Abstract
Mutant N4316 is conditionally lethal at 43°. At 36° it suppresses the termination codons UGA and UAA, but not the UAG codon or a missense mutant of T4 bacteriophage. In vitro, a factor rescues protein synthesis from a temperature-dependent arrest when N4316 extracts are used with RNA from bacteriophage f2. Analyses of the substrate in the arrested synthesis and of the product of the rescue reaction indicate that the factor works at the level of coat protein termination, and that it also affects the synthesis of noncoat protein products. The rescue factor is different from the release factors RF-1, RF-2, and RF-3. Model systems previously used to study release fail to score for at least one vital function in protein chain termination.
Keywords: ribosomes, f2 bacteriophage, coding, peptidyl-tRNA, thermolabile proteins
Full text
PDF
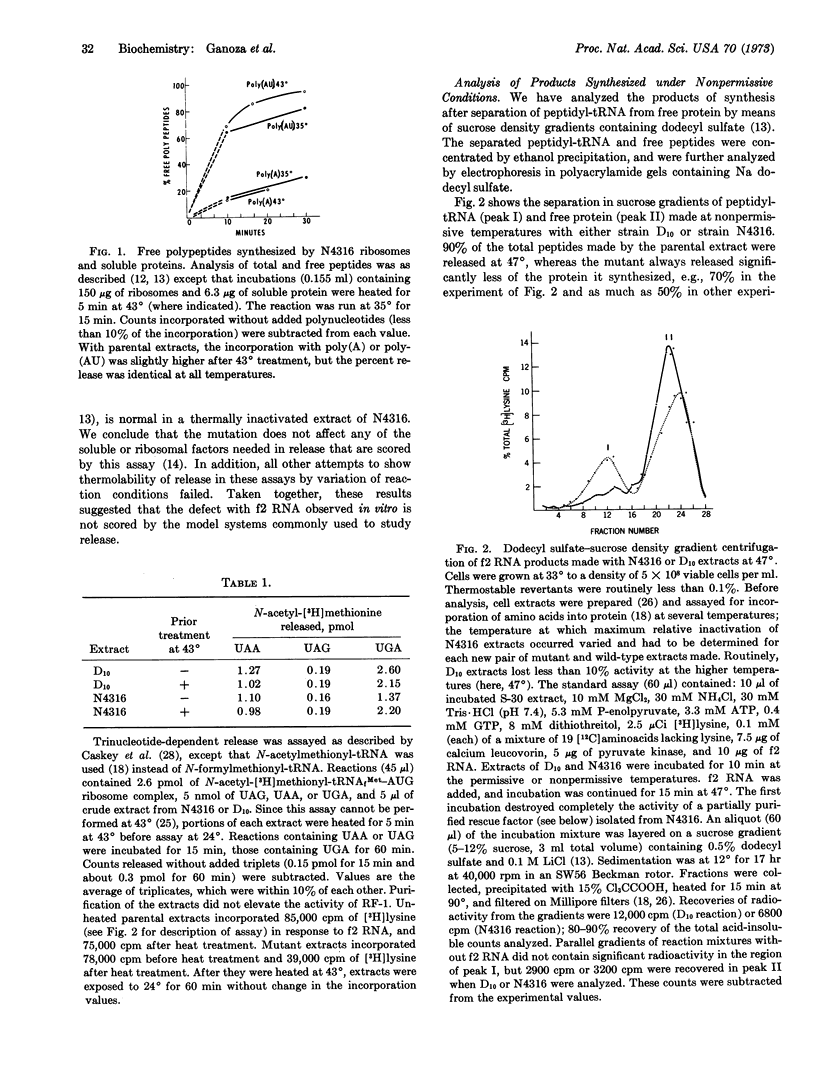
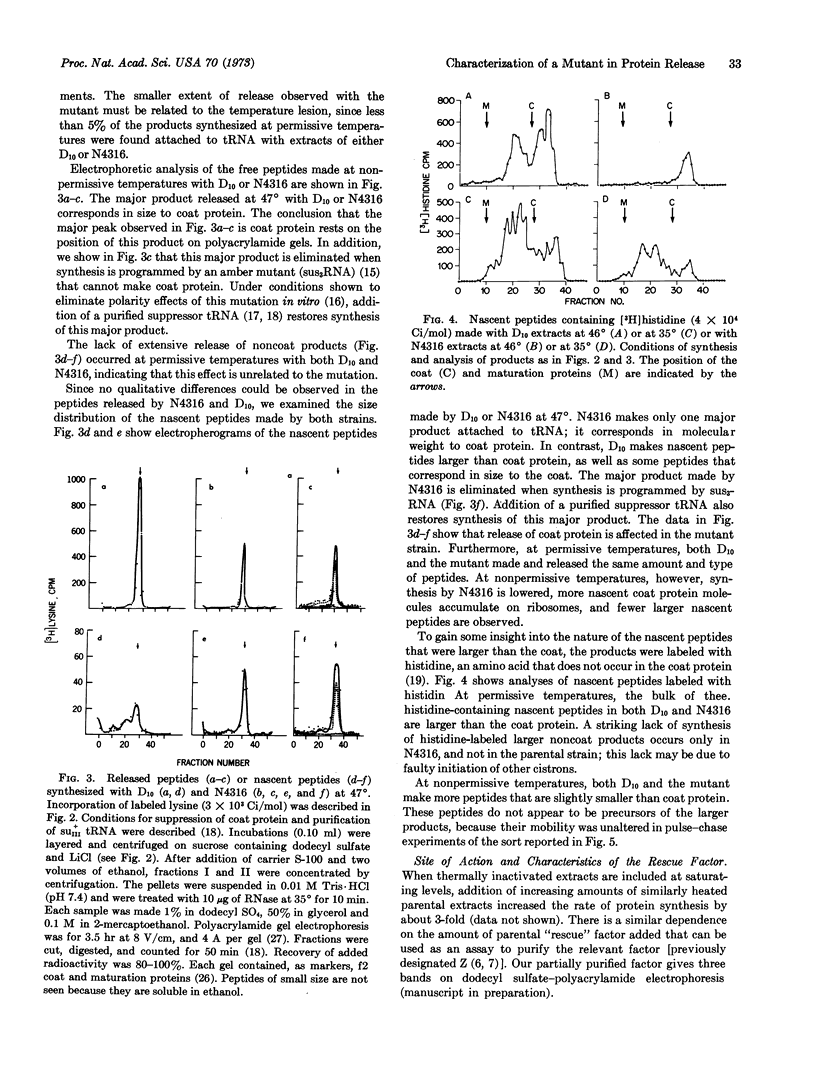
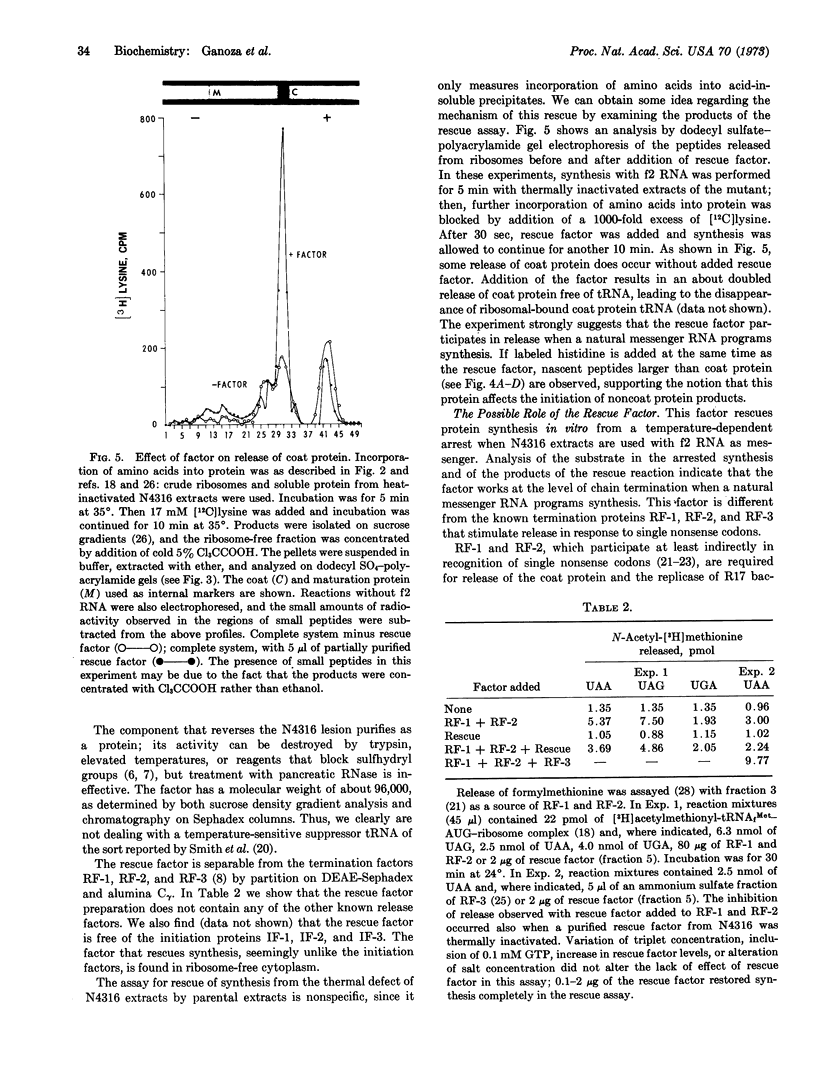

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D., Phillips S. L., Schlessinger D. Approaches to the genetics of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:117–128. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Release factor translation of RNA phage terminator codons. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):38–40. doi: 10.1038/227038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Goodman H. M., Menninger J. R., Smith J. D. Polypeptide chain termination using synthetic polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK F. H., BARNETT L., BRENNER S., WATTS-TOBIN R. J. General nature of the genetic code for proteins. Nature. 1961 Dec 30;192:1227–1232. doi: 10.1038/1921227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R., Klein H. A. Release factors mediating termination of complete proteins. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1029–1033. doi: 10.1038/2261029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Polarity in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey C. T., Tompkins R., Scolnick E., Caryk T., Nirenberg M. Sequential translation of trinucleotide codons for the initiation and termination of protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):135–138. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey T., Scolnick E., Tompkins R., Goldstein J., Milman G. Peptide chain termination, codon, protein factor, and ribosomal requirements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:479–488. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt D. L., Webster R. E., Wilhelm R. C., Zinder N. In vitro studies on the mechanism of suppression of a nonsense mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1791–1797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Nakamoto T. Studies on the mechanism of polypeptide chain termination in cell-free extracts of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):162–169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Thach R. E. Further studies on peptide chain termination in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:488–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Tomkins J. K. Polypeptide chain termination in vitro: competition for nonsense codons between a purified release factor and suppressor tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Russell R. L. Role modifications in tyrosine transfer RNA: a modified base affecting ribosome binding. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Ghosh K., Ganoza M. C. Mechanism of polypeptide chain termination. Translation of tandem amber termination codons by an amber suppressor transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5322–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Goldstein J., Scolnick E., Caskey T. Peptide chain termination. 3. Stimulation of in vitro termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):183–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. L. Nucleotide sequence from the polypeptide chain termination region of the coat protein cistron in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):147–151. doi: 10.1038/225147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. L., Schlessinger D., Apirion D. Mutants in Escherichia coli ribosomes: a new selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):772–777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. L., Schlessinger D., Apirion D. Temperature-dependent suppression of UGA and UAA codons in a temperature-sensitive mutant of Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:499–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. L. Termination of messenger RNA translation in a temperature-sensitive mutant of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Hille M. B., Last J. A., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message, ii. Effect of initiation factors on the binding of formyl-methionyl-trna to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):387–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Fluck M., Epstein R. The influence of the reading context upon the suppression of nonsense codons. 3. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:513–520. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination. V. The role of release factors in mRNA terminator codon recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1235–1241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Barnett L., Brenner S., Russell R. L. More mutant tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Polypeptide chain initiation: nucleotide sequences of the three ribosomal binding sites in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):957–964. doi: 10.1038/224957a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Iwasaki K., Miller M. J., Sabol S., Sillero M. A., Vasquez C. Initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. Role of the initiation factors in polypeptide synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:291–299. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Fate of the message-ribosome complex upon translation of termination signals. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]