Abstract
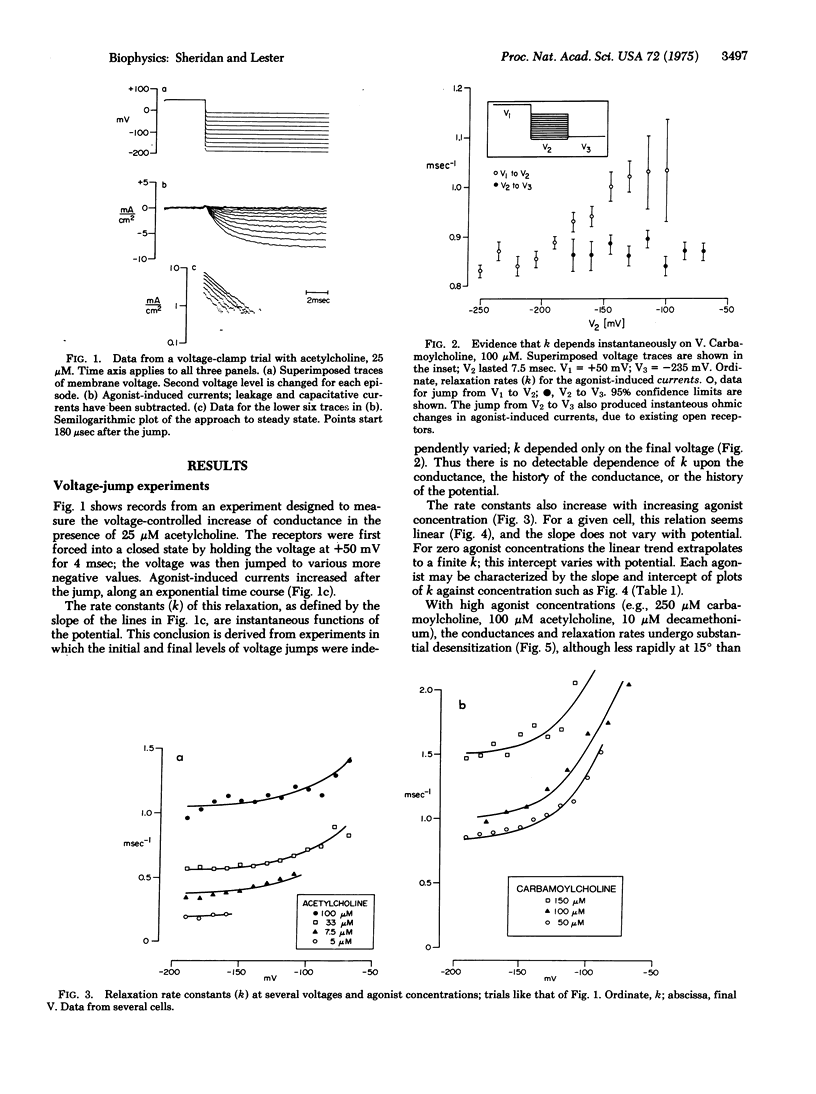
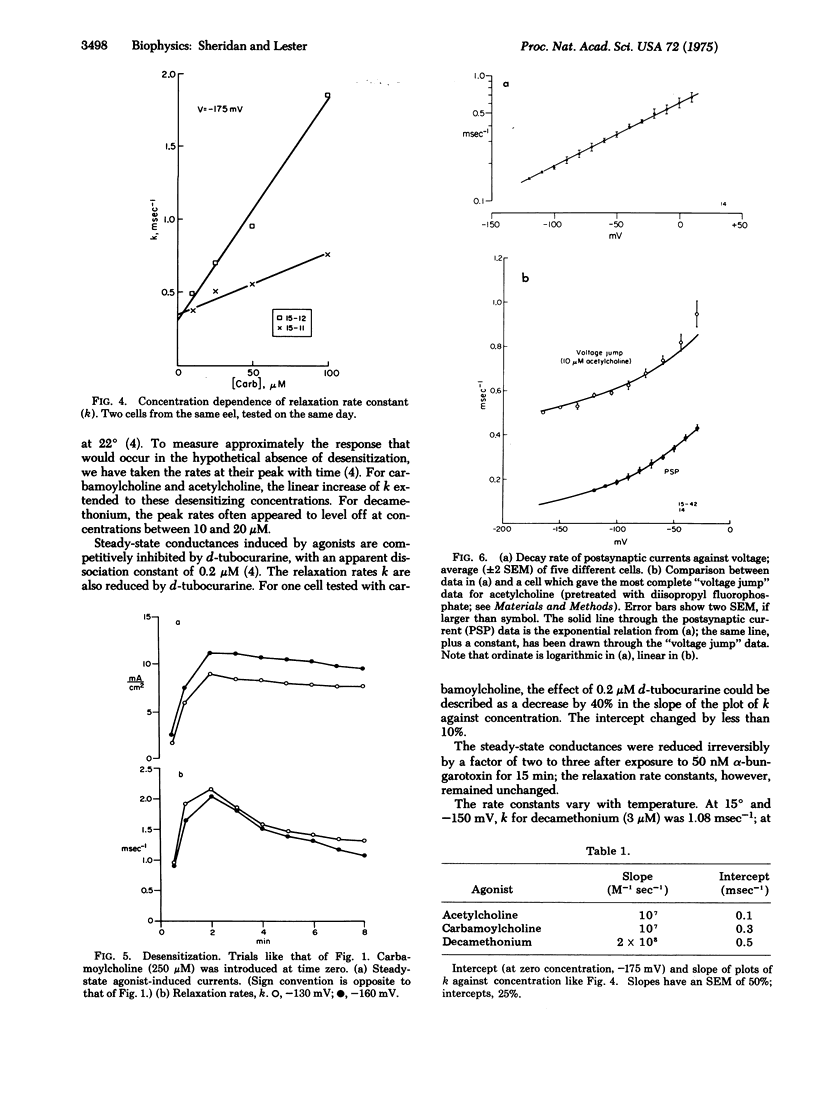
In Electrophorus electroplaques, the agonist-induced postsynaptic conductance depends on membrane potential. During steady exposure to agonists, after a voltage step the conductance relaxes on a millisecond time scale, exponentially approaching a new equilibrium value. The relaxation rate constant k is an instantaneous function of voltage, insensitive to the past or present conductance. Two components sum to form k. A concentration-sensitive component increases linearly with agonist concentration and decreases during desensitization or exposure to curare. Thus this component reflects the average frequency at which acetylcholine receptors are opening. The voltage-sensitive component, obtained by extrapolating k to zero agonist concentration, increases at more positive potentials. For acetylcholine, the voltage-sensitive component equals the rate constant for the exponential decay of postsynaptic currents; it thus seems to be the closing rate for active receptors. The voltage-sensitive component has the relative amplitudes acetylcholine less than carbamoylcholine less than decamethonium, and for each agonist equals the closing rate determined from "noise" measurements at neuromuscular junctions. The kinetic data explain several aspects of the steady-state conductance induced by agonists, but shed no light on apparent cooperative effects.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Kinetics of agonist conductance changes during hyperolarization at frog endplates. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):308–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Läuger P. Channel formation kinetics of gramicidin A in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973;11(2):177–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01869820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The characteristics of 'end-plate noise' produced by different depolarizing drugs. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):707–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. I. The effects of prostigmine and of the ratio of Mg 2+ to Ca 2+ . J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):317–332. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. II. Temperature. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):333–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Voltage-dependence of drug-induced conductance in frog neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. W., Darzynkiewicz Z., Salpeter M. M., Ostrowski K., Barnard E. A. Quantitative studies on enzymes in structures in striated muscles by labeled inhibitor methods. I. The number of acetylcholinesterase molecules and of other DFP-reactive sites at motor endplates, measured by radioautography. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):665–685. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Manresa F., Grundfest H. Synaptic electrogenesis in eel electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jan;57(1):71–92. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Manresa F., Ruarte A. C., Schwartz T. L., Grundfest H. Potassium inactivation and impedance changes during spike electrogenesis in eel electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):33–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E., NACHMANSOHN D. An isolated single electroplax preparation. I. New data on the effect of acetylcholine and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


