Abstract
The bacterial genera Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium, nitrogen-fixing symbionts of legumes, secrete specific lipo-chitooligosaccharides that induce the formation of nodules on their host plants. When preparations of such nodulation-inducing factors (Nod factors) were added to suspension-cultured tomato cells, a rapid and transient alkalinization of the culture medium occurred. Lipo-oligosaccharide preparations from Rhizobium or Bradyrhizobium treated with flavonoids, known inducers of Nod factor synthesis, were up to 100 times more potent in inducing alkalinization than the ones from untreated bacteria. The activity was absent from preparations of the mutant strain Rhizobium sp. NGR234 delta nodABC, unable to produce any Nod factors. Preparations of Nod factors from various bacteria as well as individual, highly purified Nod factors from Rhizobium sp. NGR(pA28) induced alkalinization in the tomato cell cultures at nanomolar concentrations. This demonstrates that Nod factors can be perceived by tomato, a nonhost of rhizobia. Using the alkalinization response as a sensitive bioassay, Nod factors were found to be inactivated by plant chitinases. Root chitinases purified from different legumes differed in their potential to inactivate differently substituted Nod factors produced by Rhizobium sp. NGR(pA28). This indicates that the specificity of the bacterium-host plant interaction may be due, at least in part, to differential inactivation of Nod factors by root chitinases.
Full text
PDF
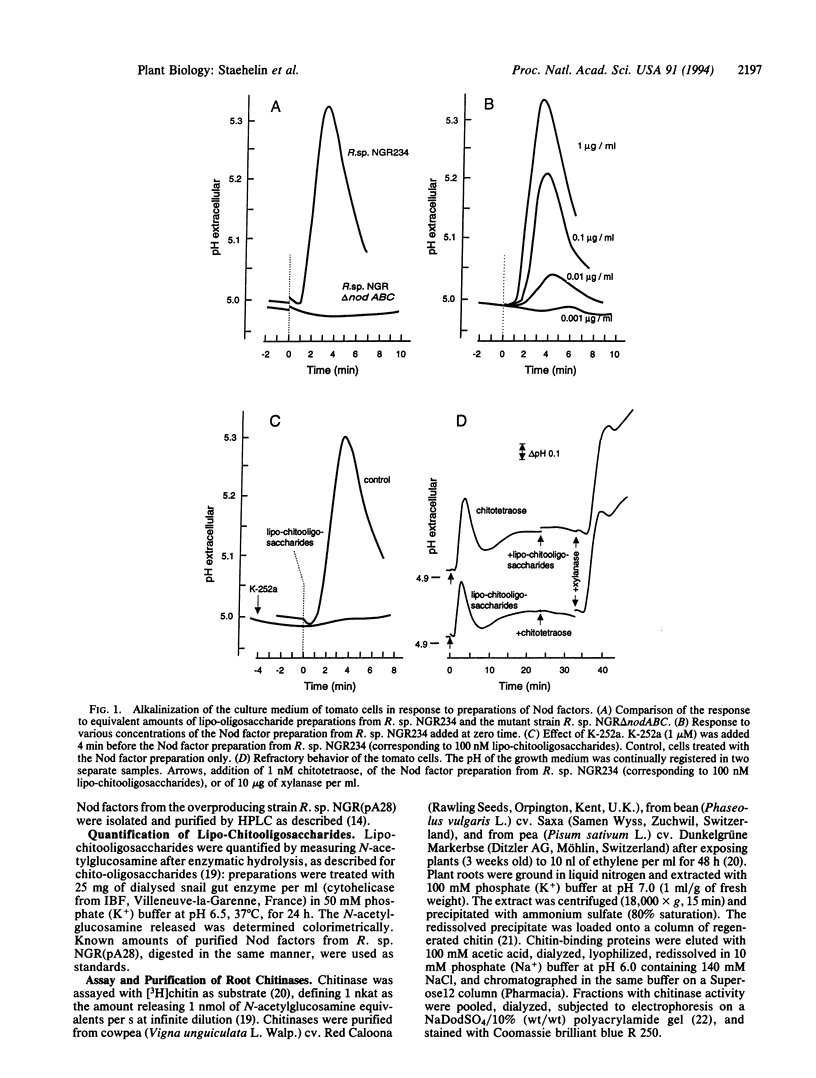
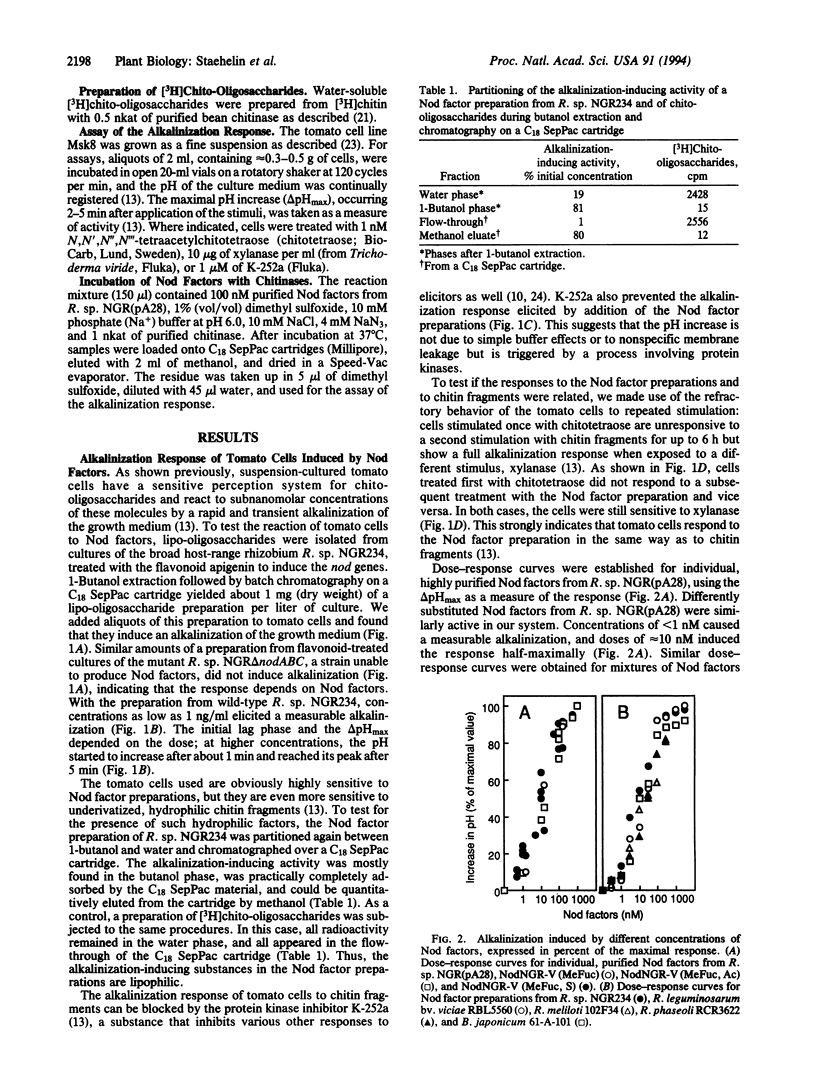
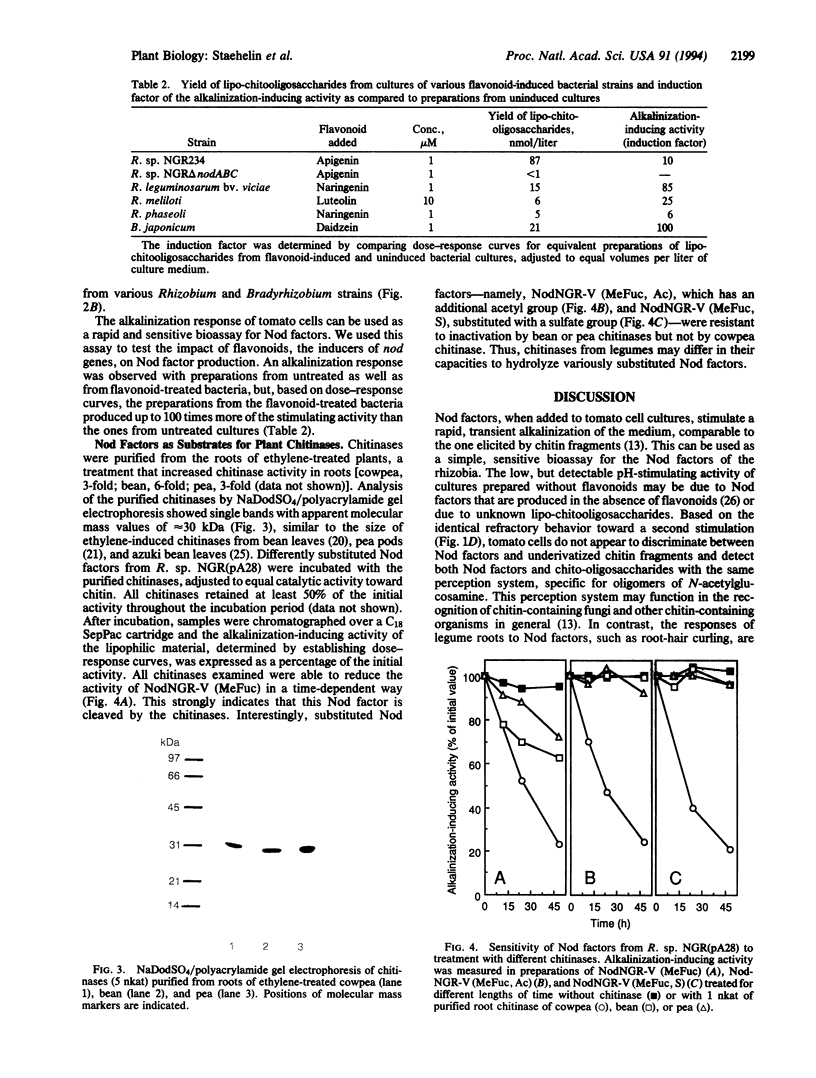

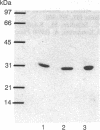
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caetano-Anollés G., Gresshoff P. M. Plant genetic control of nodulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:345–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge D. B., Kragh K. M., Mikkelsen J. D., Nielsen K. K., Rasmussen U., Vad K. Plant chitinases. Plant J. 1993 Jan;3(1):31–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.t01-1-00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. J., Cordewener J., Lo Schiavo F., Terzi M., Vandekerckhove J., Van Kammen A., De Vries S. C. A carrot somatic embryo mutant is rescued by chitinase. Plant Cell. 1992 Apr;4(4):425–433. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. J., Heidstra R., Spaink H. P., Hartog M. V., Meijer E. A., Hendriks T., Schiavo F. L., Terzi M., Bisseling T., Van Kammen A. Rhizobium Lipooligosaccharides Rescue a Carrot Somatic Embryo Mutant. Plant Cell. 1993 Jun;5(6):615–620. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dénarié J., Debellé F., Rosenberg C. Signaling and host range variation in nodulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:497–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt D. W., Atkinson E. M., Long S. R. Depolarization of alfalfa root hair membrane potential by Rhizobium meliloti Nod factors. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.10744524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G., Grosskopf D. G., Regenass M., Basse C. W., Boller T. Elicitor-induced ethylene biosynthesis in tomato cells: characterization and use as a bioassay for elicitor action. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):19–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G., Grosskopf D. G., Regenass M., Boller T. Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8831–8834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Rhizobium--plant signal exchange. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):655–660. doi: 10.1038/357655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougère F., Le Rudulier D. Uptake of glycine betaine and its analogues by bacteroids of Rhizobium meliloti. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):157–163. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosskopf D. G., Felix G., Boller T. K-252a inhibits the response of tomato cells to fungal elicitors in vivo and their microsomal protein kinase in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishige F., Mori H., Yamazaki K., Imaseki H. Cloning of a complementary DNA that encodes an acidic chitinase which is induced by ethylene and expression of the corresponding gene. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993 Jan;34(1):103–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Hadwiger L. A., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : I. Purification and Characterization of Two Chitinases and Two beta-1,3-Glucanases Differentially Regulated during Development and in Response to Fungal Infection. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jun;87(2):325–333. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. P., Relić B., Talmont F., Lewin A., Promé D., Pueppke S. G., Maillet F., Dénarié J., Promé J. C., Broughton W. J. Broad-host-range Rhizobium species strain NGR234 secretes a family of carbamoylated, and fucosylated, nodulation signals that are O-acetylated or sulphated. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Dec;6(23):3575–3584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P., Lerouge P., Ponthus C., Promé J. C. Structural determination of bacterial nodulation factors involved in the Rhizobium meliloti-alfalfa symbiosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10933–10940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheel D., Parker J. E. Elicitor recognition and signal transduction in plant defense gene activation. Z Naturforsch C. 1990 Jun;45(6):569–575. doi: 10.1515/znc-1990-0601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Aarts A., Stacey G., Bloemberg G. V., Lugtenberg B. J., Kennedy E. P. Detection and separation of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium Nod metabolites using thin-layer chromatography. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Jan-Feb;5(1):72–80. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P. Rhizobial lipo-oligosaccharides: answers and questions. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Dec;20(5):977–986. doi: 10.1007/BF00027167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Sheeley D. M., van Brussel A. A., Glushka J., York W. S., Tak T., Geiger O., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N., Lugtenberg B. J. A novel highly unsaturated fatty acid moiety of lipo-oligosaccharide signals determines host specificity of Rhizobium. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):125–130. doi: 10.1038/354125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijn I., das Nevas L., van Kammen A., Franssen H., Bisseling T. Nod factors and nodulation in plants. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1764–1765. doi: 10.1126/science.8511583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Z. M., Laby R. J., Zumoff C. H., Bauer D. W., He S. Y., Collmer A., Beer S. V. Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.1621099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]