Abstract
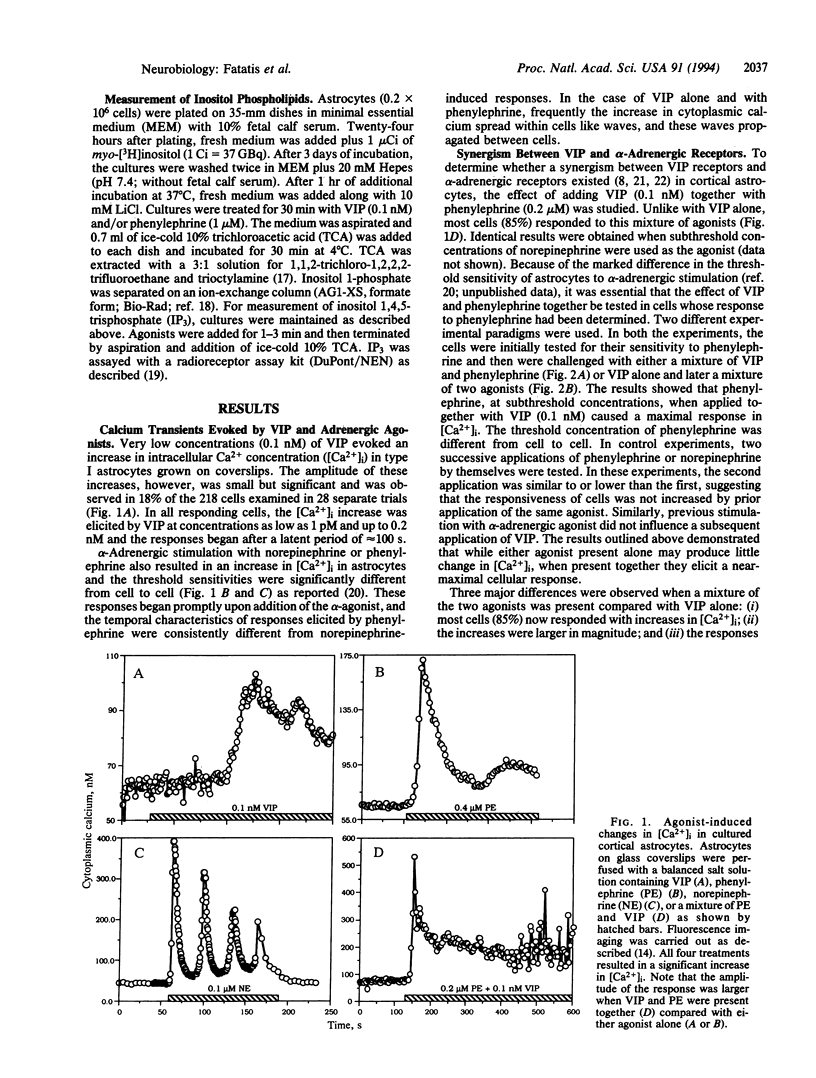
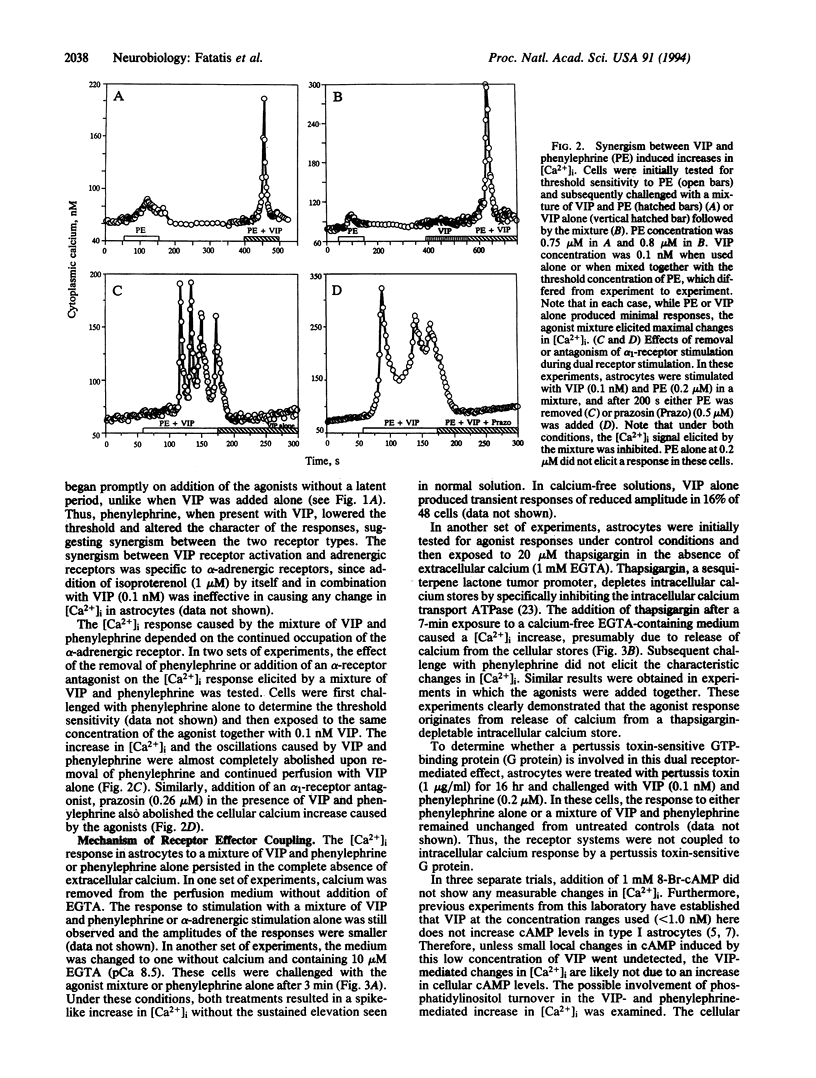
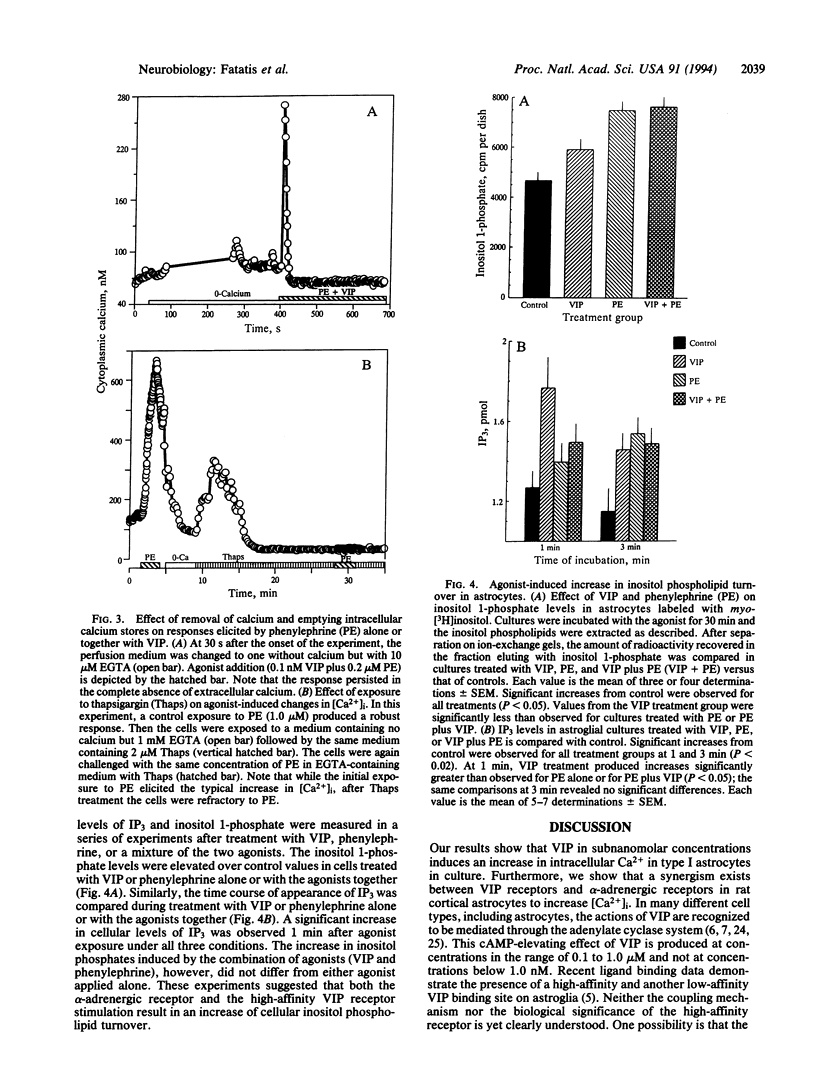
In type I astrocytes from rat cerebral cortex, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) at concentrations below 1 nM evoked an increase in intracellular calcium ion concentration. This response, however, was observed in only 18% of the astrocytes examined. alpha-Adrenergic stimulation with phenylephrine or norepinephrine also resulted in an intracellular calcium response in these cells and the threshold sensitivity of astrocytes to phenylephrine was vastly different from cell to cell. Treatment of these astrocytes with VIP (0.1 nM) together with phenylephrine at subthreshold concentrations produced large increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and oscillations. The continued occupation of the alpha-adrenergic receptor was required for sustained synergism. Both alpha-receptor stimulation and stimulation with the mixture of agonists induced the cellular calcium response by triggering release of calcium from cellular stores, since the response persisted in the absence of extracellular calcium. Furthermore, thapsigargin pretreatment, which depletes intracellular stores, abolished the agonist-induced [Ca2+]i response. VIP (0.1 nM) and phenylephrine were found to increase cellular levels of inositol phosphates; however, there was no apparent additivity in this response when the agonists were added together. These observations suggest a calcium-mediated second messenger system for the high-affinity VIP receptor in astrocytes and that alpha-adrenergic receptors act synergistically with the VIP receptor to augment an intracellular calcium signal. The synergism between diverse receptor types may constitute an important mode of cellular signaling in astroglia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Mourey R. J., Snyder S. H. A simple, sensitive, and specific radioreceptor assay for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in biological tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):976–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Nicol T., Warren D., Bowers L. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a neurotrophic releasing agent and an astroglial mitogen. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Mar;25(3):386–394. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Hou C., Sidiropoulos D., Stock J. B., Jakobs K. H., Gierschik P. Stimulation of phospholipase C by guanine-nucleotide-binding protein beta gamma subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chik C. L., Ho A. K., Klein D. C. Alpha 1-adrenergic potentiation of vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulation of rat pinealocyte adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate: evidence for a role of calcium and protein kinase-C. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):702–708. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chneiweiss H., Glowinski J., Premont J. Do secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide have independent receptors on striatal neurons and glial cells in primary cultures? J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):608–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cholewinski A. J., Wilkin G. P. Astrocytes from forebrain, cerebellum, and spinal cord differ in their responses to vasoactive intestinal peptide. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1626–1633. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Robberecht P., Christophe J. Characterization of VIP-sensitive adenylate cyclase in guinea pig brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80645-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. D., Villegas J. The action of vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonists on peptidergic modulation of the squid Schwann cell. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;138:259–269. doi: 10.1242/jeb.138.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatatis A., Russell J. T. Spontaneous changes in intracellular calcium concentration in type I astrocytes from rat cerebral cortex in primary culture. Glia. 1992;5(2):95–104. doi: 10.1002/glia.440050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozes I., Brenneman D. E. VIP: molecular biology and neurobiological function. Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Winter;3(4):201–236. doi: 10.1007/BF02740606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozes I., McCune S. K., Jacobson L., Warren D., Moody T. W., Fridkin M., Brenneman D. E. An antagonist to vasoactive intestinal peptide affects cellular functions in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., Daly J. W. Accumulation of inositol phosphates and cyclic AMP in guinea-pig cerebral cortical preparations. Effects of norepinephrine, histamine, carbamylcholine and 2-chloroadenosine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 20;847(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J., Manthorpe M., Bloom F. E., Varon S. Functional receptors for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cultured astroglia from neonatal rat brain. Regul Pept. 1983 Apr;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J. Regulation of glycogenolysis by neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. Diabete Metab. 1988 May-Jun;14(3):237–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., Salm A. K. Pharmacologically-distinct subsets of astroglia can be identified by their calcium response to neuroligands. Neuroscience. 1991;41(2-3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90330-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quik M., Iversen L. L., Bloom S. R. Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and other peptides on cAMP accumulation in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(18):2209–2213. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., De Neef P., Lammens M., Deschodt-Lanckman M., Christophe J. P. Specific binding of vasoactive intestinal peptide to brain membranes from the guinea pig. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostène W. H. Neurobiological and neuroendocrine functions of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Prog Neurobiol. 1984;22(2):103–129. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(84)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salm A. K., McCarthy K. D. Norepinephrine-evoked calcium transients in cultured cerebral type 1 astroglia. Glia. 1990;3(6):529–538. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Mishler K. Beta-adrenergic receptor regulation, through cyclic AMP, of nerve growth factor expression in rat cortical and cerebellar astrocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Sep;10(3):447–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00711186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P. Neurotransmitters as neurotrophic factors: a new set of functions. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1992;34:1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shain W., Bausback D., Fiero A., Madelian V., Turner J. N. Regulation of receptor-mediated shape change in astroglial cells. Glia. 1992;5(3):223–238. doi: 10.1002/glia.440050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. P., Pert C. B. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: specific binding to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):660–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Azmitia P. M., Azmitia E. C. [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine binding to brain astroglial cells: differences between intact and homogenized preparations and mature and immature cultures. J Neurochem. 1986 Apr;46(4):1186–1189. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin G. P., Marriott D. R., Cholewinski A. J. Astrocyte heterogeneity. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Feb;13(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90065-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


