Abstract
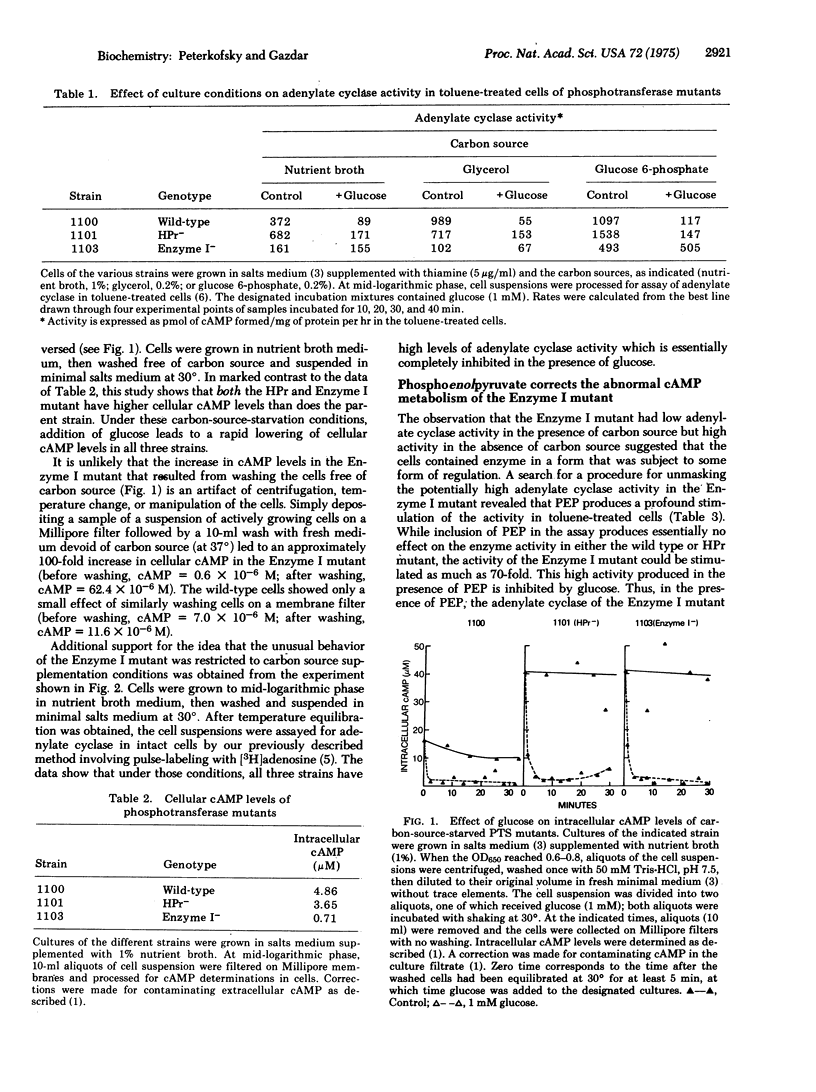
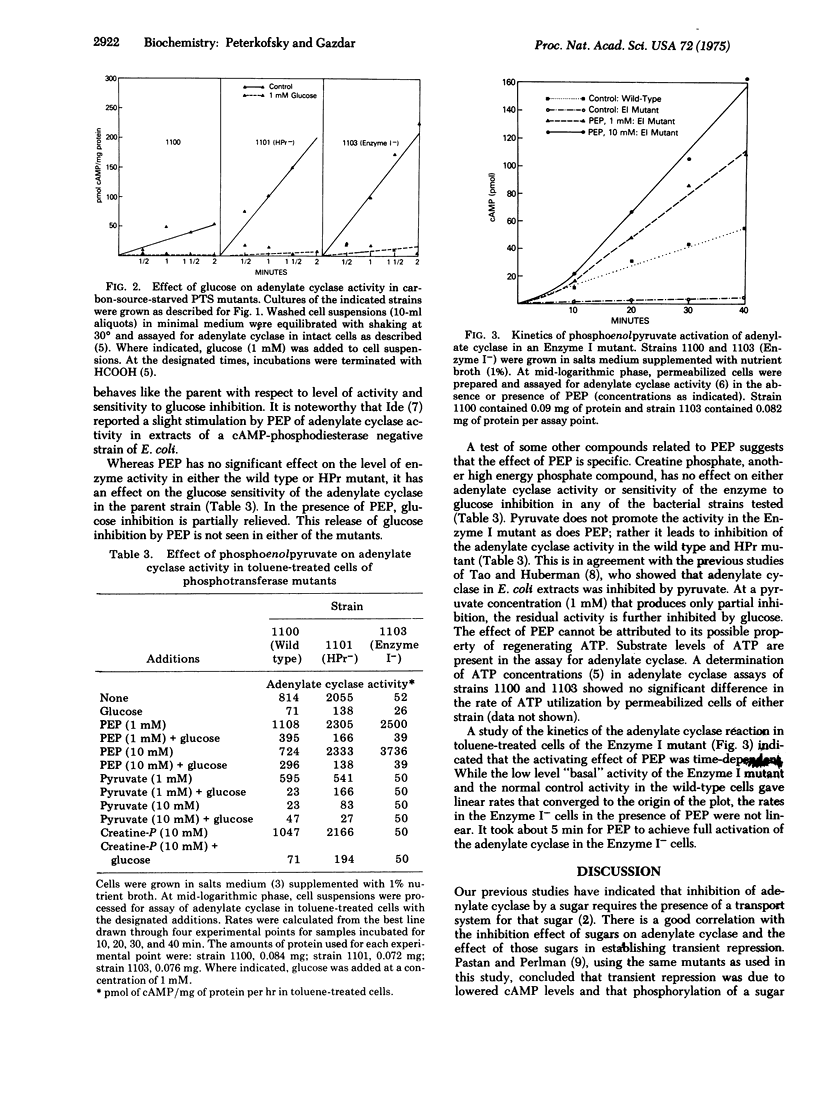
Transient repression by glucose of induced enzyme synthesis involves lowering of intracellular cAMP levels. This glucose effect is partially explained by a glucose inhibition of adenylate cyclase [EC 4.6.1.1; ATP pyrophosphate-lyase(cyclizing)]. Since the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system has been implicated in repression phenomena, an investigation was made of adenylate cyclase activity in mutants of that transport system. The results suggest that glucose phosphorylation is not necessary for inhibition of adenylate cyclase since an HPr mutant retained sensitivity to glucose inhibition. The results also suggest that adenylate cyclase activity requires the presence of Enzyme I in a phosphorylated form and that adenylate cyclase activity may be regulated by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constantopoulos A., Najjar V. A. The activation of adenylate cyclase. II. The postulated presence of (A) adenylate cyclase in a phospho (inhibited) form (B) a dephospho (activated) form with a cyclic adenylate stimulated membrane protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):794–799. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Peterkofsky A. Glucose-sensitive adenylate cyclase in toluene-treated cells of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4656–4662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide M. Adenyl cyclase of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90646-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo T. C., Rayman M. K., Sanwal B. D. Transport of succinate in Escherichia coli. I. Biochemical and genetic studies of transport in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6323–6331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis by glucose in phosphotransferase mutants of Escherichia coli. Repression in the absence of glucose phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5836–5842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Glucose inhibition of adenylate cyclase in intact cells of Escherichia coli B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Measurements of rates of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate synthesis in intact Escherichia coli B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2149–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Roseman S. Inducer exclusion and repression of enzyme synthesis in mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):972–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Levinthal M., Kundig F. D., Kundig W., Anderson B., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Genetic evidence for the role of a bacterial phosphotransferase system in sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1963–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Schrecker O., Lauppe H. F., Hengstenberg H. The staphylococcal PEP dependent phosphotransferase system: demonstration of a phosphorylated intermediate of the enzyme I component. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 15;42(1):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Huberman A. Some properties of Escherichia coli adenyl cyclase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Physiological basis of transient repression of catabolic enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):411–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.411-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


