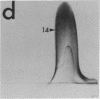
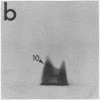
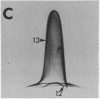
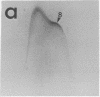
Abstract
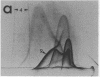
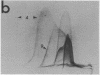
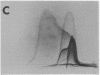
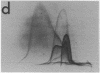
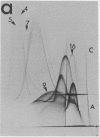
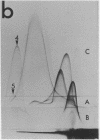
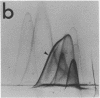
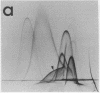
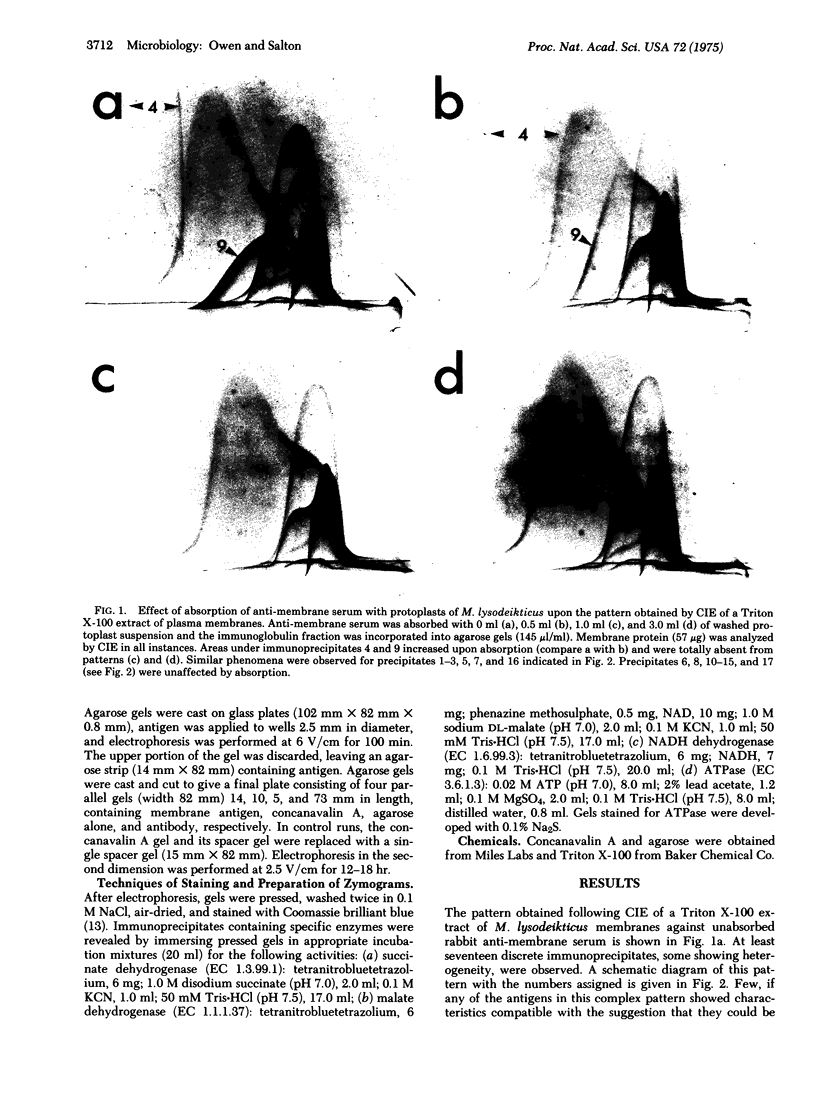
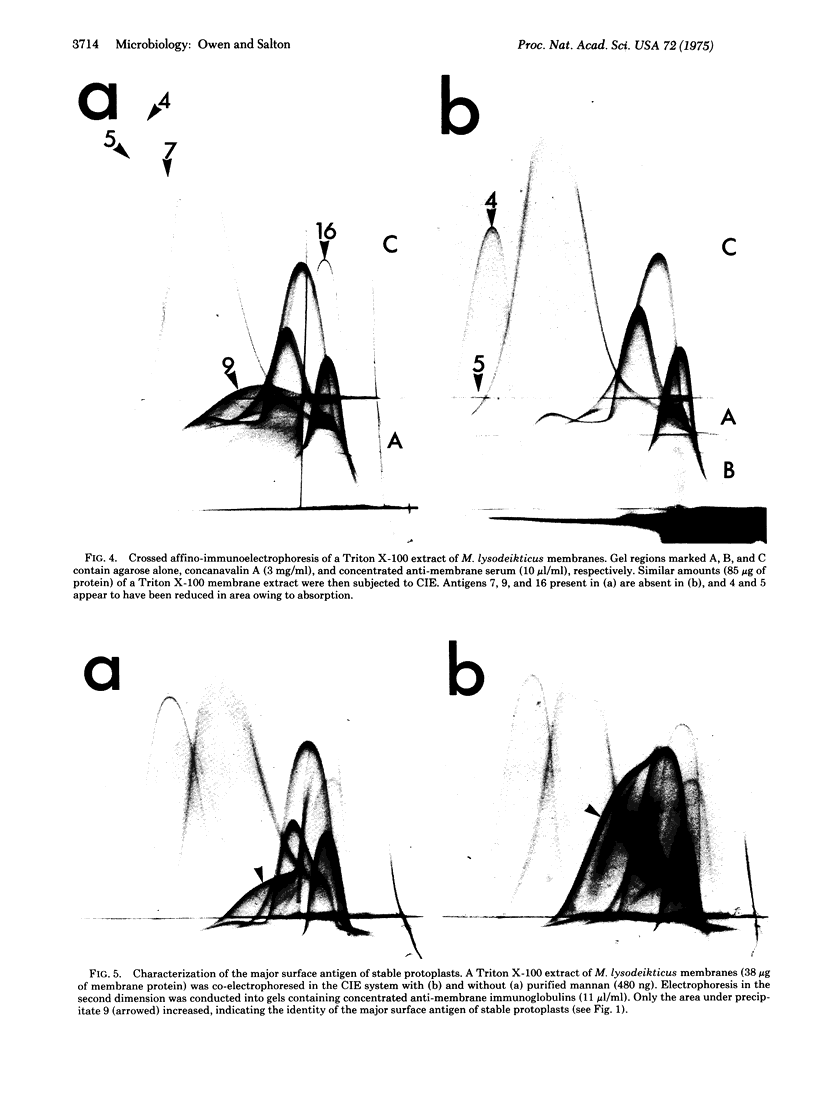
By crossed immunoelectrophoresis with membrane antiserum, 17 antigens have been detected in fractions from plasma membranes of M. lysodeikticus solubilized with Triton X-100. Absorption tests with protoplasts have demonstrated that eight of the antigens are expressed on the surface. Of these antigens the major one has been identified as a succinylated mannan. Five of the principal immunoprecipitates unaffected by absorption with protoplasts were shown by zymograms to possess the following enzymic activites: succinate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.1), ATPase (EC 3.6.1.3), NADH dehyrogenase (EC 1.6.99.3)(two separate components), and malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37). These enzymes or enzyme-complexes are, therefore, not expressed on the outer surface of the protoplast membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomberg F., Raftell M. Enzyme polymorphism in rat-liver microsomes and plasma membranes. 1. An immunochemical study of multienzyme complexes and other enzyme-active antigens. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bog-Hansen T. C. Crossed immuno-affinoelectrophoresis. An analytical method to predict the result of affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):480–488. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Woodside E. E., Fishel C. W. Protein-polyelectrolyte interactions. The concanavalin A precipitin reaction with polyelectrolytes and polysaccharide derivatives. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj1060035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Nachbar M. S., Salton M. R. Immunological properties of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):86–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.86-92.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K. The mesosome--a clue to the evolution of the plasma membrane. Subcell Biochem. 1974 Dec;3(4):311–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. D., Salton M. R. Localization and distribution of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membrane ATPase determined by ferritin labeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):297–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Freer J. H. Isolation and properties of mesosomal membrane fractions from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):907–917. doi: 10.1042/bj1290907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. A succinylated mannan in the membrane system of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftell M., Blomberg F. Enzyme polymorphism in rat-liver microsomes and plasma membranes. 2. An immunochemical comparison of enzyme-active antigens solubilized by detergents, papain or phospholipases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):31–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch V. M., Jr, Burger M. M. The bacterial mesosome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 3;300(1):79–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Bacterial membranes. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1971 May;1(1):161–197. doi: 10.3109/10408417109104480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Schor M. T. Subunit structure and properties of two forms of adenosine triphosphatase released from Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. IX. Application of the quantitative hapten inhibition technique to polysaccharide-concanavalin A interaction. Some comments on the forces involved n concanavalin A-polysaccharide interaction. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):158–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. A manual of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. 1. General remarks on principles, equipment, reagents and procedures. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:15–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]