Abstract
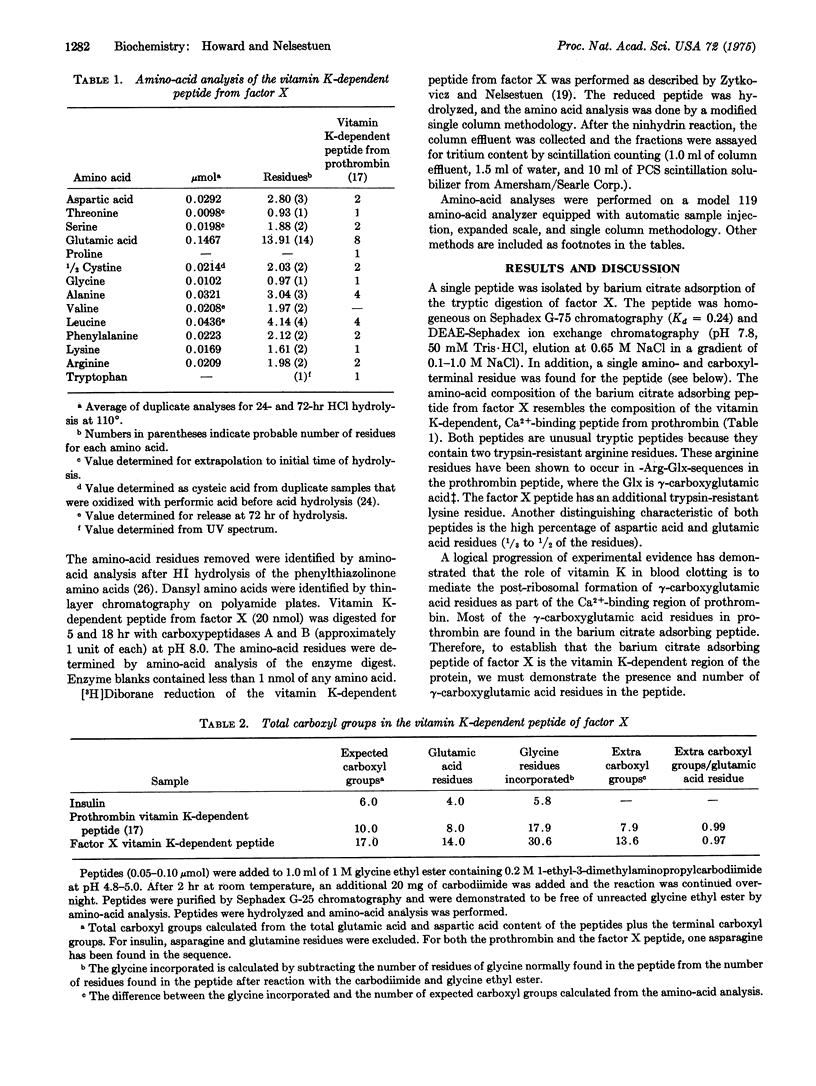
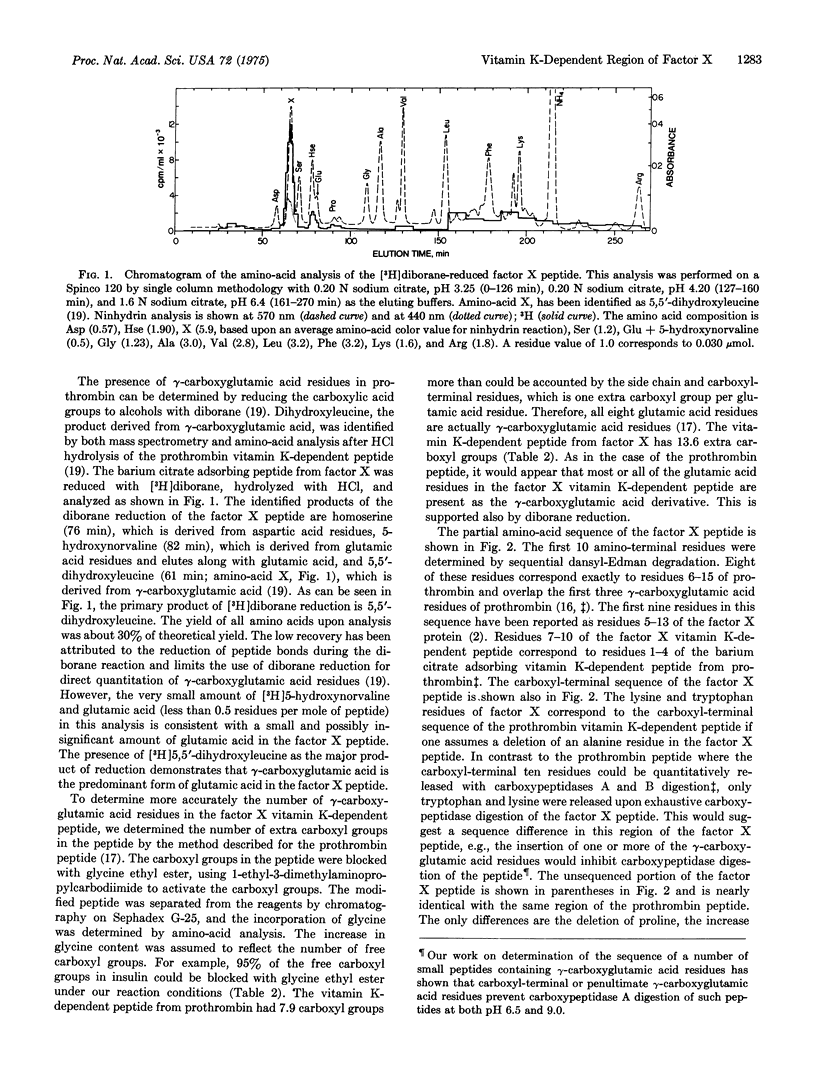
A 39-residue peptide from the tryptic digestion of bovine blood clotting factor X has been isolated by specific adsorption on barium citrate. The amino- and carboxyl-terminal sequences of the peptide were determined and compared to the vitamin K-dependent Ca2+-binding region from bovine prothrombin. The factor X peptide was found to contain gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, and the results of independent analysis are consistent with all 14 glutamic acid residues as gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. The similarity of the factor X peptide to the prothrombin peptide supports the hypothesis that the vitamin K-dependent blood clotting proteins are descended from a common ancestral gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Enfield D. L., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. A comparison of bovine prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), and factor X (Stuart factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):427–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1 (Stuart factor). Mechanism of activation by protein from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4892–4899. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Kato H., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by bovine factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4508–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitel S. N., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. A polypeptide region of bovine prothrombin specific for binding to phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1344–1348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldebrant C. M., Butkowski R. J., Bajaj S. P., Mann K. G. The activation of prothrombin. II. Partial reactions, physical and chemical characterization of the intermediates of activation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7149–7163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougie C., Denson K. W., Biggs R. A study of the reaction product of factor 8 and factor IX by gel filtration. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Aug 15;18(1-2):211–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Nelsestuen G. L. Properties of a Ca2+ binding peptide from prothrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):757–763. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M. Characterization of two glycoprotein variants of bovine factor X and demonstration that the factor X zymogen contains two polypeptide chains. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4873–4882. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBLAD R. L., DAVIE E. W. THE ACTIVATION OF ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR (FACTOR 8) BY ACTIVATED CHRISTMAS FACTOR (ACTIVATED FACTOR9 9). Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1720–1725. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. Mode of action of vitamin K. Calcium binding properties of bovine prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4961–4964. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The carbohydrate of bovine prothrombin. Partial structural determination demonstrating the presence of -galactose residues. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6096–6102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The mode of action of vitamin K. Isolation of a peptide containing the vitamin K-dependent portion of prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3366–3370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Suttie J. W. The purification and properties of an abnormal prothrombin protein produced by dicumarol-treated cows. A comparison to normal prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8176–8182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Zytkovicz T. H., Howard J. B. The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6347–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAHADJOPOULOS D., HANAHAN D. J. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INTERACTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AND CERTAIN CLOTTING FACTORS IN PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATOR FORMATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 19;90:436–439. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. D., Nehrlich S., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Determination of the amino acid sequence of the monkey, sheep, and dog proinsulin C-peptides by a semi-micro Edman degradation procedure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Vitamin K and the biosynthesis of prothrombin. 3. Structural comparison of an NH2-terminal fragment from normal and from dicoumarol-induced bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6325–6332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Hermodson M. A., Fujikawa K., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1a (activated Stuart factor). Evidence of homology with mammalian serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4899–4903. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


