Abstract
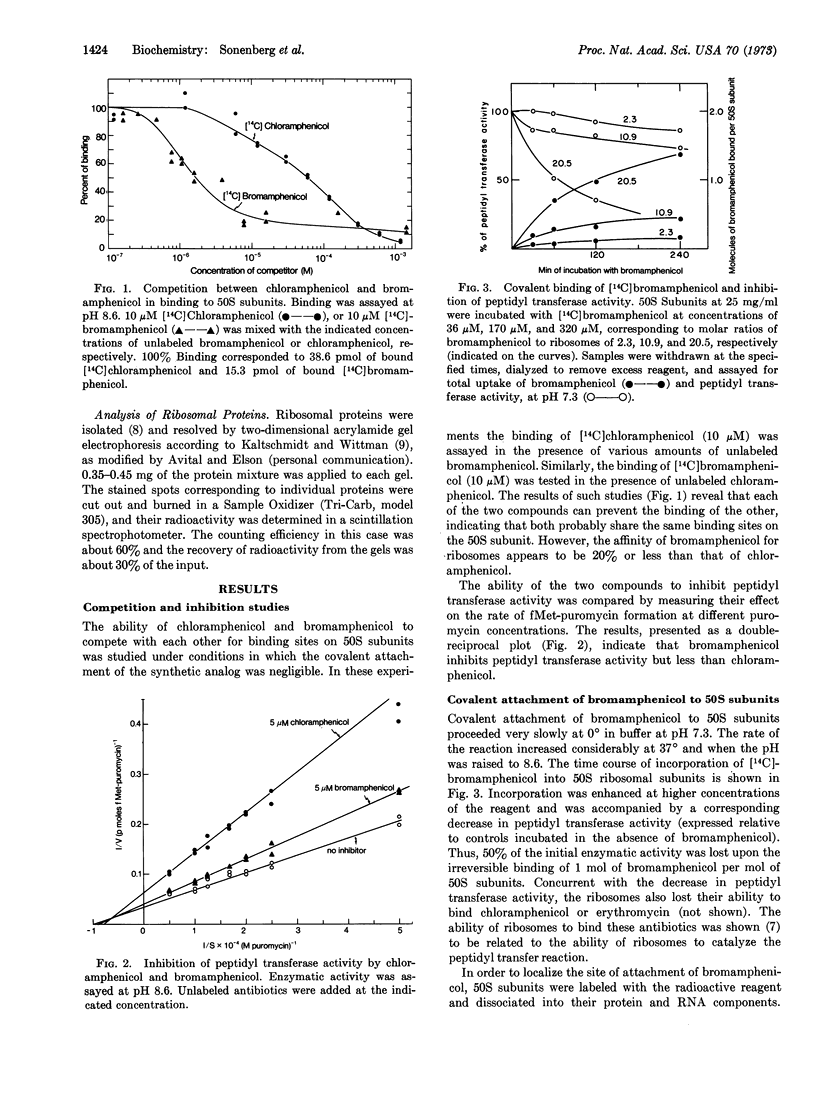
The method of affinity labeling has been used to identify protein components of 50S ribosomal subunits involved in peptidyl transferase activity. E. coli 50S ribosomal subunits were mapped by reaction with the N-bromoacetyl analog of chloramphenicol, an antibiotic known to interact specifically with the active center of the enzyme. The synthetic analog competes with chloramphenicol in binding to 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits peptidyl transferase activity. It attaches covalently to the ribosome under appropriate conditions and causes an irreversible loss in peptidyl transferase activity. The reagent specifically alkylates cysteine residues of proteins L2 and L27.
Keywords: ribosomal proteins, bromamphenicol, N-bromoacetyl derivatives, 50S subunit
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bald R., Erdmann V. A., Pongs O. Irreversible binding of chloramphenicol analogues to E. coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 1;28(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva E. S., Budker V. G., Girshovich A. S., Knorre D. G., Teplova N. M. An approach to specific labelling of ribosome in the region of peptidyl-transferase center using N-acylaminoacyl-tRNA with an active alkylating grouping. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 1;19(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80493-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes: Binding of UACCA-Leu to 50 S subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Mar 16;13(4):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80546-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Kuechler E. Affinity label for the tRNA binding site on the Escherichia coli ribosome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):667–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XII. Number of proteins in small and large ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli as determined by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Zamir A., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: the peptidyl transferase activity of the 50 s subunit of Escherihia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):355–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E. Catalysis of peptide bond formation by 50 S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Ribosome-catalysed peptidyl transfer: effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. Reaction of N-ethyl maleimide with the ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):169–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90456-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Oen H., Cantor C. R. Covalent attachment of a peptidyl-transfer RNA analog to the 50S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XIX. Effect of antibiotics on peptidyl puromycin synthesis on polyribosoms from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITNIK-ELSON P. THE PREPARATION OF RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH LITHIUM CHLORIDE AND UREA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 17;18:557–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90790-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobin L. I. Sulfhydryl groups of Escherichia coli Ribosomes and ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P. A new approach to the fractionation of ribosomal protein. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut R. R., Haenni A. L. The effect of sulfhydryl reagents on ribosome activity. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jul;2(1):4–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Vogel T., Zamir A., Elson D. Correlation between the peptidyl transferase activity of the 50 s ribosomal subunit and the ability of the subunit to interact with antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



