Abstract
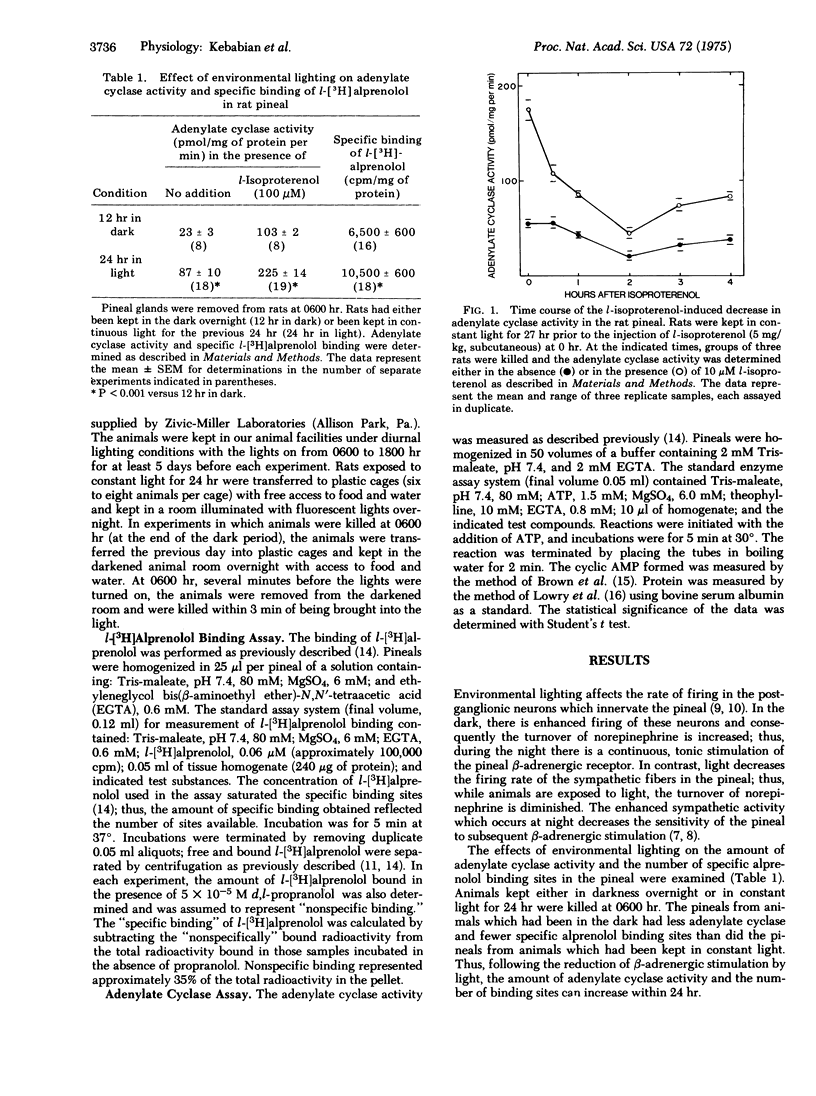
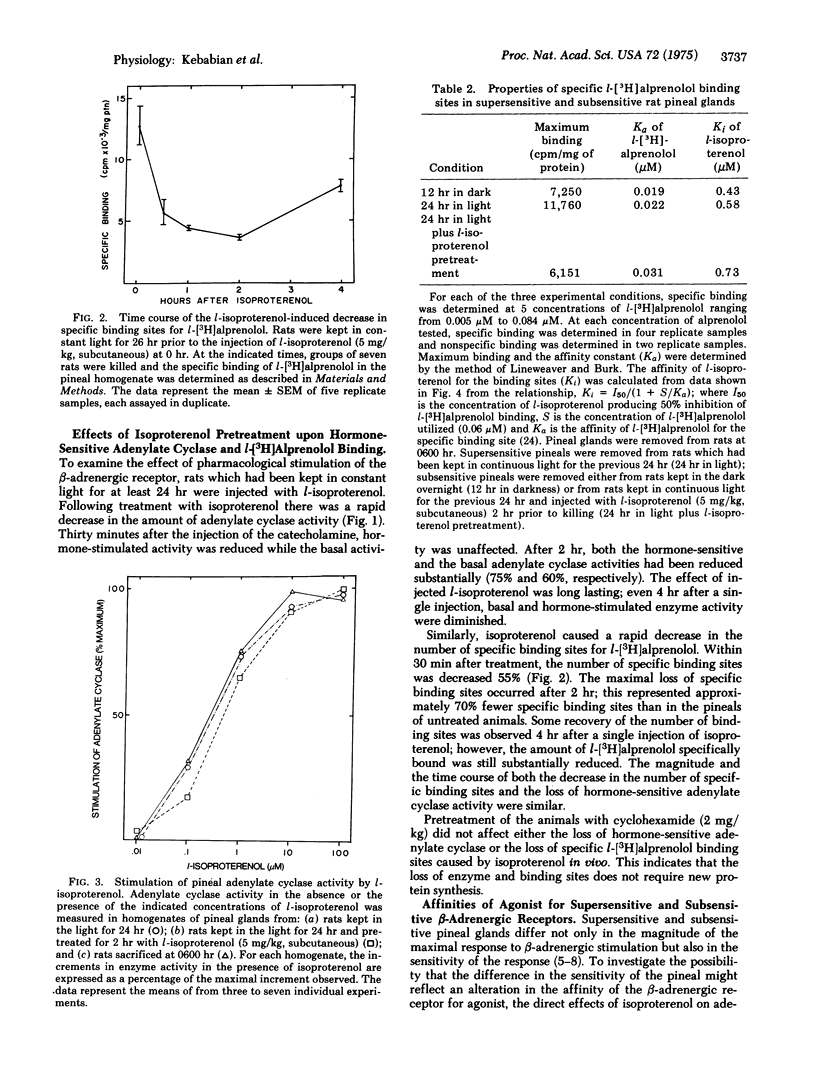
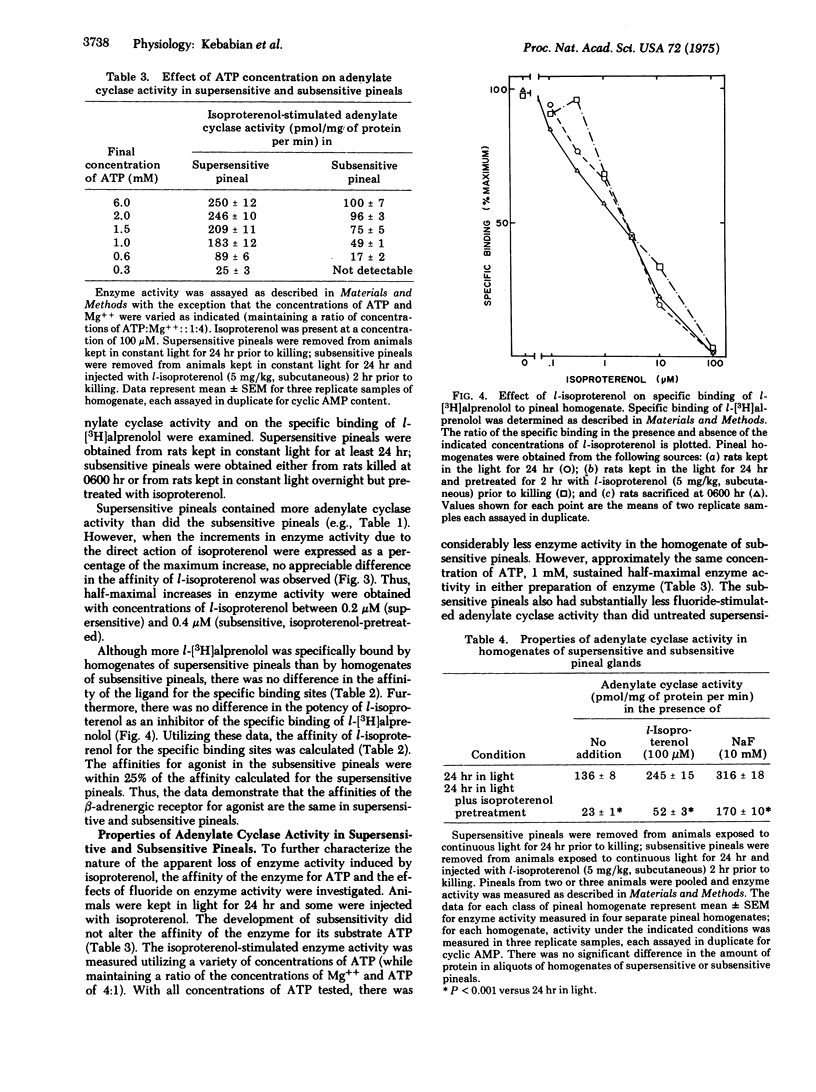
The properties of the beta-adrenergic receptor which regulates adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing)8 EC 4.6.1.1] in the pineal gland are similar to the properties of the sites which specifically bind l-[3H]alprenolol, a potent beta-adrenergic antagonist. Stimulation of the beta-adrenergic receptor results in a 30-fold increase in the activity of N-acetyltransferase (= arylamine acetyltransferase; acetyl CoA:arylamine N-acetyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.5), an enzyme involved in the synthesis of thepineal hormone melatonin. In the normal diurnal light-dark cycle there is greater physiological stimulation of the beta-adrenergic receptor in the pineal during the night than during the day. Pineals from rats kept in constant light for 24 hr possess more hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase and specifically bind more l-[3H]alprenolol than do pineals from rats kept in the dark overnight. When rats, exposed to light for 24 hr, are treated with the beat-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol, there is a rapid loss of both hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity and specific l-[3H]alprenolol binding sites. There is no change in the affinity of adenylate cyclase for isoproterenol or for its substrate, ATP. Similarly, although there are fewer binding sites, there is no change in the affinity of the remaining sites for either agonist or antagonist. Inhibition of protein synthesis with cycloheximide does not affect the loss of either adenylate cyclase activity or specific binding sites. The data suggest that stimulation of the beta-adrenergic receptor causes a rapid decrease in the number of available receptors and in hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity; conversely, lack of stimulation causes an increase in these parameters. It is suggested that these changes contribute to the phenomena of super- and subsensitivity in the pineal gland by regulating the capacity of the pineal to synthesize cyclic AMP in response to beta-adrenergic stimulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurbach G. D., Fedak S. A., Woodard C. J., Palmer J. S., Hauser D., Troxler F. Beta-adrenergic receptor: stereospecific interaction of iodinated beta-blocking agent with high affinity site. Science. 1974 Dec 27;186(4170):1223–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4170.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J. The pineal gland: a neurochemical transducer. Science. 1974 Jun 28;184(4144):1341–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4144.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M., Axelrod J. Pineal gland: 24-hour rhythm in norepinephrine turnover. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):163–165. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Axelrod J. Control of circadian change of serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity in the pineal organ by the beta--adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2547–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Axelrod J. Superinduction of serotonin N-acetyltransferase and supersensitivity of adenyl cyclase to catecholamines in denervated pineal gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;9(5):612–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Axelrod J. Supersensitivity and subsensitivity of the beta-adrenergic receptor in pineal gland regulated by catecholamine transmitter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2411–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Foster S. J. Hormone-induced desensitisation of hormonal control of cyclic AMP levels in human diploid fibroblasts. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 5;246(153):146–148. doi: 10.1038/newbio246146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. C., Berg G. R., Weller J. Melatonin synthesis: adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and norepinephrine stimulate N-acetyltransferase. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):979–980. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mukherjee C., Coverstone M., Caron M. G. Stereospecific (3H)(minus)-alprenolol binding sites, beta-adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Atlas D., Steer M. L. The binding characteristics and number of beta-adrenergic receptors on the turkey erythrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2773–2776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H. Properties of adenylate cyclase of lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Caron M. G., Coverstone M., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors in frog erythrocytes with (minus)-[3-H] alprenolol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4869–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Catecholamine-induced subsensitivity of adenylate cyclase associated with loss of beta-adrenergic receptor binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. A., Axelrod J. Pineal beta-adrenergic receptor: diurnal variation in sensitivity. Science. 1974 Jun 7;184(4141):1091–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4141.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. A., Axelrod J. Regulation of sensitivity to beta-adrenergic stimulation in induction of pineal N-acetyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1661–1665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strada S. J., Weiss B. Increased response to catecholamines of the cyclic AMP system of rat pineal gland induced by decreased sympathetic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. N., Wilson R. W. Electrophysiological evidence for the action of light on the pineal gland in the rat. Experientia. 1970 Mar 15;26(3):267–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01900087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


