Abstract
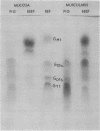
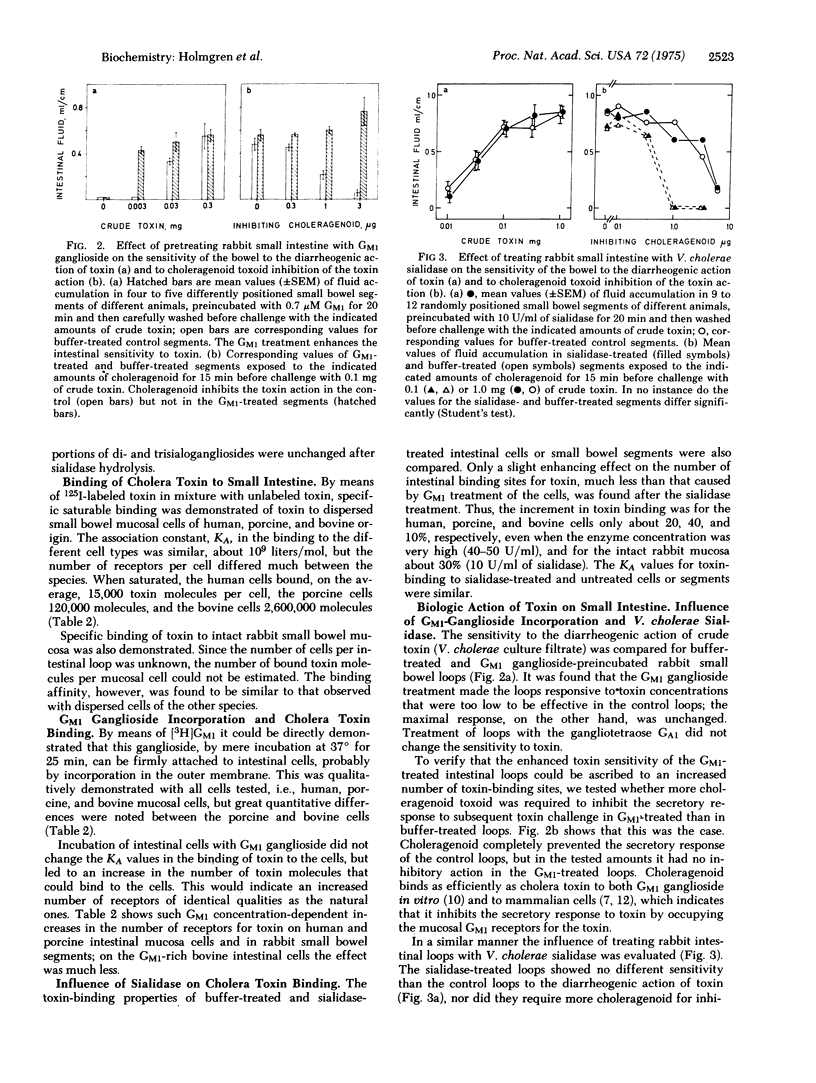
Ganglioside GM1 was isolated from the small intestinal mucosa of man, pig, and beef and amounted to 0.1, 2.0, and 43 nmol per g fresh weight, respectively. These differences in GM1 content were associated with a quantitatively differing ability of the mucosal cells to bind cholera toxin. Human cells bound about 15,000 toxin molecules when saturated with the toxin, porcine cells 120,000, and bovine cells 2,600,000 molecules. The association constant (KA) of the cholera toxin binding was, for cells of all three species, about 10(9) liters/mol. Exogenously added GM1 ganglioside was incorporated in intestinal mucosal cells as well as in intact rabbit small bowel. The increment in GM1 was associated with a correspondingly increased number of binding sites for cholera toxin, whereas KA was unchanged. GM1 incorporation increased the sensitivity of the rabbit small bowel to the diarrheogenic action of cholera toxin. Vibrio cholerae sialidase hydrolyzed isolated intestinal diand trisialogangliosides to GM1. However, the enzyme did not change the ganglioside pattern of intestinal mucosa, had very little influence on the number of toxin binding sites on intestinal cells, and did not alter the sensitivity of the small bowel to the diarrheogenic action of the toxin. These results demonstrate a relationship in the intestinal mucosa between the GM1 ganglioside concentration, the number of binding sites for cholera toxin, and the sensitivity to the biologic action of the toxin. Thus, the study strongly supports the concept that the GM1 ganglioside is the intestinal binding receptor for cholera toxin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Parikh I., Hollenberg M. D. Affinity chromatography and structural analysis of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin-ganglioside agarose and the biological effects of ganglioside-containing soluble polymers. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4253–4264. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Vibrio cholerae choleragenoid. Mechanism of inhibition of cholera toxin action. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3577–3581. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M: Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Production of highly purified choleragen and choleragenoid. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):63+–63+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm M., Månsson J. E., Vanier M. T., Svennerholm L. Gangliosides of human, bovine and rabbit retina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 5;280(2):356–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. I. Binding properties and interference with lectin-induced cellular stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):801–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lonnroth I. Oligomeric structure of cholera toxin: characteristics of the H and L subunits. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):49–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai G. J., Burrows W. The titration of cholera toxin and antitoxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):606–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Van Heyningen W. E. Deactivation of cholera toxin by a sialidase-resistant monosialosylganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):639–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T., Månsson J. E., Vanier M. T., Svennerholm L. Structure of the major glucosamine-containing ganglioside of human tissues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2634–2636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Holmgren J. Subunit structure of cholera toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jun;76(2):417–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-2-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Differential inhibitory effects of cholera toxoids and ganglioside on the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):1009–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Carpenter C. C., Jr Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin and its mode of action. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.1-13.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S., Hof L., Bradley R. M., Brady R. O. Lactosylceramide galactosidase: comparison with other sphingolipid hydrolases in developing rat brain. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Holm M., Månsson J. E., Svennerholm L. The distribution of lipids in the human nervous system--V. Gangliosides and allied neutral glycolipids of infant brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1375–1384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Holm M., Ohman R., Svennerholm L. Developmental profiles of gangliosides in human and rat brain. J Neurochem. 1971 Apr;18(4):581–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. K., Ledeen R. W. Gangliosides of human, bovine, and rabbit plasma. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]