Abstract
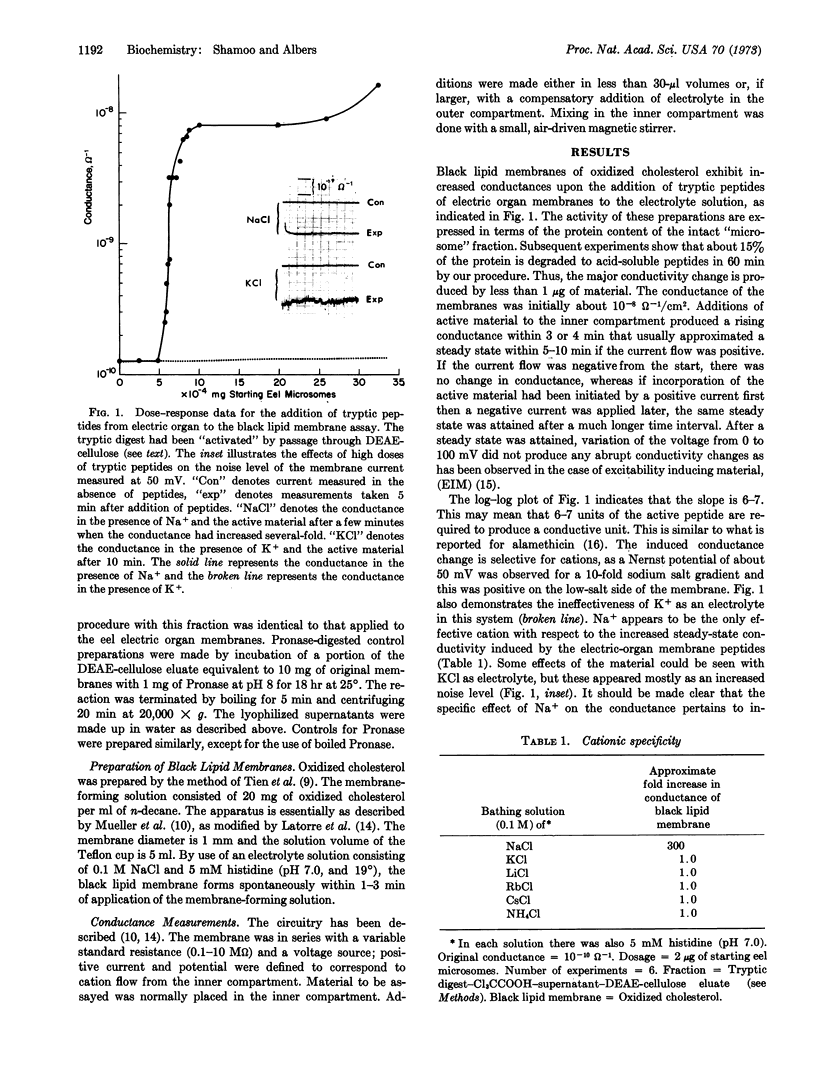
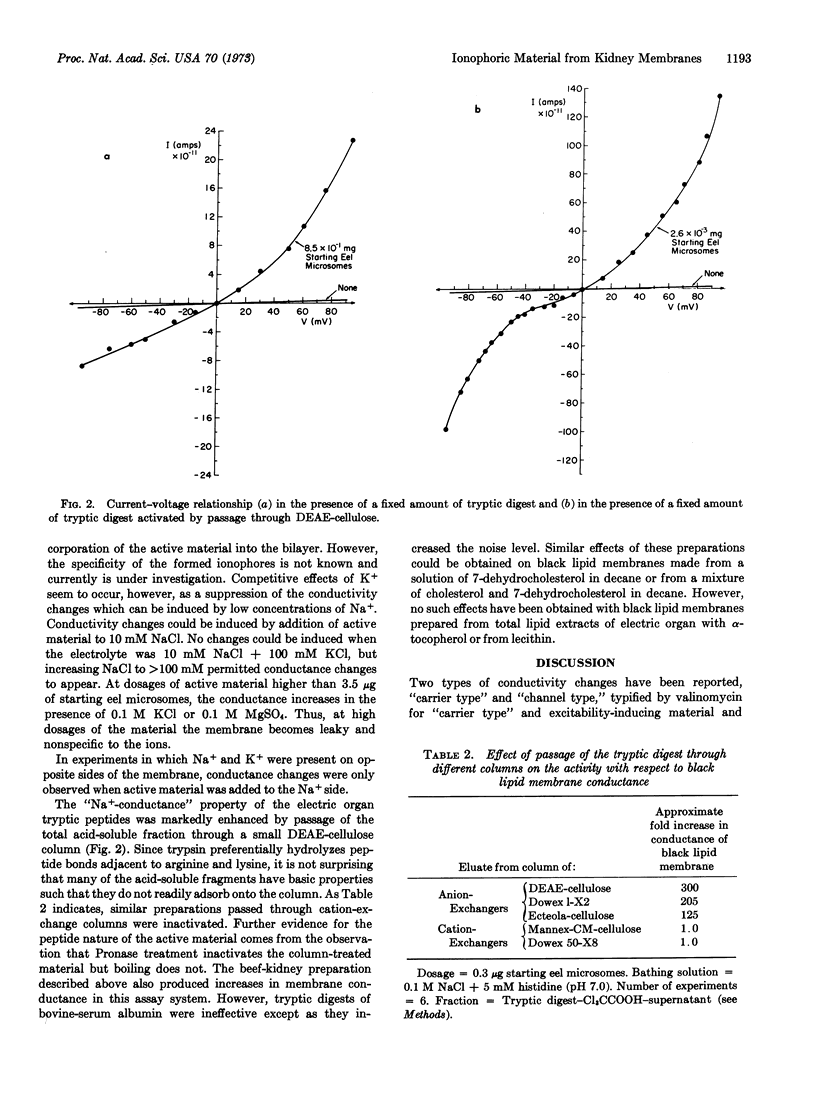
Material that increases black lipid-membrane (oxidized cholesterol) conductance has been demonstrated in the acid-soluble fraction of tryptic digests of membrane fractions from Electrophorus electric organ and beef kidney. The conductance change elicited by this material is highly selective for Na+. The activity of the material was greatly enhanced by passage through DEAE-cellulose. Activity could be destroyed by further incubation with Pronase. Since conductivity increases exponentially with dose of ionophore, the conductive unit may be an oligomer.
Keywords: Electrophorus, black lipid membranes, peptides
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERS R. W., FAHN S., KOVAL G. J. THE ROLE OF SODIUM IONS IN THE ACTIVATION OF ELECTROPHORUS ELECTRIC ORGAN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:474–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein G., Lecar H., Nossal R. The nature of the negative resistance in bimolecular lipid membranes containing excitability-inducing material. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):119–133. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S. S., Albers R. W. Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. IX. The role of phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):867–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C., Sachs G. Extraction of K + selective channels from excitable tissue. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):252–253. doi: 10.1038/newbio237252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Strickholm A., Cordes E. H. Reconstitution of an ATP-mediated active transport system across black lipid membranes. Nature. 1969 May 31;222(5196):871–872. doi: 10.1038/222871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., White F. P., Strickholm A., Williams E., Cordes E. H. Studies concerning the possible reconstitution of an active cation pump across an artificial membrane. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(4):363–388. doi: 10.1007/BF01868111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L., Skou J. C. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. I. The influence of detergents on the activity of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):366–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Purification of the sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Ehrenstein G., Lecar H. Ion transport through excitability-inducing material (EIM) channels in lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jul;60(1):72–85. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClare C. W. Chemical machines, Maxwell's demon and living organisms. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jan;30(1):1–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Action potentials induced in biomolecular lipid membranes. Nature. 1968 Feb 24;217(5130):713–719. doi: 10.1038/217713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redwood W. R., Müldner H., Thompson T. E. Interaction of a bacterial adenosine triphosphatase with phospholipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):989–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoo A. E., Brodsky W. A. Functions of the E-atp and E-P complexes in the membrane ATPase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesugi S., Dulak N. C., Dixon J. F., Hexum T. D., Dahl J. L., Perdue J. F., Hokin L. E. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. VI. Large scale partial purification and properties of a lubrol-solubilized bovine brain enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):531–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H., Burgermeister W., Otting W., Möhle W., Shemyakin M. M., Ovchinnikov Y. A., Ivanov V. T., Malenkov G. G. Affinity of antamanide for sodium ions. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T. The discovery, isolation, elucidation of structure, and synthesis of antamanide. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1968 Mar;7(3):204–208. doi: 10.1002/anie.196802041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


