Abstract
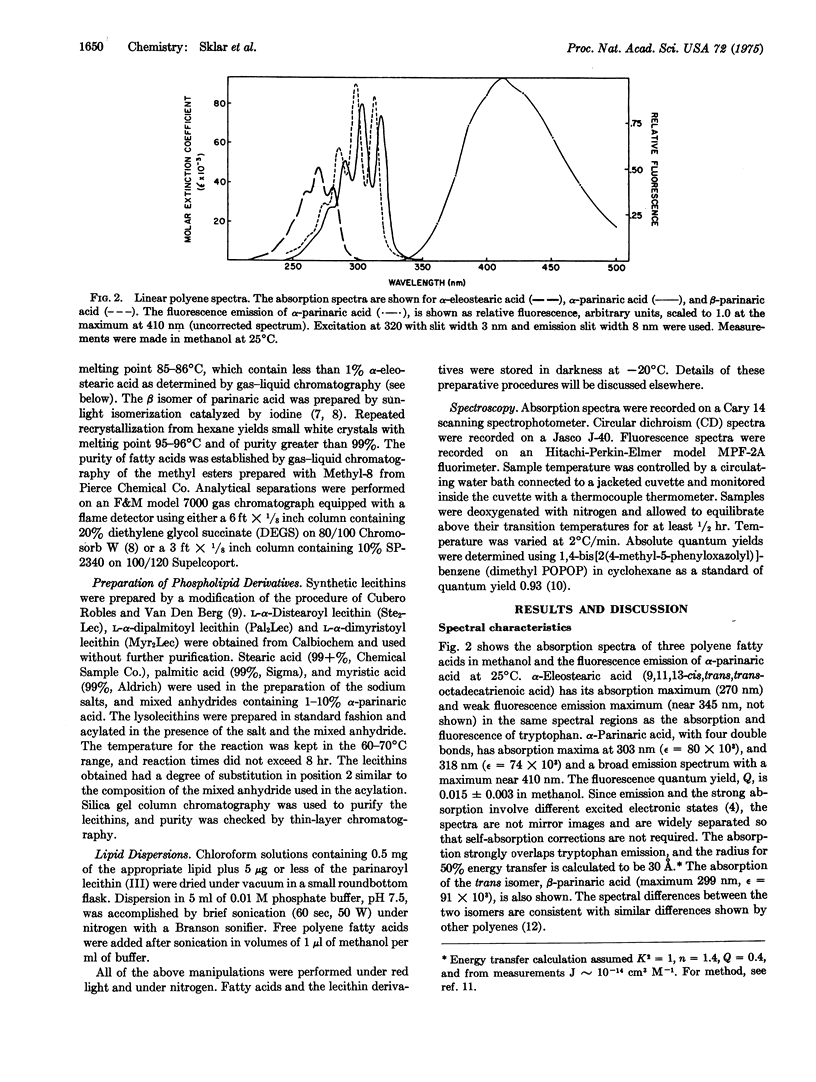
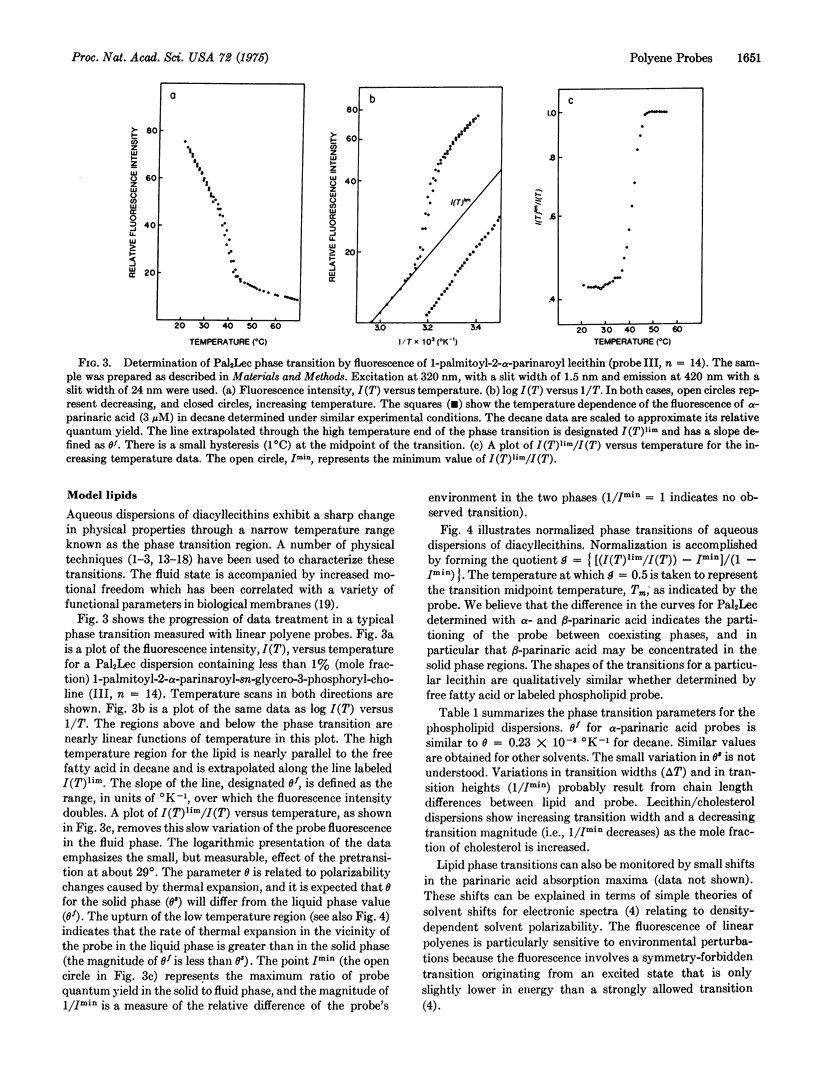
The use of fluorescent conjugated polyenoic fatty acids as probes of membrane structure is introduced. alpha- and beta-parinaric acid (cis, trans, trans, cis-, and all trans-9,11,13,15-octadecatetraenoic acid) and synthetic lecithins containing an alpha-parinaric acid chain in position 2 are prepared and their absorption and fluorescence properties are determined. Phase transitions are detected as fluorescence changes at characteristic temperatures when either the free fatty acid probes or the labeled phospholipid probe are included in sonicated aqueous dispersions of L-alpha-dimyristoyl lecithin, L-alpha dipalmitoyl lecithin, or L-alpha-distearoyl lecithin. The phase transitions are detected at about 23 degrees C (dimyristoyl), 44 degrees C (dipalmitoyl), and 53 degrees C (distearoyl lecithin). Binding of alpha-parinaric acid to bovine serum albumin is measured by shifts in the absorption spectrum and enhanced quantum yield of the fatty acid upon binding and by energy transfer between 2 tryptophyl residues in bovine serum albumin and alpha-parinaric acid. Approximately six binding sites are detected. Other applications of these probe molecules, including phase transitions of phospholipid/cholesterol dispersions, induced circular dichroism of parinaric acid bound to albumin, and biosynthetic incorporation of parinaric acid into biological membranes, are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein E. A., Vedenkina N. S., Ivkova M. N. Fluorescence and the location of tryptophan residues in protein molecules. Photochem Photobiol. 1973 Oct;18(4):263–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1973.tb06422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero Robles E., van den Berg D. Synthesis of lecithins by acylation of O-(sn-glycero-3-phosphoryl) choline with fatty acid anhydrides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 17;187(4):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Chapman D. Thermal analysis of lipids, proteins and biological membranes. A review and summary of some recent studies. Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Dec;3(4):304–356. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Williams R. M., Chapman D. Studies on lecithin-cholesterol-water interactions by differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Klotz I. M. Amino acid sequence adjoining the lone tryptophan of human serum albumin. A binding site of the protein. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2570–2574. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Overath P. The structure of Escherichia coli membranes studied by fluorescence measurements of lipid phase transitions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 25;307(3):491–512. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S., Stryer L. Fluorescent probes of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):579–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Verma S. P., Weidekamm E., Bieri V. Hydrophobic binding sites in bovine serum albumin and erythrocyte ghost proteins. Study by spin-labelling, paramagnetic fluorescence quenching and chemical modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):68–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Stryer L. Proximity relationships in rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]