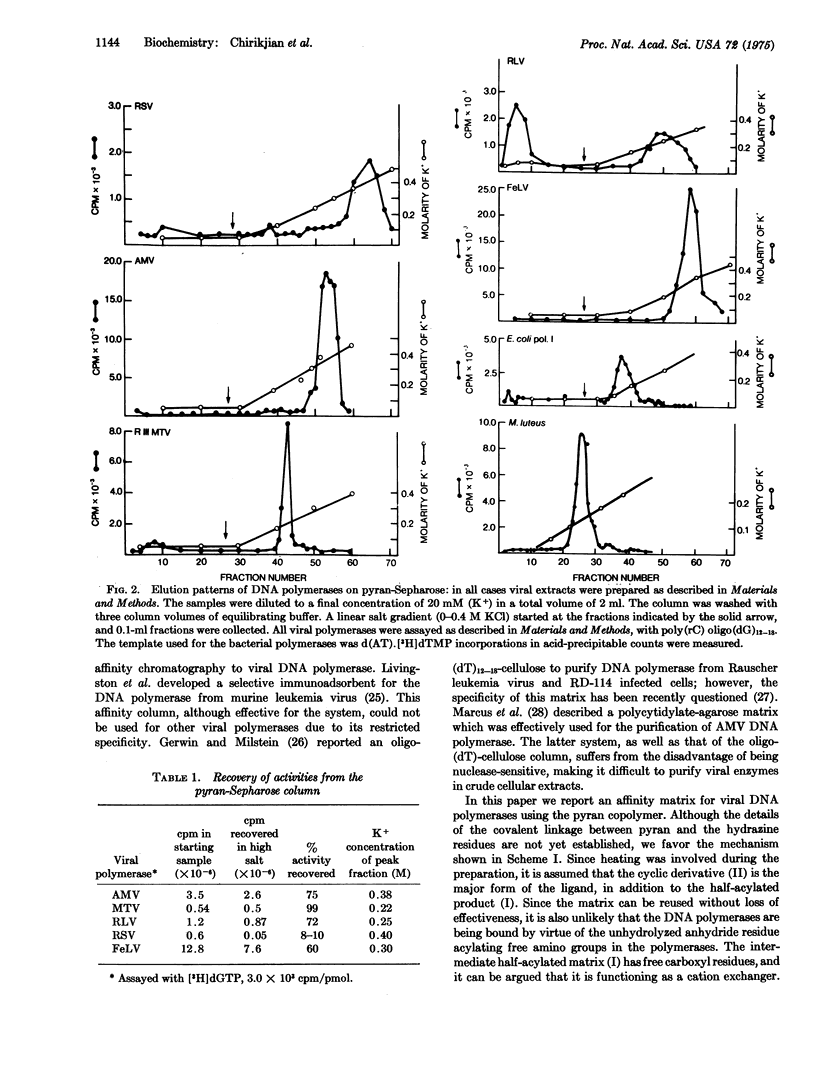
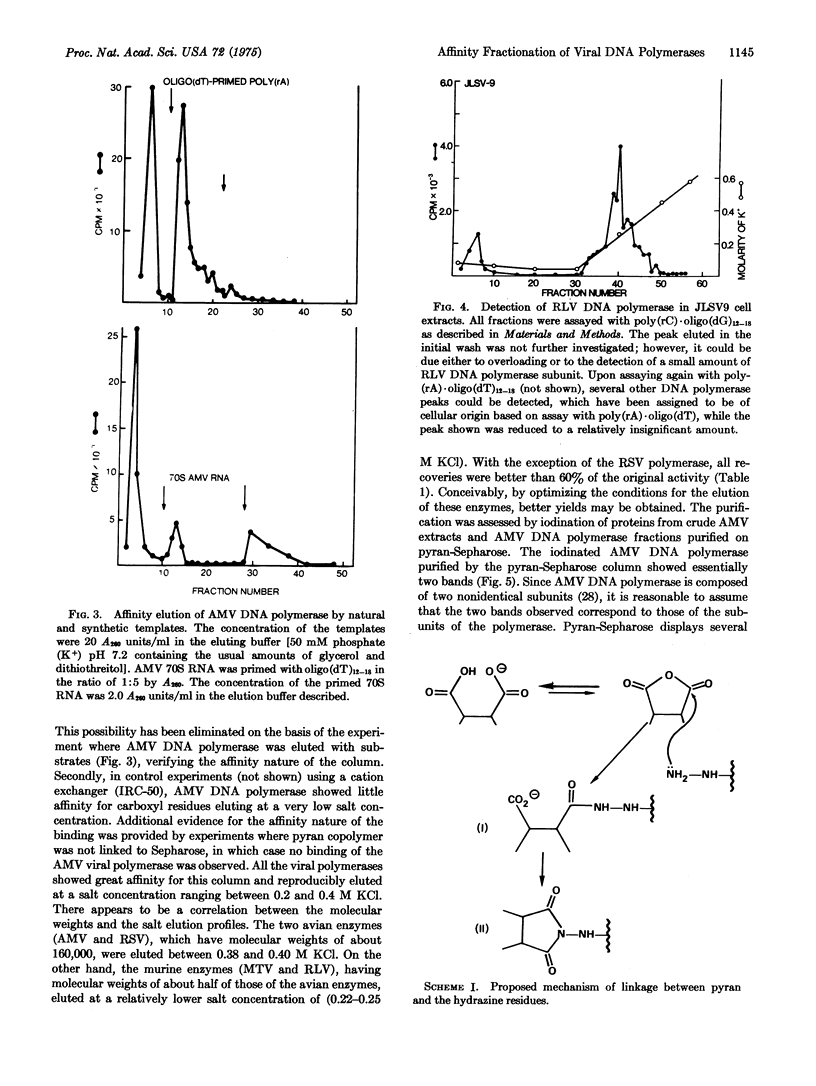

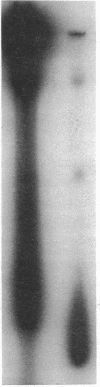
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray D., Brownlee S. M. Peptide mapping of proteins from acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow D. S., Edwards E. I., Newburg N. R. Divinyl ether-maleic anhydride (pyran) copolymer used to demonstrate the effect of molecular weight on biological activity. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):160–162. doi: 10.1038/246160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra P., Zunino F., Götz A., Gericke D., Thorbeck R., Di Marco A. Specific inhibition of DNA-polymerases from RNA tumor viruses by some new daunomycin derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 1;21(3):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirikjian J. G., Papas T. S. Inhibition of AMV DNA polymerase by polyriboadenylic acid containing epsilon-adenosine residues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):489–495. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography of macromolecules. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1972;36:29–89. doi: 10.1002/9780470122815.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in viruses and cells: views on the current state. Blood. 1972 Jan;39(1):117–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Milstien J. B. An oligonucleotide affinity column for RNA-dependent DNA polymerase from RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2599–2603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Gerard G. F. RNA-directed DNA polymerase--properties and functions in oncogenic RNA viruses and cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1974;14(0):187–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurgo C., Ray R., Green M. Rifamycin derivatives strongly inhibiting RNA leads to DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase) of murine sarcoma viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jul;49(1):61–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Faras A., Woodson B., Jackson J., Bishop J. M. Inhibition of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of Rous sarcoma virus by thiosemicarbazones and several cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):164–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. T. Affinity chromatography of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase from RNA tumor viruses on a solid phase immunoadsorbent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):393–397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. L., Modak M. J., Cavalieri L. F. Purification of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase by affinity chromatography on polycytidylate-agarose. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):853–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.853-859.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K., Seidel H. J. Inhibitors acting on nucleic acid synthesis in an oncogenic RNA virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):143–145. doi: 10.1038/newbio232143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papas T. S., Chirikjian J. G., Pry T. W., Massicot J. G., Irwin R. D., Chirigos M. A. Effect of chemically modified 70S RNA from avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) upon the activity of AMV DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1108–1114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1108-1114.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papas T. S., Pry T. W., Chirigos M. A. Inhibition of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus by pyran copolymer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):367–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papas T. S., Sandhaus L., Chirigos M. A., Furusawa E. Inhibition of DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus by an alkaloid extract from Narcissus tazetta L. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90957-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., SCHILDKRAUT C. L., APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. XIV. FURTHER PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríman J., Beaudreau G. S. Viral DNA-dependent DNA polymerase and the properties of thymidine labelled material in virions of an oncogenic RNA virus. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):427–430. doi: 10.1038/228427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer M. P., Chirigos M. A., Papas T. S. Inhibition of Rauscher leukemia virus and avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerases by tilorone (NSC-143969) and its analogs. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1974 Nov-Dec;58(6):821–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlabach A., Fridlender B., Bolden A., Weissbach A. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases from HeLa cell nuclei. II. Template and substrate utilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):879–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90793-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Wirthlin L. S., Scott J. F., Zamecnik P. C. The 3'-terminal nucleosides of the high molecular weight RNA of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1176–1180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuominen F. W., Kenney F. T. Inhibition of RNA-directed DNA polymerase from Rauscher leukemia virus by the 5'-triphosphate of cytosine arabinoside. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1469–1475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90879-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuominen F. W., Kenney F. T. Inhibition of the DNA polymerase of Rauscher leukemia virus by single-stranded polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Herrera F. M., Smith R. G., Reitz M. S., Lancini G., Ting R. C., Gallo R. C. Rifamycin antibiotics: inhibitors of Rauscher murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase and of purified DNA polymerases from human normal and leukemic lymphoblasts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jul;49(1):7–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Haar F. Affinity elution as a purification method for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):84–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]