Abstract
For many compounds (neurotrophic factors, antibodies, growth factors, genetic vectors, enzymes) slow diffusion in the brain severely limits drug distribution and effect after direct drug administration into brain parenchyma. We investigated convection as a means to enhance the distribution of the large and small molecules 111In-labeled transferrin (111In-Tf; M(r), 80,000) and [14C]sucrose (M(r), 359) over centimeter distances by maintaining a pressure gradient during interstitial infusion into white matter to generate bulk flow through the brain interstitium. The volume of distribution (Vd) containing > or = 1% concentration of infusion solution increased linearly with the infusion volume (Vi) for 111In-Tf(Vd/Vi, 6:1) and [14C]sucrose (Vd/Vi, 13:1). Twenty-four hours after infusion, the distribution of 111In-Tf was increased and more homogeneous, and penetration into gray matter had occurred. By using convection to supplement simple diffusion, enhanced distribution of large and small molecules can be obtained in the brain while achieving drug concentrations orders of magnitude greater than systemic levels.
Full text
PDF
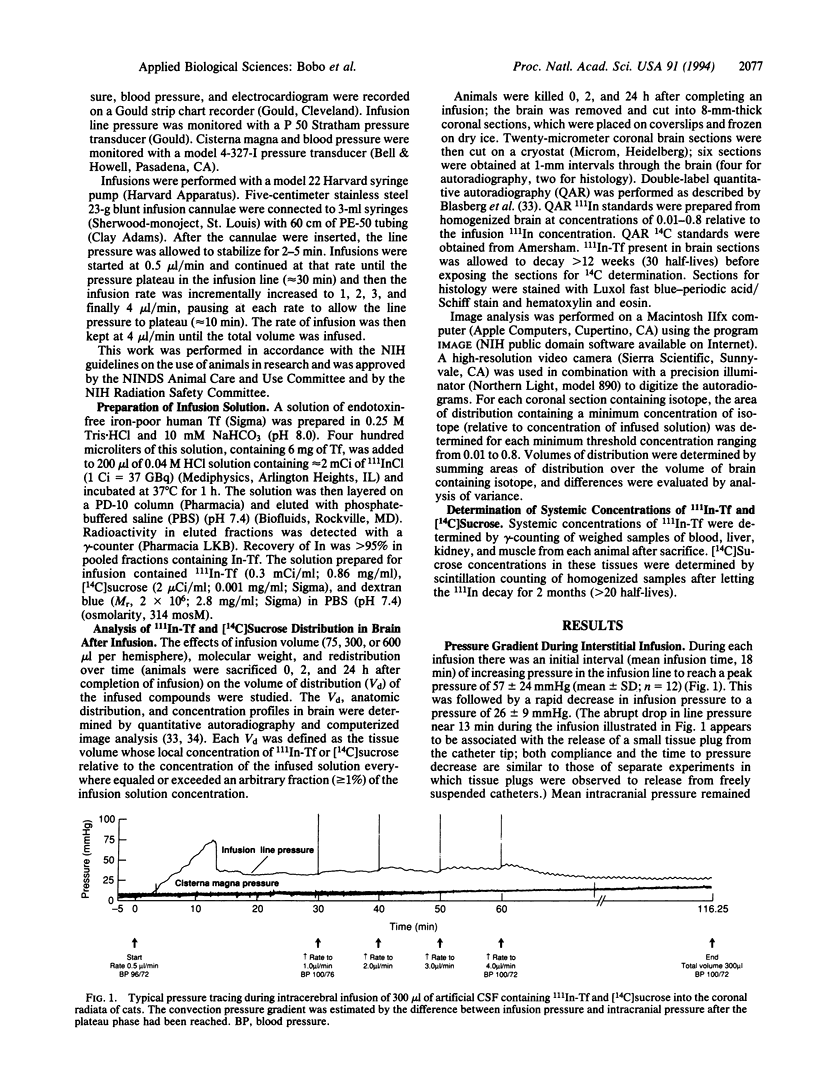

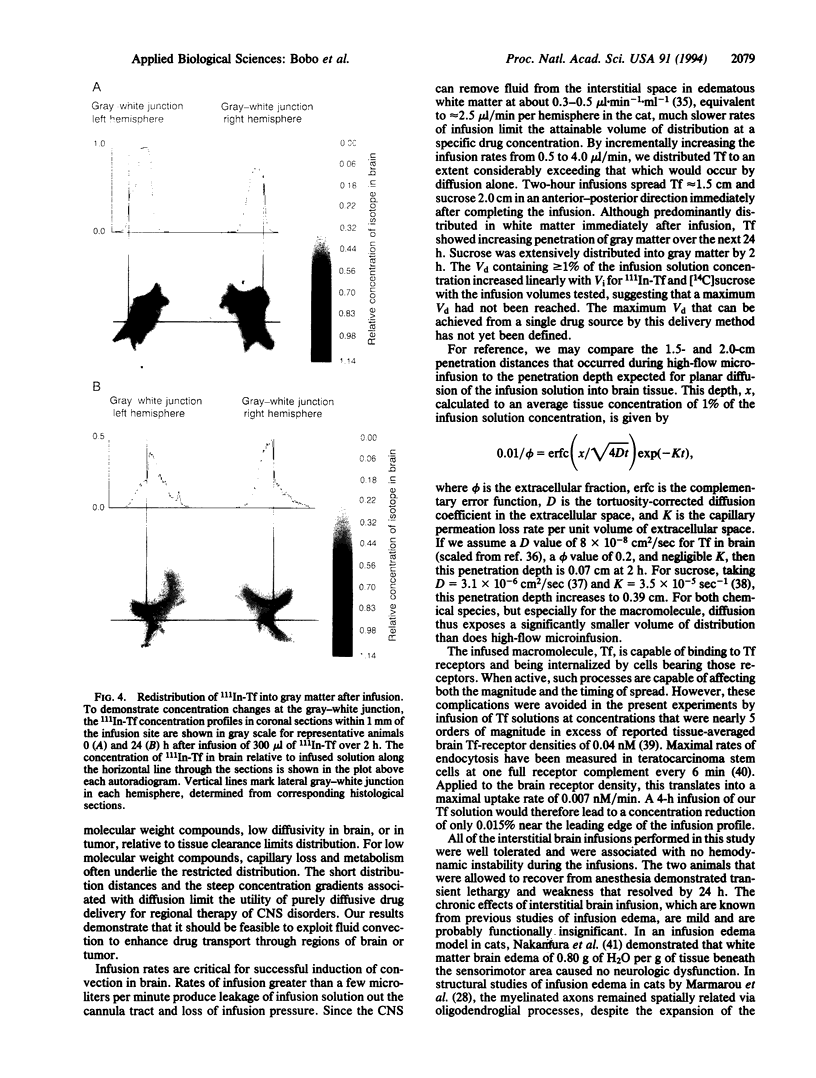

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barba D., Saris S. C., Holder C., Rosenberg S. A., Oldfield E. H. Intratumoral LAK cell and interleukin-2 therapy of human gliomas. J Neurosurg. 1989 Feb;70(2):175–182. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.70.2.0175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R. G., Gazendam J., Patlak C. S., Fenstermacher J. D. Quantitative autoradiographic studies of brain edema and a comparison of multi-isotope autoradiographic techniques. Adv Neurol. 1980;28:255–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R. G., Patlak C., Fenstermacher J. D. Intrathecal chemotherapy: brain tissue profiles after ventriculocisternal perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Oct;195(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch D. A., Hindmarsch T., Larsson S., Backlund E. O. Intraneoplastic administration of bleomycin in intracerebral gliomas: a pilot study. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1980;30:441–444. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8592-6_58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier G., Penn R. D., Kroin J. S., Beique R., Guerard M. J. Direct delivery of medication into a brain tumor through multiple chronically implanted catheters. Neurosurgery. 1987 Feb;20(2):286–291. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198702000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem H., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Vick N. A., Black K. L., Schold S. C., Jr, Burger P. C., Friedman A. H., Ciric I. S., Eller T. W., Cozzens J. W. Interstitial chemotherapy with drug polymer implants for the treatment of recurrent gliomas. J Neurosurg. 1991 Mar;74(3):441–446. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.3.0441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F., Ostrach L. H. Bulk flow of interstitial fluid after intracranial injection of blue dextran 2000. Exp Neurol. 1974 Oct;45(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Flessner M. F. Pharmacokinetic considerations on monoclonal antibodies. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;288:429–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfield J., Dayan A. D. Postoperative intracavitary chemotherapy of malignant gliomas. A preliminary study using methotrexate. J Neurosurg. 1973 Sep;39(3):315–322. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.39.3.0315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfield J., Dayan A. D., Weller R. O. Postoperative intracavitary chemotherapy of malignant supratentorial astrocytomas using BCNU. Clin Oncol. 1975 Sep;1(3):213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbaugh R. E. Novel CNS-directed drug delivery systems in Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. M., Ruff M. R., Weber R. J., Pert C. B. Transferrin receptors in rat brain: neuropeptide-like pattern and relationship to iron distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4553–4557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossmann K. A., Blöink M., Wilmes F., Wechsler W. Experimental peritumoral edema of the cat brain. Adv Neurol. 1980;28:323–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito U., Reulen H. J., Tomita H., Ikeda J., Saito J., Maehara T. A computed tomography study on formation, propagation, and resolution of edema fluid in metastatic brain tumors. Adv Neurol. 1990;52:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K. Delivery of novel therapeutic agents in tumors: physiological barriers and strategies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Apr 19;81(8):570–576. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.8.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K. Transport of molecules in the tumor interstitium: a review. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3039–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Mintz B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in developmentally totipotent mouse teratocarcinoma stem cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroin J. S., Penn R. D. Intracerebral chemotherapy: chronic microinfusion of cisplatin. Neurosurgery. 1982 Mar;10(3):349–354. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198203000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewellen T. K., Graham M. M., Spence A. M. Quantitative autoradiography using a personal computer. J Nucl Med. 1986 Apr;27(4):549–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant R. E., Merchant L. H., Cook S. H., McVicar D. W., Young H. F. Intralesional infusion of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells and recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) for the treatment of patients with malignant brain tumor. Neurosurgery. 1988 Dec;23(6):725–732. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198812000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morantz R. A., Kimler B. F., Vats T. S., Henderson S. D. Bleomycin and brain tumors. A review. J Neurooncol. 1983;1(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00165609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison P. F., Dedrick R. L. Transport of cisplatin in rat brain following microinfusion: an analysis. J Pharm Sci. 1986 Feb;75(2):120–128. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600750204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierenberg D., Harbaugh R., Maurer L. H., Reeder T., Scott G., Fratkin J., Newman E. Continuous intratumoral infusion of methotrexate for recurrent glioblastoma: a pilot study. Neurosurgery. 1991 May;28(5):752–761. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199105000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obbens E. A., Feun L. G., Leavens M. E., Savaraj N., Stewart D. J., Gutterman J. U. Phase I clinical trial of intralesional or intraventricular leukocyte interferon for intracranial malignancies. J Neurooncol. 1985;3(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00165173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohata K., Marmarou A. Clearance of brain edema and macromolecules through the cortical extracellular space. J Neurosurg. 1992 Sep;77(3):387–396. doi: 10.3171/jns.1992.77.3.0387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohata K., Marmarou A., Povlishock J. T. An immunocytochemical study of protein clearance in brain infusion edema. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(2):162–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00334505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Lipid solubility and drug penetration of the blood brain barrier. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Dec;147(3):813–815. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Fenstermacher J. D. Measurements of dog blood-brain transfer constants by ventriculocisternal perfusion. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):877–884. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Kroin J. S., Harris J. E., Chiu K. M., Braun D. P. Chronic intratumoral chemotherapy of a rat tumor with cisplatin and fluorouracil. Appl Neurophysiol. 1983;46(1-4):240–244. doi: 10.1159/000101269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Thompson H. K. Osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier in the monkey without associated neurological deficits. Science. 1973 Jun 1;180(4089):971–971. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4089.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reulen H. J., Graham R., Spatz M., Klatzo I. Role of pressure gradients and bulk flow in dynamics of vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg. 1977 Jan;46(1):24–35. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.46.1.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringkjob R. Treatment of intracranial gliomas and metastatic carcinomas by local application of cytostatic agents. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(3):318–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. A., Kyner W. T., Estrada E. Bulk flow of brain interstitial fluid under normal and hyperosmolar conditions. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):F42–F49. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.1.F42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. C., Ommaya A. K., Henderson E. S., Bering E. A., Rall D. P. Cerebrospinal fluid perfusion for central nervous system neoplasms. Neurology. 1966 Jul;16(7):680–692. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.7.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANTZ E. J., LAUFFER M. A. Diffusion measurements in agar gel. Biochemistry. 1962 Jul;1:658–663. doi: 10.1021/bi00910a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendelbeck S. L., Urquhart J. Spatial distribution of dopamine, methotrexate and antipyrine during continuous intracerebral microperfusion. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 4;328(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zovickian J., Johnson V. G., Youle R. J. Potent and specific killing of human malignant brain tumor cells by an anti-transferrin receptor antibody-ricin immunotoxin. J Neurosurg. 1987 Jun;66(6):850–861. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.6.0850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]