Abstract
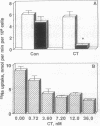
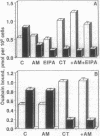
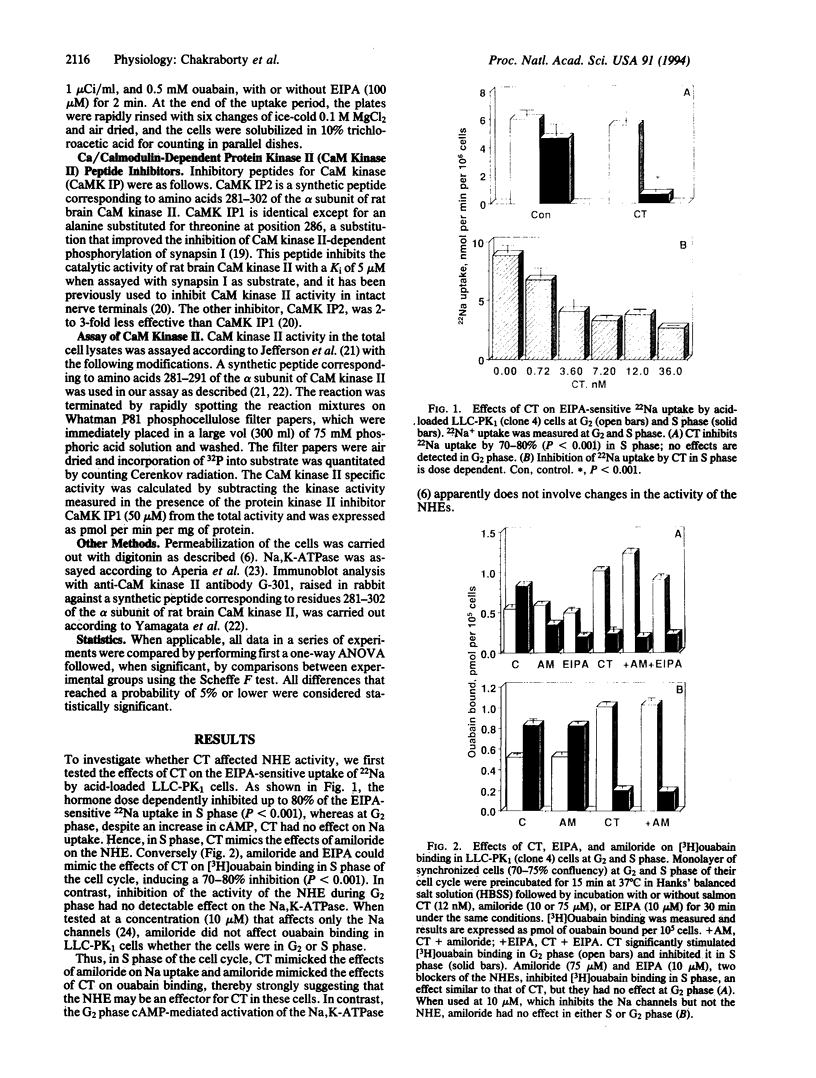
Calcitonin (CT), which regulates serum calcium through its actions in bone and the kidney tubule, also has a potent natriuretic effect in vivo. Na reabsorption in the proximal kidney tubule is mostly dependent on the activity of the Na,K-ATPase and the apical Na/H exchanger. We have previously shown that CT regulates the activity of the Na,K-ATPase in the proximal kidney tubule cell line LLC-PK1 in a cell cycle-dependent manner. We report here that, in the same cells, CT also regulates the Na/H exchanger through a cell cycle-specific activation of the Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. In G2 phase, no changes in ethylisopropyl amiloride-sensitive 22Na uptake is observed, despite an increase in cAMP. In contrast, the hormone inhibits the apical exchanger when the cells are in S phase, resulting in an 80% inhibition of 22Na uptake. These results demonstrate that CT affects the activity of the two major proximal tubule Na transport systems and may help clarify the mechanisms by which CT regulates Na+ reabsorption.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal N., Haggerty J. G., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Isolation and characterization of a Na-H antiporter-deficient mutant of LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):C825–C830. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.5.C825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Bertorello A., Seri I. Dopamine causes inhibition of Na+-K+-ATPase activity in rat proximal convoluted tubule segments. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):F39–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.1.F39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Ibarra F., Svensson L. B., Klee C., Greengard P. Calcineurin mediates alpha-adrenergic stimulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7394–7397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou R. Kidney and calcitonin. Nephron. 1975;15(3-5):250–260. doi: 10.1159/000180515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Romey G., Honoré E., Schmid-Alliana A., Mattéi M. G., Lesage F., Ricard P., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Cloning, functional expression, and regulation of two K+ channels in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8650–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Reuss E., Higashi Y., Kaneda Y. Dopamine decreases fluid reabsorption in straight portions of rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F634–F640. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Aperia A., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11359–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A., Aperia A. Na+-K+-ATPase is an effector protein for protein kinase C in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F370–F373. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijvoet O. L., van der Sluys Veer J., de Vries H. R., van Koppen A. T. Natriuretic effect of calcitonin in man. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 1;284(13):681–688. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104012841301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavola V., Helmle-Kolb C., Murer H. Separate regulatory control of apical and basolateral Na+/H+ exchange in renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):833–837. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Imbert-Teboul M., Montégut M., Clique A., Morel F. Distribution of calcitonin-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity along the rabbit kidney tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre O., Conklin B. R., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F., Wilson E., Ives H. E., Catanzariti L., Hemmings B. A., Bourne H. R. A recombinant calcitonin receptor independently stimulates 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate and Ca2+/inositol phosphate signaling pathways. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):551–556. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1316547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty M., Chatterjee D., Kellokumpu S., Rasmussen H., Baron R. Cell cycle-dependent coupling of the calcitonin receptor to different G proteins. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1078–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.1847755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Limbird L. E. Na(+)-H+ exchanger subtypes: a predictive review. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C945–C953. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Reinlib L., Watson A. J., Gorelick F., Rys-Sikora K., Tse M., Rood R. P., Czernik A. J., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Rabbit ileal villus cell brush border Na+/H+ exchange is regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, a brush border membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8990–8994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Gordon S. Properties and distribution of a lectin-like hemagglutinin differentially expressed by murine stromal tissue macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1862–1875. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer E., Rood R. P., Wesolek J. H., Cohen M. E., Braithwaite R. S., Sharp G. W., Murer H., Donowitz M. Role of calcium and calmodulin in the regulation of the rabbit ileal brush-border membrane Na+/H+ antiporter. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jun;108(3):207–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01871735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Campbell T., Albrecht F., Jose P. A. Dopamine inhibits Na(+)-H+ exchanger activity in renal BBMV by stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F297–F303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Baldi E., Manzini S., Del Bianco E., Maggi C. A., Natali A., Mannelli M. Regional differences of adenylate cyclase stimulation by calcitonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the human kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Sep;69(3):491–495. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-3-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Slayman C. W., Adelberg E. A. Na+/H+ exchanger activity in the pig kidney epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1: inhibition by amiloride and its derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra F., Aperia A., Svensson L. B., Eklöf A. C., Greengard P. Bidirectional regulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity by dopamine and an alpha-adrenergic agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):21–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Travis S. M., Schulman H. Activation of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in GH3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1484–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Harris T. L., Flannery M. S., Aruffo A., Kaji E. H., Gorn A., Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Lodish H. F., Goldring S. R. Expression cloning of an adenylate cyclase-coupled calcitonin receptor. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.1658940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnensmith R. L., Aronson P. S. The plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger and its role in physiological and pathophysiological processes. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):773–788. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Meldolesi J., Zallone A. Z., Teti A. Control of cytosolic free calcium in rat and chicken osteoclasts. The role of extracellular calcium and calcitonin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14342–14347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonga B. S., Alam A. S., Bevis P. J., Avaldi F., Soncini R., Huang C. L., Zaidi M. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in isolated rat osteoclasts by calcitonin. J Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;132(2):241–249. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1320241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Chamberlin M. E., Mandel L. J. Effects of calcitonin on cytosolic Ca in a suspension of rabbit medullary thick ascending limb tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C491–C495. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Sihra T. S., Czernik A. J., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II increases glutamate and noradrenaline release from synaptosomes. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):647–651. doi: 10.1038/343647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller W., Gstraunthaler G., Loidl P. Morphology of the differentiation and maturation of LLC-PK1 epithelia. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):247–254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y., Chakraborty M., Nathanson M. H., Baron R. Differential effects of the 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate and protein kinase C pathways on the response of isolated rat osteoclasts to calcitonin. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1497–1502. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1324163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Fisher K., Steplock D., Dinh Q., Chang L., Shenolikar S. Regulation of reconstituted renal Na+/H+ exchanger by calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;103(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01993983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W., Shenolikar S. Regulation of the renal Na+-H+ exchanger by protein phosphorylation. Kidney Int. 1989 Oct;36(4):519–525. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata Y., Czernik A. J., Greengard P. Active catalytic fragment of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Purification, characterization, and structural analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15391–15397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun C. H., Gurubhagavatula S., Levine S. A., Montgomery J. L., Brant S. R., Cohen M. E., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Pouyssegur J., Tse C. M., Donowitz M. Glucocorticoid stimulation of ileal Na+ absorptive cell brush border Na+/H+ exchange and association with an increase in message for NHE-3, an epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]