Abstract
Ultrastructural studies of the mouthparts of the calanoid copepod Diaptomus pallidus have revealed the presence of numerous chemoreceptors, and the apparent absence of mechanoreceptors. The setae contain no muscles, and the setules are noncellular extensions of their chitin wall. This allows a new insight into the selective feeding of zooplankters.
Full text
PDF
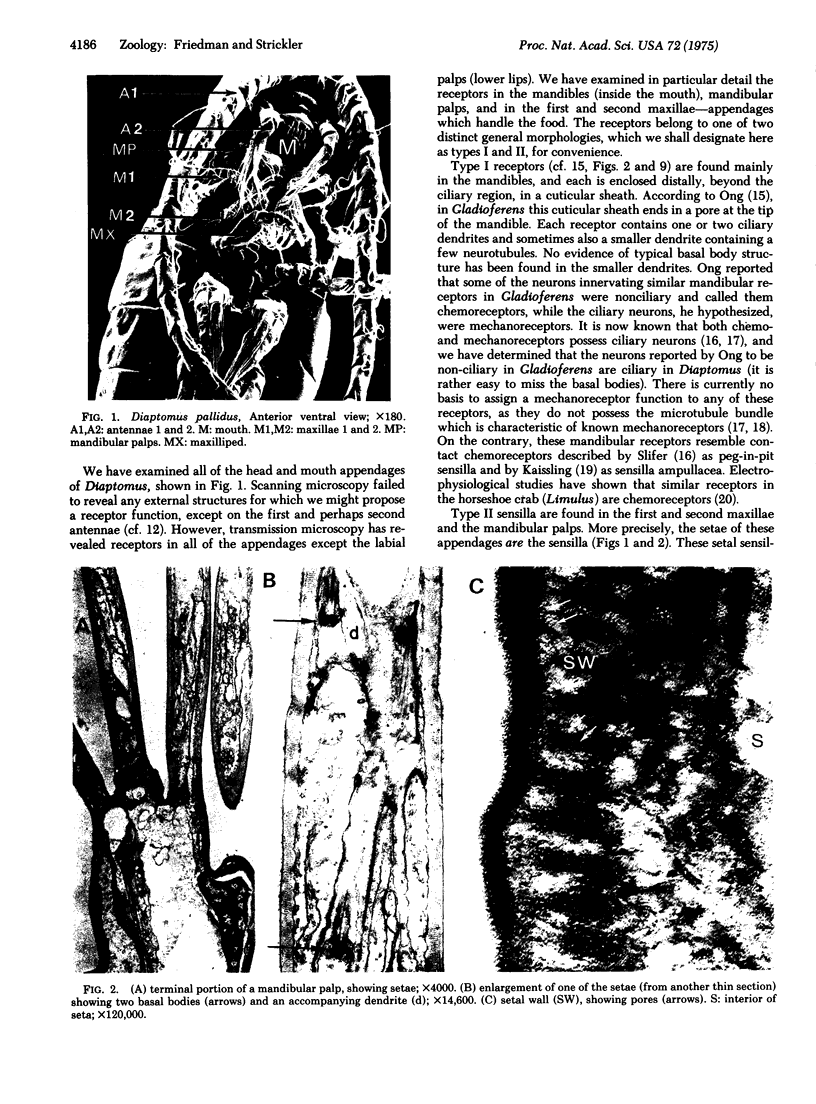


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ache B. W. Amino acid receptors in the antennules of Homarus americanus. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jul 1;42(3):807–811. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90458-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altner H., Thies G. Reizleitende Strukturen und Ablauf der Häutung an Sensillen einer euedaphischen Collembolenart. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;129(2):196–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst K. D. Die Feinstruktur von Riechsensillen auf der Antenne des Aaskäfers Necrophorus (Coleoptera) Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;94(1):72–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galun R., Margalit J. Adenine nucleotides as feeding stimulants of the tsetse fly Glossina austeni Newst. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):583–584. doi: 10.1038/222583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharagozlou-van Ginneke, Bouligand Y. Ultrastructures tegumentaires chez un crustace copepode Cletocamptus retrogressus. Tissue Cell. 1973;5(3):413–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes W. F. Fine structure of the chemoreceptor sensillum in Limulus. J Morphol. 1971 Feb;133(2):205–239. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051330207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVERACK M. S. ASPECTS OF CHEMORECEPTION IN CRUSTACEA. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1963 Feb;9:141–151. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(63)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levandowsky M., Hodgson E. S. Amino acid and amine receptors of lobsters. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Sep;16(1):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIver S. B. Structure of cuticular mechanoreceptors of arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol. 1975;20:381–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.20.010175.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustaparta H. Olfactory sensilla on the antennae of the pine weevil, Hylobius abietis. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Nov 15;144(4):559–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00307381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong J. E. The fine structure of the mandibular sensory receptors in the brackish water calanoid copepod Gladioferens pectinatus (Brady). Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969 May 23;97(2):178–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00344756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecht R. A. Der Feinbau olfaktorischer Sensillen des Seidenspinners (Insecta, Lepidoptera). Rezeptorfortsätze und reizleitender Apparat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Jun 7;139(4):533–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler J. R., Bal A. K. Setae of the First Antennae of the Copepod Cyclops scutifer (Sars): Their Structure and Importance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2656–2659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker R. H., Feeny P. P. Allelochemics: chemical interactions between species. Science. 1971 Feb 26;171(3973):757–770. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3973.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]