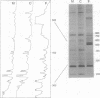
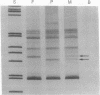
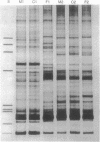
Abstract
Low-stringency single specific primer PCR (LSSP-PCR) is an extremely simple PCR-based technique that detects single or multiple mutations in gene-sized DNA fragments. A purified DNA fragment is subjected to PCR using high concentrations of a single specific oligonucleotide primer, large amounts of Taq polymerase, and a very low annealing temperature. Under these conditions the primer hybridizes specifically to its complementary region and nonspecifically to multiple sites within the fragment, in a sequence-dependent manner, producing a heterogeneous set of reaction products resolvable by electrophoresis. The complex banding pattern obtained is significantly altered by even a single-base change and thus constitutes a unique "gene signature." Therefore LSSP-PCR will have almost unlimited application in all fields of genetics and molecular medicine where rapid and sensitive detection of mutations and sequence variations is important. The usefulness of LSSP-PCR is illustrated by applications in the study of mutants of smooth muscle myosin light chain, analysis of a family with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, and identity testing using human mitochondrial DNA.
Full text
PDF
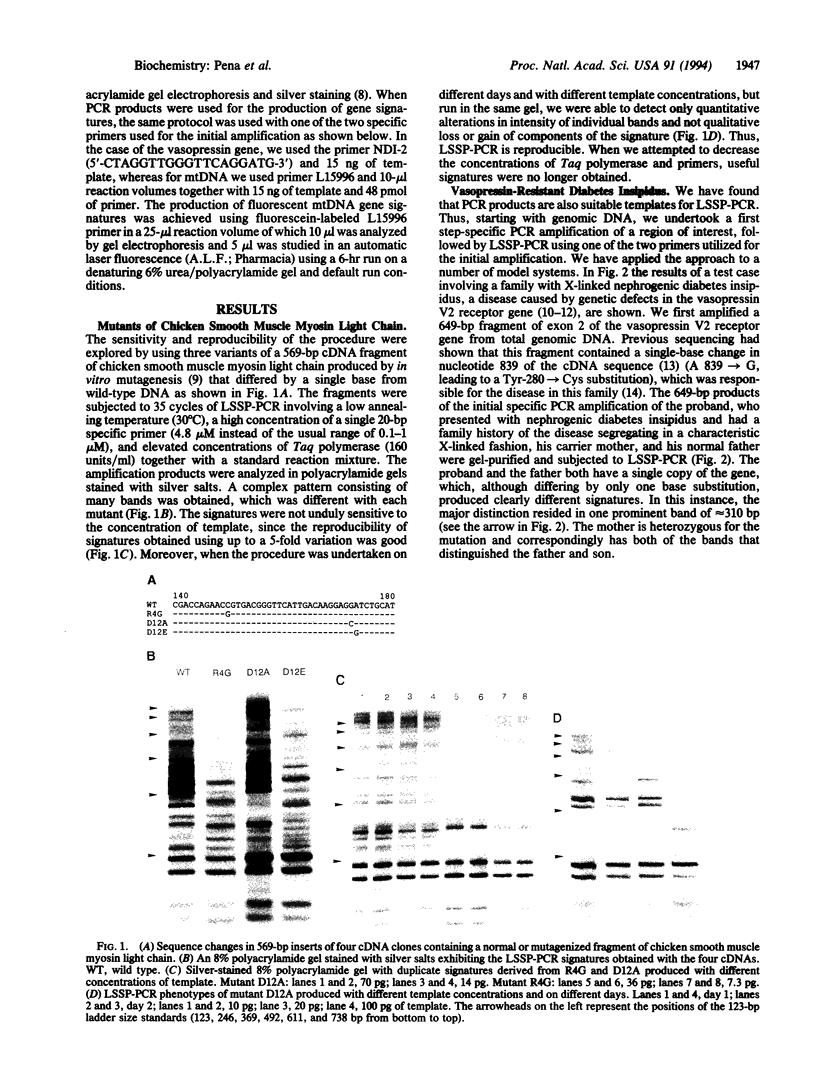

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer M., Seibold A., Gilbert S., Ishido M., Barberis C., Antaramian A., Brabet P., Rosenthal W. Molecular cloning of the receptor for human antidiuretic hormone. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):333–335. doi: 10.1038/357333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginther C., Issel-Tarver L., King M. C. Identifying individuals by sequencing mitochondrial DNA from teeth. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):135–138. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Kondo R., Murayama K., Hayashi S., Koike H., Nakai N. Phylogenetic affiliation of ancient and contemporary humans inferred from mitochondrial DNA. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 30;333(1268):409–417. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1991.0091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Metzenberg A., Das S., Jing B., Gitschier J. Mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene are associated with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):103–106. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena S. D., Macedo A. M., Gontijo N. F., Medeiros A. M., Ribeiro J. C. DNA bioprints: simple nonisotopic DNA fingerprints with biotinylated probes. Electrophoresis. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):146–152. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150120209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinach F. C., Nagai K., Kendrick-Jones J. Site-directed mutagenesis of the regulatory light-chain Ca2+/Mg2+ binding site and its role in hybrid myosins. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):80–83. doi: 10.1038/322080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Walsh P. S., Levenson C. H., Erlich H. A. Genetic analysis of amplified DNA with immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos F. R., Pena S. D., Epplen J. T. Genetic and population study of a Y-linked tetranucleotide repeat DNA polymorphism with a simple non-isotopic technique. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):655–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00202486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoneking M., Hedgecock D., Higuchi R. G., Vigilant L., Erlich H. A. Population variation of human mtDNA control region sequences detected by enzymatic amplification and sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):370–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Pennington R., Harpending H., Kocher T. D., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA sequences in single hairs from a southern African population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9350–9354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. Y., Ugozzoli L., Pal B. K., Qian J., Wallace R. B. The effect of temperature and oligonucleotide primer length on the specificity and efficiency of amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;10(3):233–238. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Dreesen J. C., Verdijk M., Knoers N. V., Monnens L. A., Rocchi M., van Oost B. A. Mutations in the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) associated with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):99–102. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]