Abstract
The wild-type New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus generated two types of defective interfering T-particles. The physical properties of these particles and the wild-type virion were determined by laser light scattering spectroscopy, sedimentation measurements, and electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF
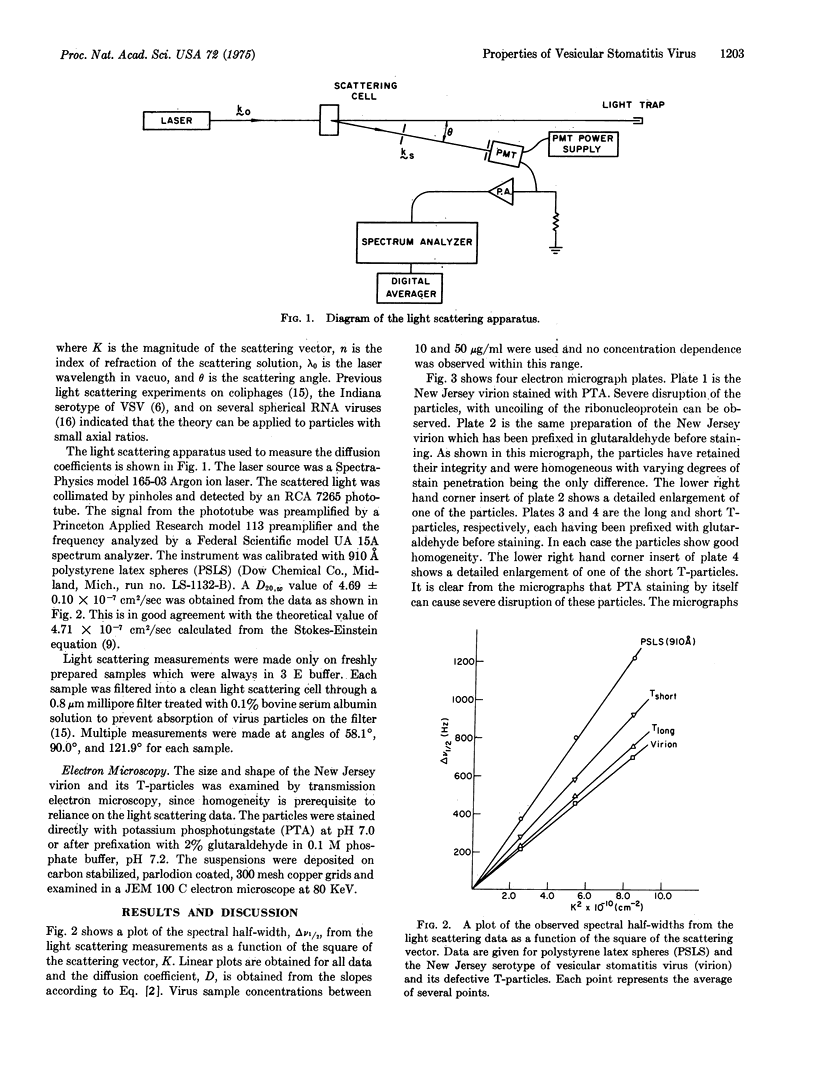
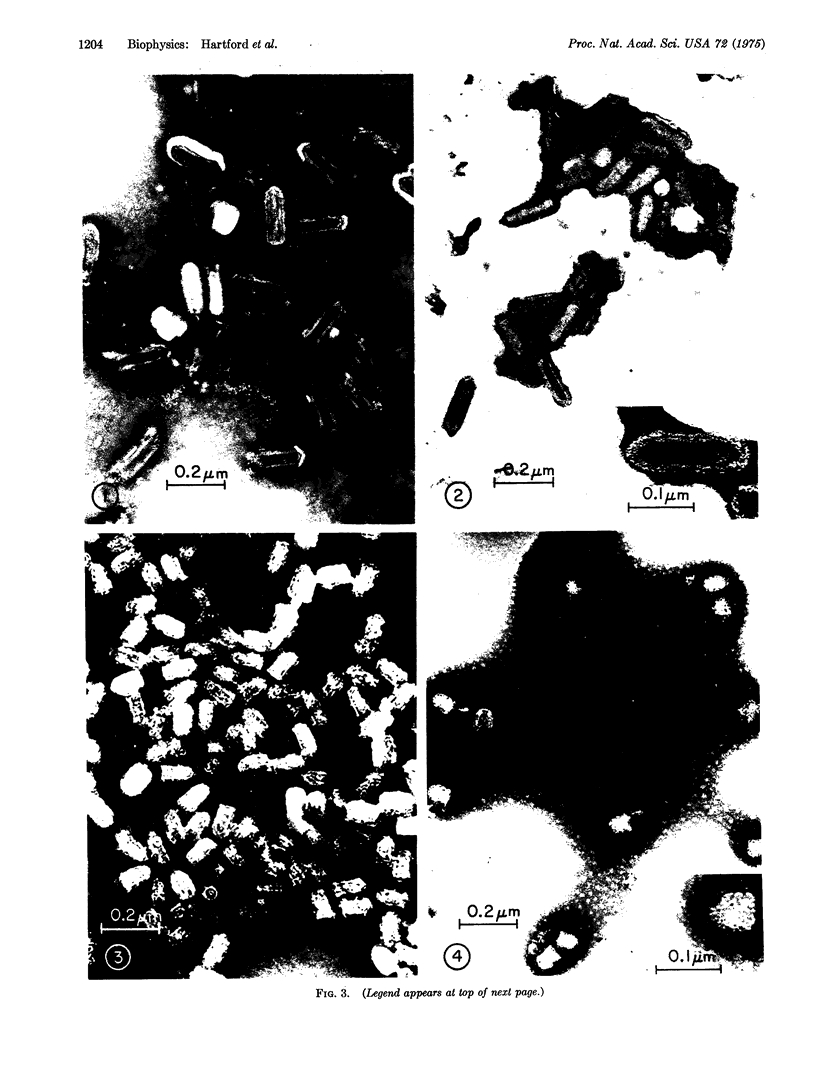
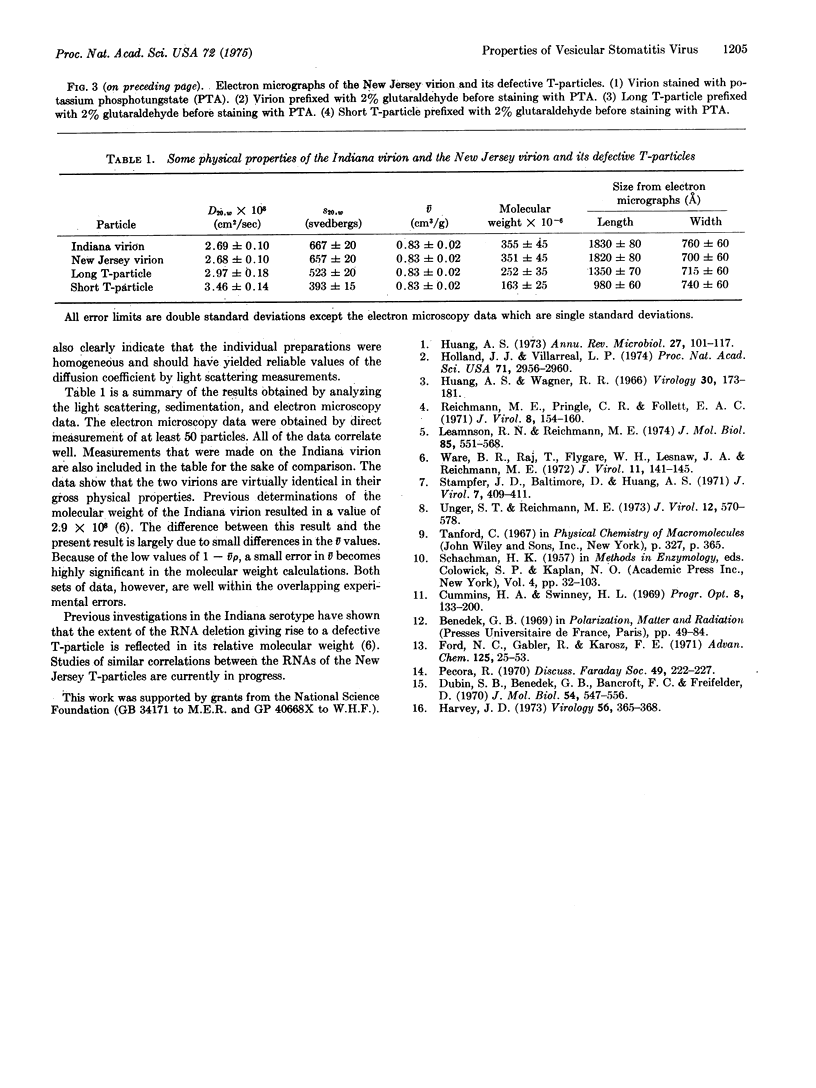
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubin S. B., Benedek G. B., Bancroft F. C., Freifelder D. Molecular weights of coliphages and colip- hage DNA. II. Measurement of diffusion coefficients using optical mixing spectroscopy, and measurement of sedimentation coefficients. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. D. Diffusion coefficients and hydrodynamic radii of three spherical RNA viruses by laser light scattering. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Biologic role in homologous interference. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leamnson R. N., Reichmann M. E. The RNA of defective vesicular stomatitis virus particles in relation to viral cistrons. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichmann M. E., Pringle C. R., Follett E. A. Defective particles in BHK cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):154–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.154-160.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Absence of interference during high-multiplicity infection by clonally purified vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):409–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.409-411.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger J. T., Reichmann M. E. RNA synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.570-578.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware B. R., Raj T., Flygare W. H., Lesnaw J. A., Reichmann M. E. Molecular weights of vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective particles by laser light-scattering spectroscopy. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):141–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.141-145.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]