Abstract
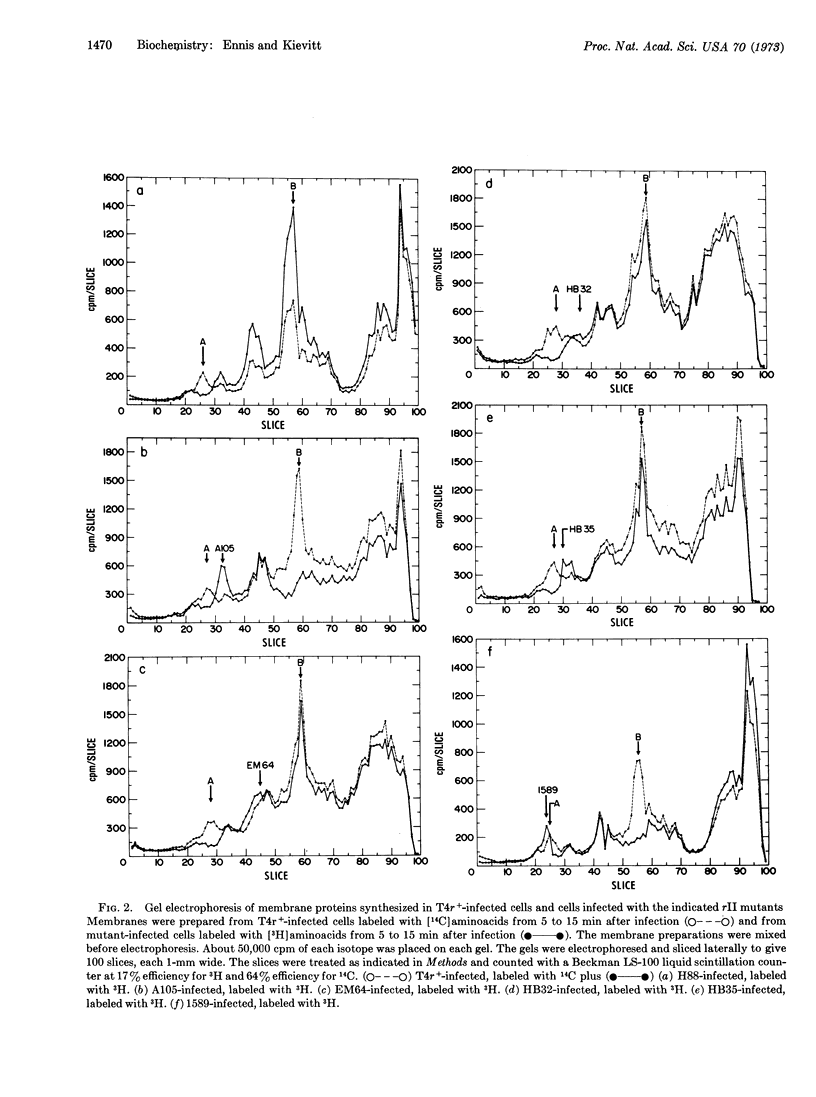
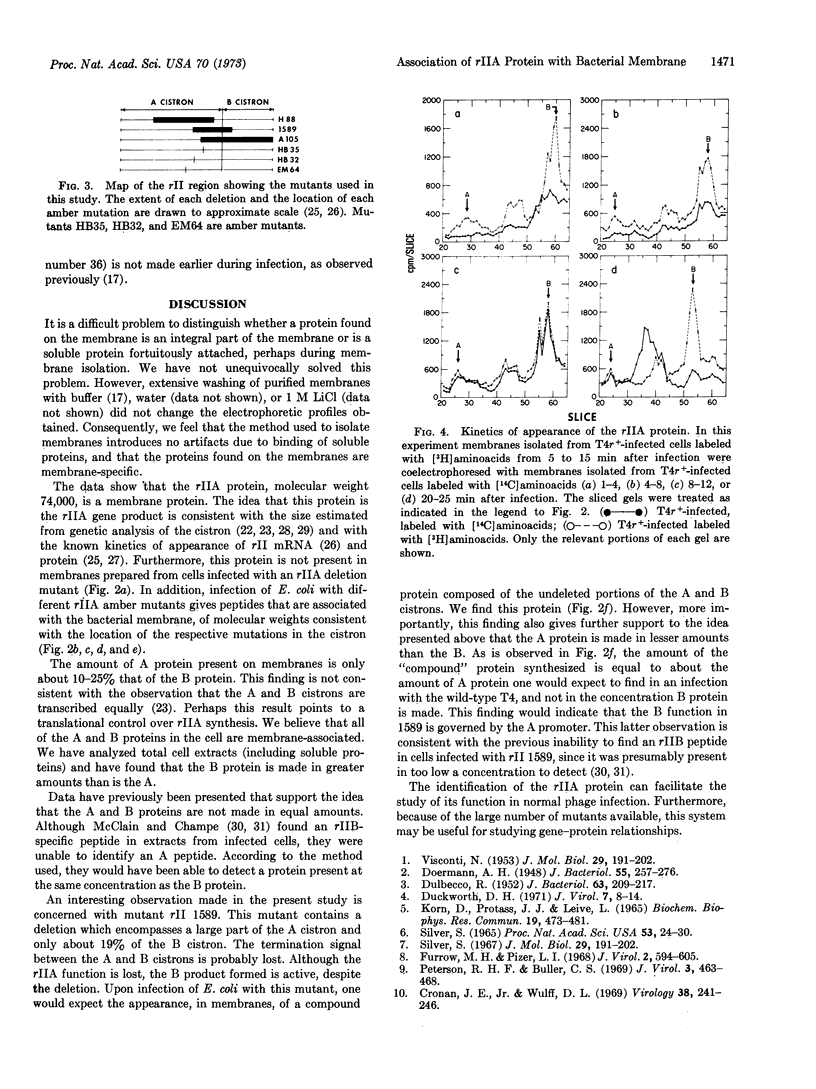
Cell membrane proteins synthesized after infection of Escherichia coli B with wild-type phage T4 and rIIA mutants were analyzed by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A protein with an approximate molecular weight of 74,000 is present in membranes isolated from T4r+-infected cells, but is not found in membranes prepared from cells infected with an rIIA mutant in which the major part of the rIIA cistron is deleted. In addition, infection of E. coli B with different rIIA amber mutants and deletions gives peptides, which are associated with the bacterial membrane, of molecular weights consistent with the location of the respective mutations in the cistron. The rIIA protein is synthesized with delayed early kinetics. The synthesis of the rIIB protein, which is also located in the membrane, is not affected by mutations in the A cistron; conversely, synthesis of the rIIA protein is not affected by mutations in the B cistron. A mutant (rII 1589) contains a deletion that originates in the A cistron and extends into the adjacent B cistron. This mutant directs the synthesis of a compound membrane protein consisting of the undeleted portions of the A and B cistrons. The synthesis of the compound protein appears to be under the control of the A promoter.
Keywords: bacteriophage T4, E. coli, mutants
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benzer S. ON THE TOPOGRAPHY OF THE GENETIC FINE STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar;47(3):403–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujard H., Mazaitis A. J., Bautz E. K. The size of the rII region of bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P., BENZER S. An active cistron fragment. J Mol Biol. 1962 Apr;4:288–292. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P., BENZER S. Reversal of mutant phenotypes by 5-fluorouracil: an approach to nucleotide sequences in messenger-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:532–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. The requirement for potassium for bacteriophage T4 protein and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Wulff D. L. A role for phospholipid hydrolysis in the lysis of Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90365-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R. Mutual exclusion between related phages. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):209–217. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.209-217.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doermann A. H. Lysis and Lysis Inhibition with Escherichia coli Bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1948 Feb;55(2):257–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.2.257-276.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H. Inhibition of T4 bacteriophage multiplication by superinfecting ghosts and the development of tolerance after bacteriophage infection. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.8-14.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrich J. Lysis of T4-infected bacteria in the absence of lysozyme. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furrow M. H., Pizer L. I. Phospholipid synthesis in Escherichia coli infected with T4 bacteriophages. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):594–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.594-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A. Physiological effects of rII mutations in bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:151–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D. Mutation of Bacteriophage with Respect to Type of Plaque. Genetics. 1946 Nov;31(6):620–640. doi: 10.1093/genetics/31.6.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN D., PROTASS J. J., LEIVE L. A NOVEL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D IN PREVENTING BACTERIOPHAGE T4 MATURATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:473–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai T., Bautz E. K. Regulation of gene-specific RNA synthesis in bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Russel M. The time of synthesis and function of the rII + product of bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):160–167. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Champe S. P. Detection of a peptide determined by the rII B cistron of phage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1182–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Champe S. P. Genetic alterations of the rII B cistron polypeptide of phage T4. Genetics. 1970 Sep;66(1):11–21. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. F., Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. Properties of phage T4 messenger RNA synthesized in the absence of protein synthesis. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. F., Kievitt K. D., Ennis H. L. Membrane protein synthesis after infection of Escherichia coli B with phage T4: the rIIB protein. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):520–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. H., Buller C. S. Phospholipid metabolism in T4 bacteriophage infected Escherichia coli K-12 (lambda). J Virol. 1969 May;3(5):463–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.5.463-468.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVER S. ACRIFLAVINE RESISTANCE: A BACTERIOPHAGE MUTATION AFFECTING THE UPTAKE OF DYE BY THE INFECTED BACTERIAL CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:24–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sederoff R., Bolle A., Goodman H. M., Epstein R. H. Regulation of rII and region D transcription in T4 bacteriophage: a sucrose gradient analysis. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S. Acridine sensitivity of bacteriophage T2: a virus gene affecting cell permeability. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallée M., Cornett J. B. A new gene of bacteriophage T4 determining immunity against superinfecting ghosts and phage in T4-infected Escherichia coli. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. B., Frankel F. R. Identification of the T4rIIB gene product as a membrane protein. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):589–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


