Abstract
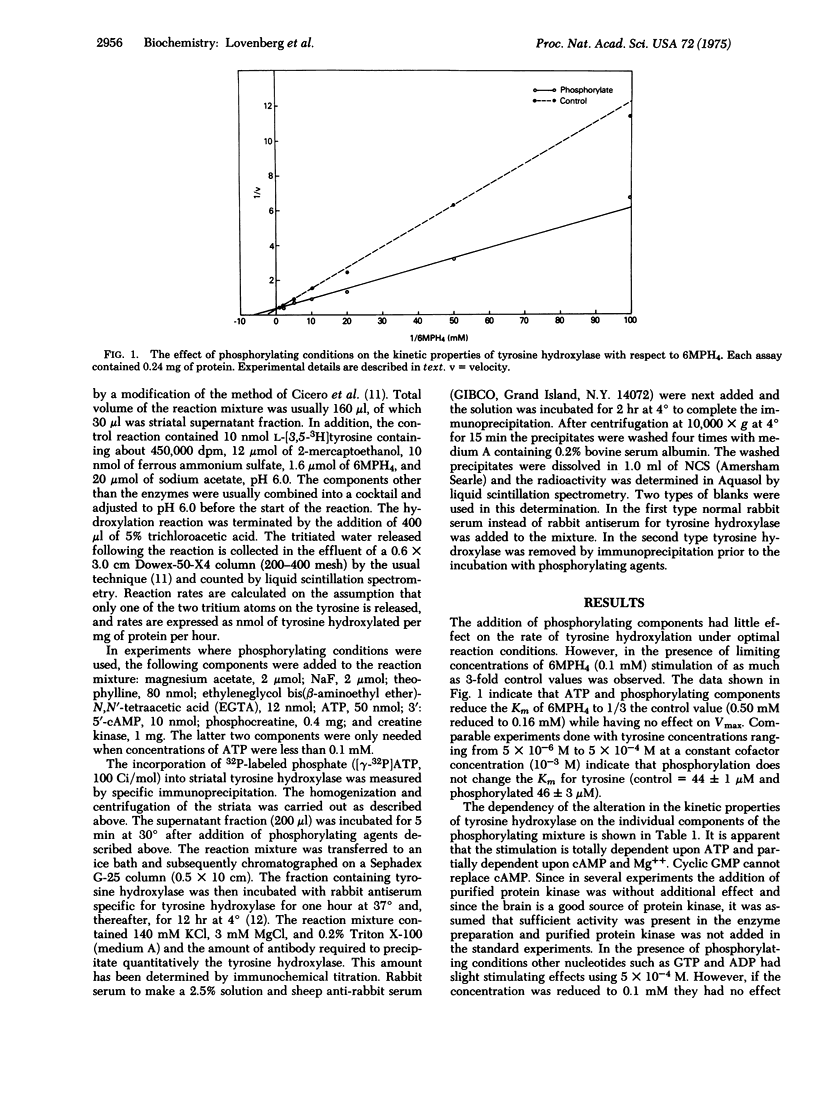
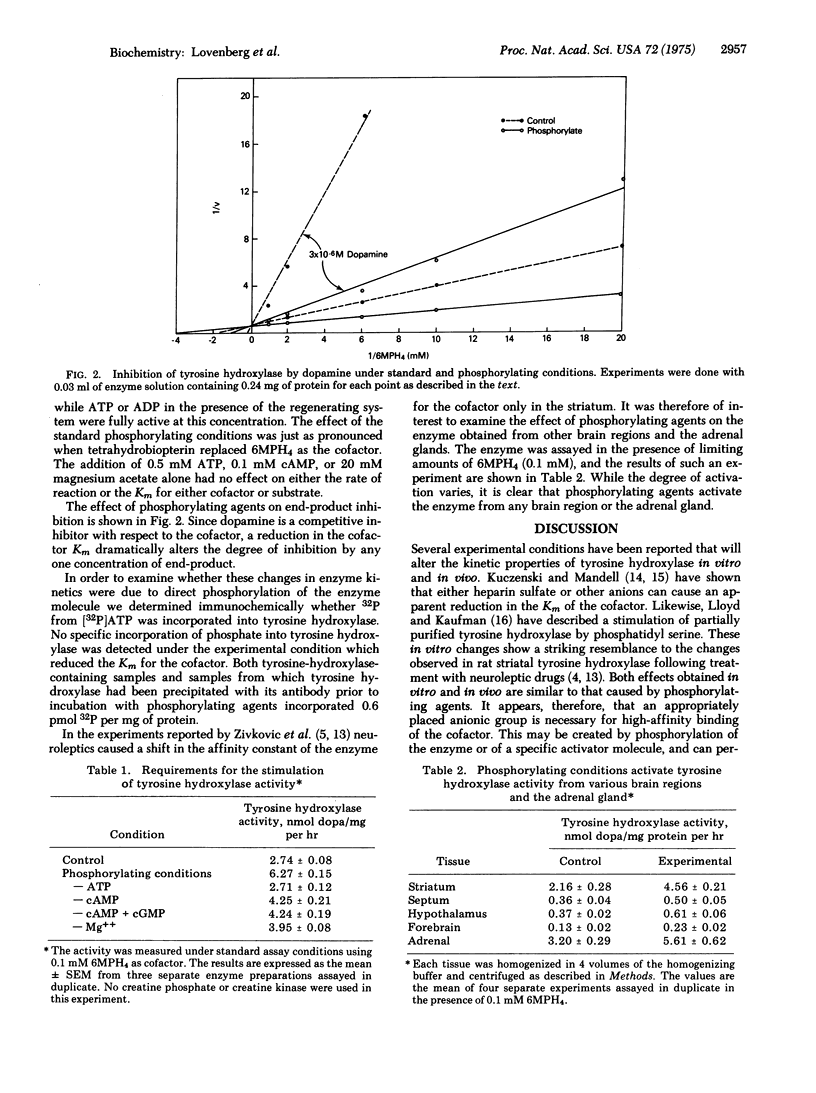
Treatment of rat striatal tyrosine hydroxylase [tyrosine 3-monooxygenase; L-tyrosine, tetrahydropteridine:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating); EC 1.14.16.2] with conditions optimal for protein phosphorylation results in the reduction of the tyrosine hydroxylase Km for the cofactor 6-methyltetrahydropterin from 0.50 mM to 0.16 mM. This reaction is dependent upon ATP, 3':5'-cAMP, and Mg++ and causes a marked decrease in the sensitivity to end-product inhibition. Other brain regions and the adrenal gland show a similar response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Bédard P., Fuxe K., Ungerstedt U. Early and selective increase in brain dopamine levels after axotomy. Experientia. 1972 Mar 15;28(3):300–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01928702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A., Kehr W., Lindqvist M. Short-term control of tyrosine hydroxylase. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;12(0):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. M., Costa E. Biosynthesis of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat adrenal medulla after exposure to cold. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4570–4574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Sharpe L. G., Robins E., Grote S. S. Regional distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Sep;19(9):2241–2243. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement-Cormier Y. C., Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in mammalian brain: a possible site of action of antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1113–1117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Zivkovic B. Short- and long-term regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;12(0):161–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. E., Morgenroth V. H., 3rd, Roth R. H., Baldessarini R. J. Regulation of catecholamine synthesis in the rat brain in vitro by cyclic AMP. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):156–158. doi: 10.1038/252156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Leitich H. Antipsychotic drugs and dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase prepared from corpus striatum of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2915–2918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in caudate nucleus of rat brain, and its similarity to the "dopamine receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczenski R. T., Mandell A. J. Allosteric activation of hypothalamic tyrosine hydroxylase by ions and sulphated mucopolysaccharides. J Neurochem. 1972 Jan;19(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczenski R. T., Mandell A. J. Regulatory properties of soluble and particulate rat brain tyrosine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3114–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd T., Kaufman S. The stimulation of partially purified bovine caudate tyrosine hydroxylase by phosphatidyl-L-serine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1262–1270. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90450-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Nagatsu T. Inhibitors of purified beef adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamabe H., De Jong W., Lovenberg W. Further studies on catecholamine synthesis in the spontaneously hypertensive rat: catecholamine synthesis in the central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;22(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zivkovic B., Guidotti A. Changes of kinetic constant of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase elicited by neuroleptics that impair the function of dopamine receptors. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 25;79(3):505–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


