Abstract
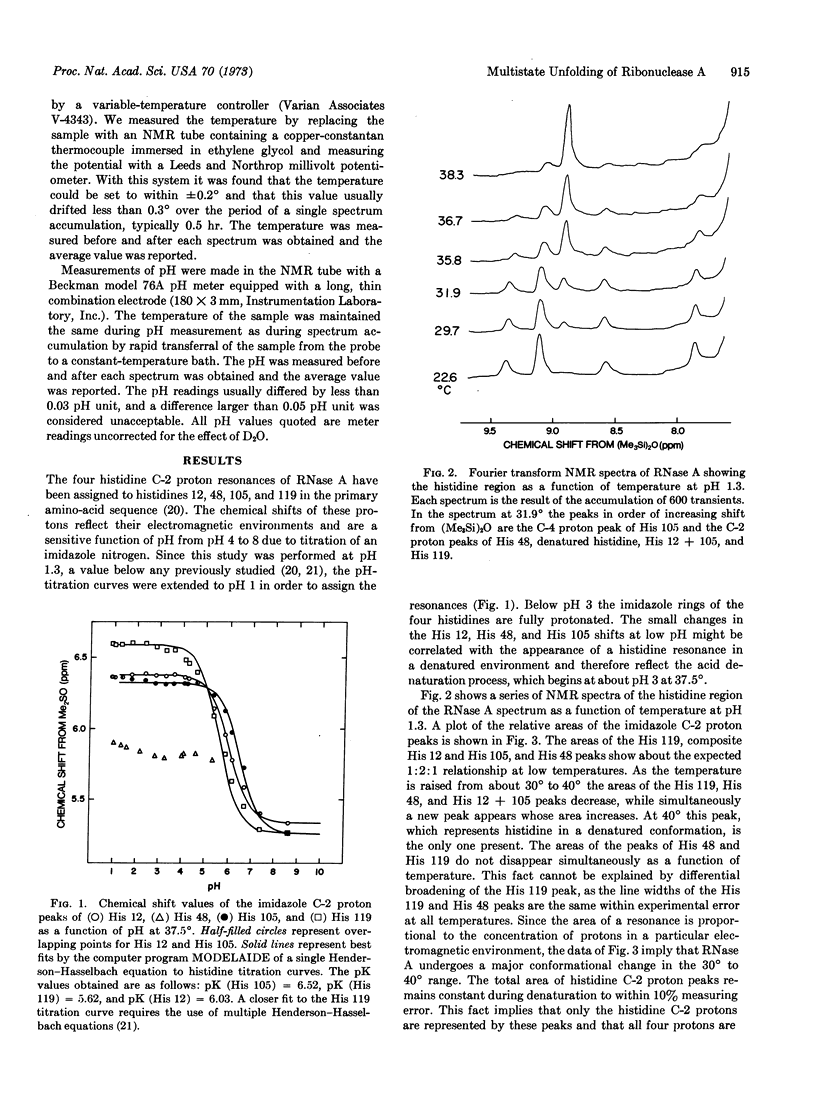
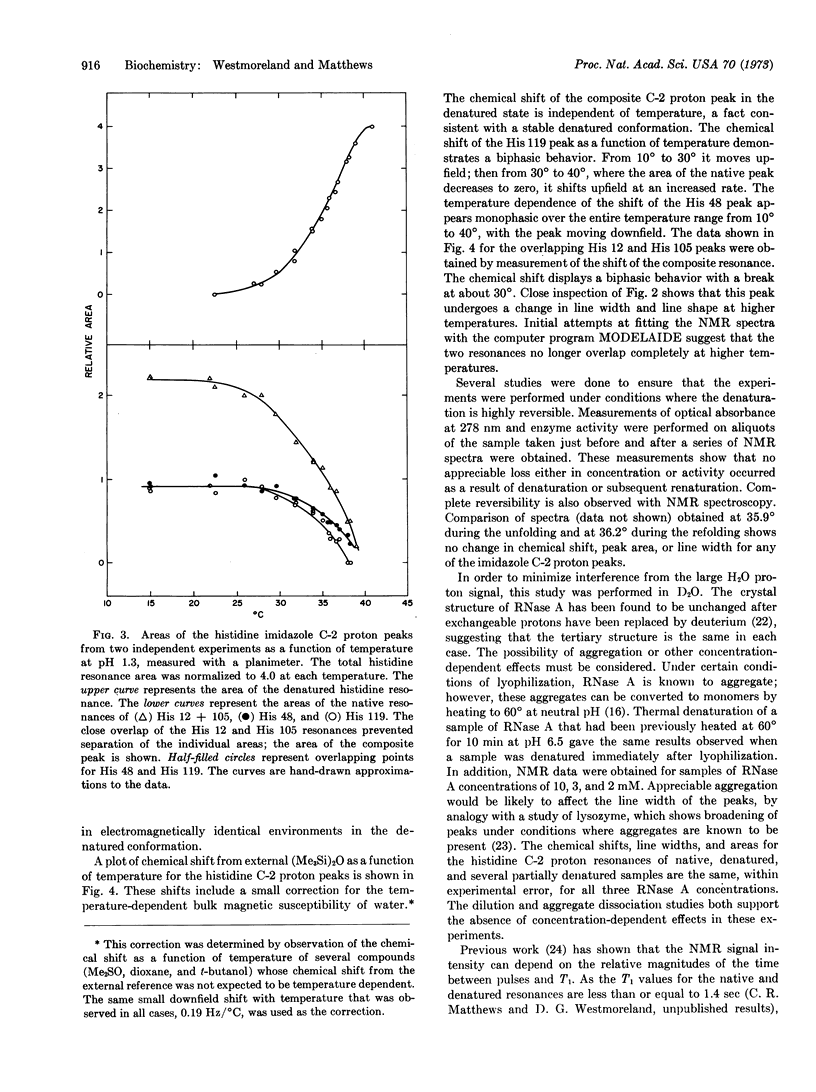
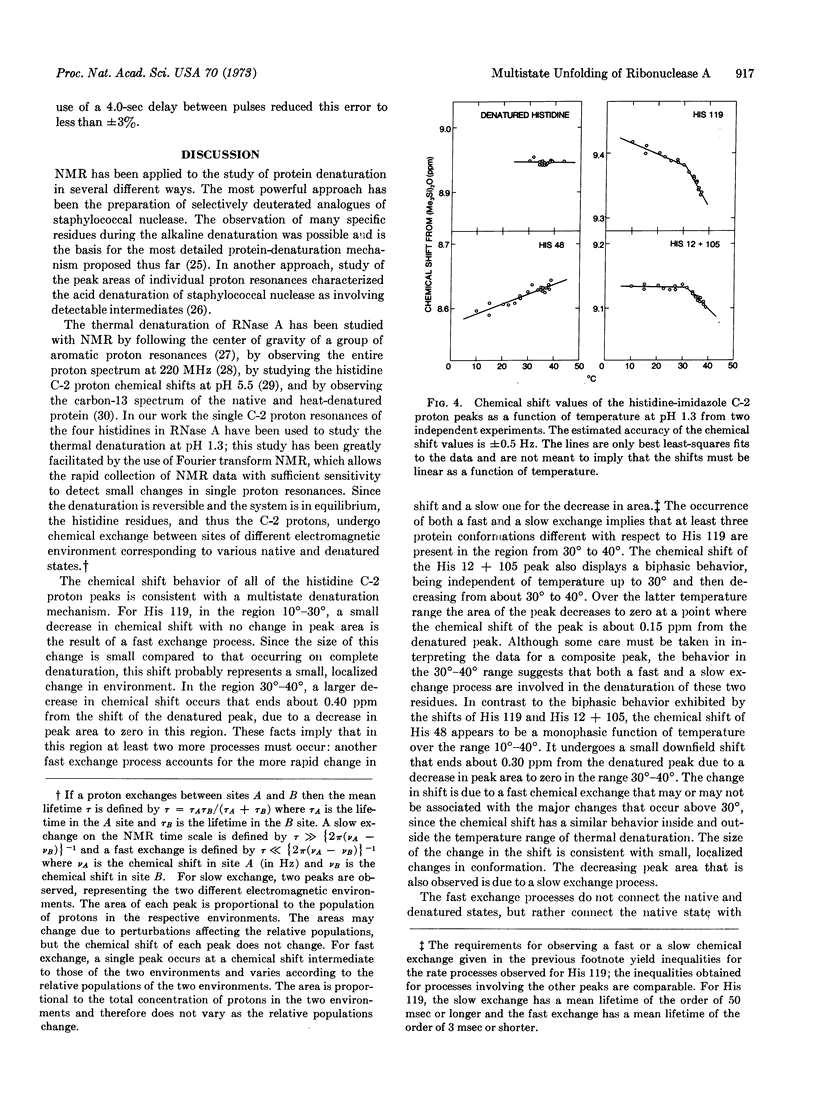
The thermal denaturation of ribonuclease A has been studied by use of Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance by monitoring the imidazole C-2 proton resonances of the histidine residues as a function of temperature at pH 1.3. As the temperature is raised, a slow chemical exchange process results in the disappearance of the peaks corresponding to the native conformation and the appearance of a single peak corresponding to histidine in the denatured state. The disappearance of the native peaks is not simultaneous, implying that at least two regions of the molecule denature at different temperatures. Also, fast chemical exchange processes result in small chemical shifts that appear to be related to local conformational changes. The observed phenomena have been shown to be reversible by the measurement of absorbance at 278 nm, enzyme activity, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The results of this equilibrium study support a multistate denaturation mechanism for ribonuclease A at pH 1.3.
Keywords: reversible unfolding, histidine, fast and slow chemical exchange
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addad J. P. Conformational changes of ribonuclease A as seen by nuclear magnetic resonance line shifts. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELLO J., HARKER D. Crystallization of deuterated ribonuclease. Nature. 1961 Nov 25;192:756–756. doi: 10.1038/192756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROOK E. M., MATHIAS A. P., RABIN B. R. Spectrophotometric assay of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease by the use of cytidine 2':3'-phosphate. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:234–238. doi: 10.1042/bj0740234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Schechter A. N., Cohen J. S. Folding of staphylococcal nuclease: magnetic resonance and fluorescence studies of individual residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2042–2046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glushko V., Lawson P. J., Gurd F. R. Conformational states of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A observed by normal and partially relaxed carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3176–3185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERMANS J., Jr, SCHERAGA H. A. The thermally induced configurational change of ribonuclease in water and deuterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:534–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O., Thielmann H., Arata Y., Markley J. L., Williams M. N. Tentative sequential model for the unfolding and refolding of staphylococcal nuclease at high pH. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:257–261. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartha G., Bello J., Harker D. Tertiary structure of ribonuclease. Nature. 1967 Mar 4;213(5079):862–865. doi: 10.1038/213862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A. Intermediate stages in the thermally induced transconformation reactions of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3736–3742. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D., Glickson J. D. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the mechanism of reversible denaturation of lysozyme. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 13;93(1):235–246. doi: 10.1021/ja00730a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Manifestations of the tertiary structures of proteins in high-frequency nuclear magnetic resonance. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Nov 22;89(24):6332–6341. doi: 10.1021/ja01000a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhie P. pH dependence of the thermal unfolding of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):879–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows D. H., Jardetzky O., Epand R. M., Ruterjans H. H., Scheraga H. A. Assignment of the histidine peaks in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of ribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):766–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELA M., ANFINSEN C. B. Some spectrophotometric and polarimetric experiments with ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 May;24(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. N., Sachs D. H., Heller S. R., Shrager R. I., Cohen J. S. Nuclear magnetic resonance titration curves of histidine ring protons. 3. Ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons E. R., Schneider E. G., Blout E. R. Thermal effects on the circular dichroism spectra of ribonuclease A and of ribonuclease S-protein. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4023–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. C. A study of the conformational properties of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A by electron paramagnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):745–757. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Baldwin R. L. A sequential model of nucleation-dependent protein folding: kinetic studies of ribonuclease A. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):453–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Baldwin R. L., Elson E. L. Properties of the refolding and unfolding reactions of ribonuclease A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1809–1812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Baldwin R. L., Elson E. L. The sequential unfolding of ribonuclease A: detection of a fast initial phase in the kinetics of unfolding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2712–2715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Baldwin R. L. Kinetic evidence for intermediate states in the unfolding of ribonuclease A. II. Kinetics of exposure to solvent of a specific dinitrophenyl group. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Hearn R. P., Wrathall D. P., Sturtevant J. M. A calorimetric study of thermally induced conformational transitions of ribonuclease A and certain of its derivatives. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2666–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaborsky O. R., Milliman G. E. The effect of temperature on the chemical shifts of the histidine residues of ribonuclease A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 21;271(2):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


