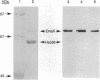
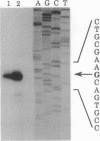
Abstract
Eukaryotic organisms have been shown to have multiple forms of hsp70-class stress-related proteins, but only a single family member, DnaK, has been found in prokaryotes. We report here the identification of a heat shock cognate gene, designated hsc, in Escherichia coli. The amino acid sequence deduced from hsc predicts a 65,647-Da polypeptide having 41% sequence identity with DnaK from E. coli, and overexpression produces a protein (Hsc66) with properties similar to DnaK. In contrast to dnaK, however, the hsc gene lacks a consensus heat shock promoter sequence, and expression is not induced by elevated temperature. The hsc gene is located near 54 min on the physical map, immediately upstream of the fdx gene, which encodes a [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin; evidence is presented that the hsc and fdx genes make up a bicistronic operon in which expression of the ferredoxin is coupled to that of Hsc66. The function of Hsc66 is not known, but the coregulation of its expression with that of ferredoxin suggests the possibility of a specific role in association with the ferredoxin protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Welch W. J. Characterization and purification of the small 28,000-dalton mammalian heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15359–15369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt M. E., Vickery L. E. Expression and characterization of human mitochondrial ferredoxin reductase in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 1;294(2):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90749-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2337-2346.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Delta dnaK52 mutants of Escherichia coli have defects in chromosome segregation and plasmid maintenance at normal growth temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6030–6038. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6030-6038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell T. G., Konforti B. B., Schmid S. L., Rothman J. E. The ATPase core of a clathrin uncoating protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):746–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang H. L., Terlecky S. R., Plant C. P., Dice J. F. A role for a 70-kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2799391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Ingolia T. D., Manseau L. J. Expression of Drosophila heat-shock cognate genes during heat shock and development. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):418–426. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Kramer J., Shilling J., Werner-Washburne M., Holmes S., Kosic-Smithers J., Nicolet C. M. SSC1, an essential member of the yeast HSP70 multigene family, encodes a mitochondrial protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3000–3008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca-Flaherty C., McKay D. B. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA of a bovine 70 kilodalton heat shock cognate protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5569–5569. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty K. M., DeLuca-Flaherty C., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of the ATPase fragment of a 70K heat-shock cognate protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):623–628. doi: 10.1038/346623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B., Kabsch W., Holmes K. C. Similarity of the three-dimensional structures of actin and the ATPase fragment of a 70-kDa heat shock cognate protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flinta C., Persson B., Jörnvall H., von Heijne G. Sequence determinants of cytosolic N-terminal protein processing. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 2;154(1):193–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Devereux J., Burgess R. R. The codon preference plot: graphic analysis of protein coding sequences and prediction of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):539–549. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Singh B. Cloning of the HSP70 gene from Halobacterium marismortui: relatedness of archaebacterial HSP70 to its eubacterial homologs and a model for the evolution of the HSP70 gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4594–4605. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4594-4605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Lysine residue 121 in the proposed ATP-binding site of the v-mos protein is required for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7894–7898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen S. L., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Levels of major proteins of Escherichia coli during growth at different temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):185–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.185-194.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L. Nonlinear relationships among evolutionary rates identify regions of functional divergence in heat-shock protein 70 genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):243–255. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawula T. H., Lelivelt M. J. Mutations in a gene encoding a new Hsp70 suppress rapid DNA inversion and bgl activation, but not proU derepression, in hns-1 mutant Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):610–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.610-619.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Lu C., Echols H., Flanagan J., Hayer M. K., Hartl F. U. Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):683–689. doi: 10.1038/356683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty J. S., Walker G. C. DnaK as a thermometer: threonine-199 is site of autophosphorylation and is critical for ATPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9513–9517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B. Structure and mechanism of 70-kDa heat-shock-related proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1993;44:67–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Generation of beta-globin by sequence-specific proteolysis of a hybrid protein produced in Escherichia coli. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):810–812. doi: 10.1038/309810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The activity of sigma 32 is reduced under conditions of excess heat shock protein production in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):2003–2010. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D., Walter W., Gross C. A. DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE heat shock proteins negatively regulate heat shock gene expression by controlling the synthesis and stability of sigma 32. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2202–2209. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ta D. T., Seaton B. L., Vickery L. E. Localization of the ferredoxin (fdx) gene on the physical map of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5760–5761. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5760-5761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ta D. T., Vickery L. E. Cloning, sequencing, and overexpression of a [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin gene from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11120–11125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli dnaK replication protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]