Abstract
During CsCl isopycnic centrifugation at 20 mM Mg++, Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits specifically lose proteins S1, S2, S3, S5, S9, S10, and S14. The resultant 30S core is unable to stimulate the GTPase activity of EF-G in the presence of 50S subunits. Activity could be restored to a small extent by adding back S2, S5, or S9. However, when S5 and S9 were added together, they cooperatively produced 30S particles 1.5 times more active than the original native 30S subunits. The small amount of activity restored by S2 was simply additive to that restored by S5 or S9. None of the other split proteins showed any restoring capability. Ability of the various protein-deficient 30S particles to couple with 50S subunits corresponded closely to their activity in the EF-G GTPase reaction. It is concluded that S5 and S9 together enable the 30S subunit to participate in the formation of a GTPase-active 30S-50S-EF-G complex.
Keywords: CsCl 30S core, ribosomal split proteins, 30S reconstitution, 30S-50S association
Full text
PDF
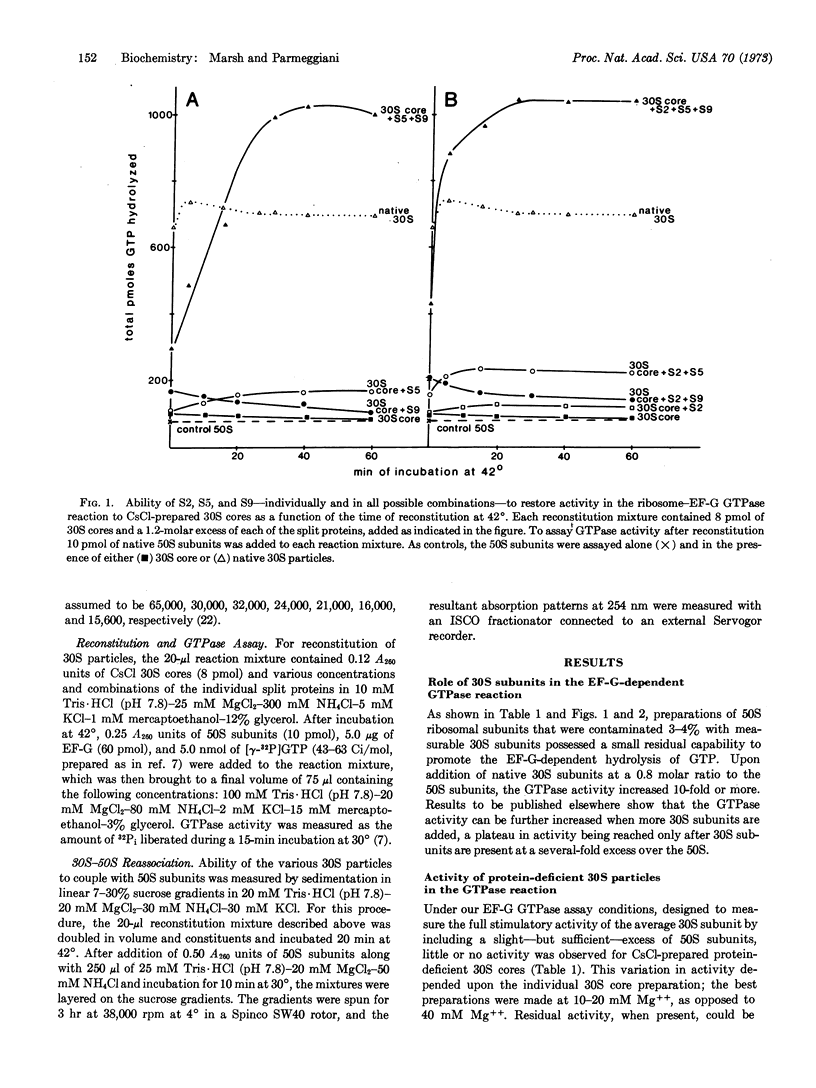
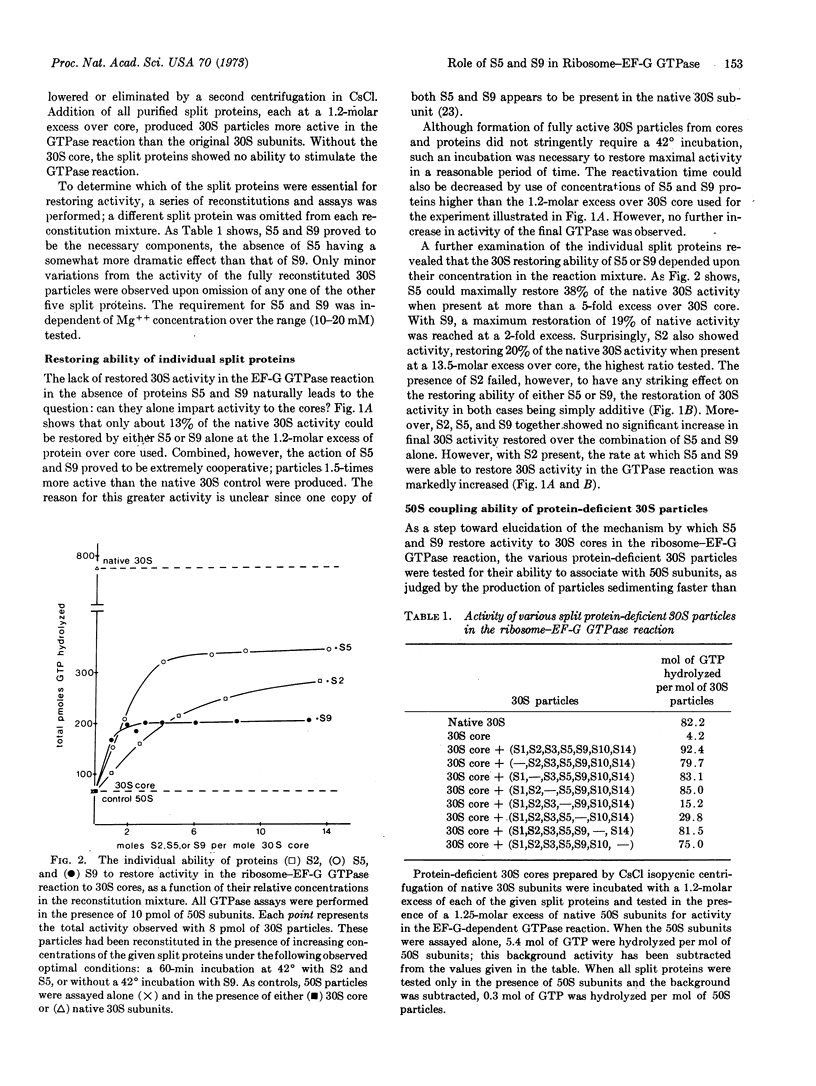
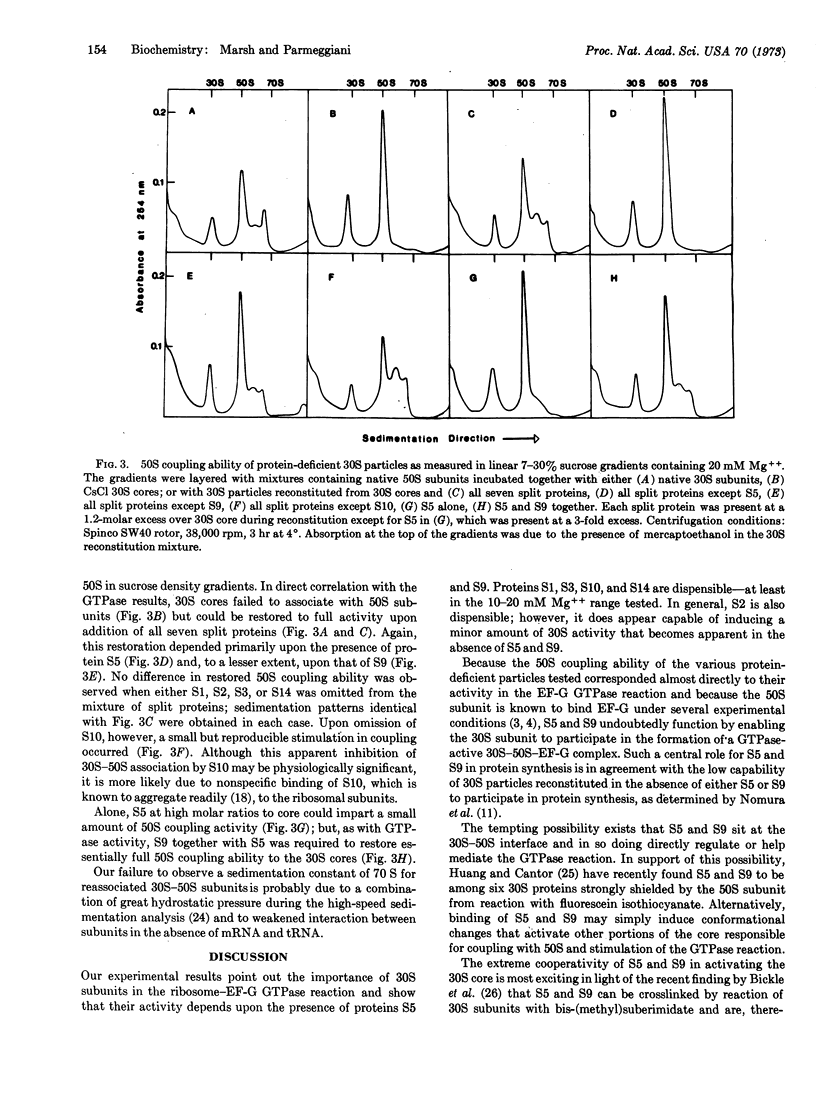

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Davies J., Davis B. D. Effect of spectinomycin on polypeptide synthesis in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickle T. A., Hershey J. W., Traut R. R. Spatial arrangement of ribosomal proteins: reaction of the Escherichia coli 30S subunit with bis-imidoesters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1327–1331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Lin L. Interaction of E. coli G factor with the 50S ribosomal subunit. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):60–61. doi: 10.1038/227060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen A., Davies J., Ozaki M., Mizushima S. Ribosomal protein conferring sensitivity to the antibiotic spectinomycin in Escherichia coli. Science. 1968 Jul 4;165(3888):85–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Spears C., Weissbach H. The interaction of transfer factor G, ribosomes, and guanosine nucleotides in the presence of fusidic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Mar;143(1):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Chemical and physical characterization of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2906–2915. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindennach I., Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. Isolation of the proteins from 30S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):7–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa K., Fujimura R. K., Nomura M. Reconstitution of functionally active ribosomes from inactive subparticles and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):198–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K., Cantor C. R. Surface topography of the 30 s Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit: reactivity towards fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Baierlein R. Pressure-induced dissociation of sedimenting ribosomes: effect on sedimentation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1780–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischa K., Möller W., Stöffler G. Reconstitution of a GTPase activity by a 50S ribosomal protein and E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio233062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBOY P. S., COX E. C., FLAKS J. G. THE CHROMOSOMAL SITE SPECIFYING A RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1367–1374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MESELSON M., NOMURA M., BRENNER S., DAVERN C., SCHLESSINGER D. CONSERVATION OF RIBOSOMES DURING BACTERIAL GROWTH. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:696–711. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Vazquez D., Monro R. E. Ribosomes, G-factor and siomycin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):109–112. doi: 10.1038/newbio230109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Traut R. R., Noller H., Pearson P., Delius H. Ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Proteins from the 30 s subunit. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):441–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. The interrelationship between guanosine triphosphatase and amino acid polymerization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Mizushima S., Ozaki M., Traub P., Lowry C. V. Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:49–61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITNIK-ELSON P. THE PREPARATION OF RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH LITHIUM CHLORIDE AND UREA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 17;18:557–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90790-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander G., Marsh R. C., Parmeggiani A. Isolation and characterization of two acidic proteins from the 50S subunit required for GTPase activities of both EF G and EF T. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):866–873. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90573-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Meselson M. In vitro recovery o ribosomes and of synthetic activity from synthetically inactive ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of Escherichia coli ribosomes. I. Partial fractionation of the functionally active ribosomal proteins and reconstitution of artificial subribosomal particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):575–593. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut R. R., Delius H., Ahmad-Zadeh C., Bickle T. A., Pearson P., Tissières A. Ribosomal proteins of E. Coli: stoichiometry and implications for ribosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:25–38. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G., Stöfflet G., Hindennach I., Kurland C. G., Birge E. A., Randall-Hazelbauer L., Nomura M., Kaltschmidt E., Mizushima S., Traut R. R. Correlation of 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli isolated in different laboratories. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(4):327–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00569784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


