Abstract
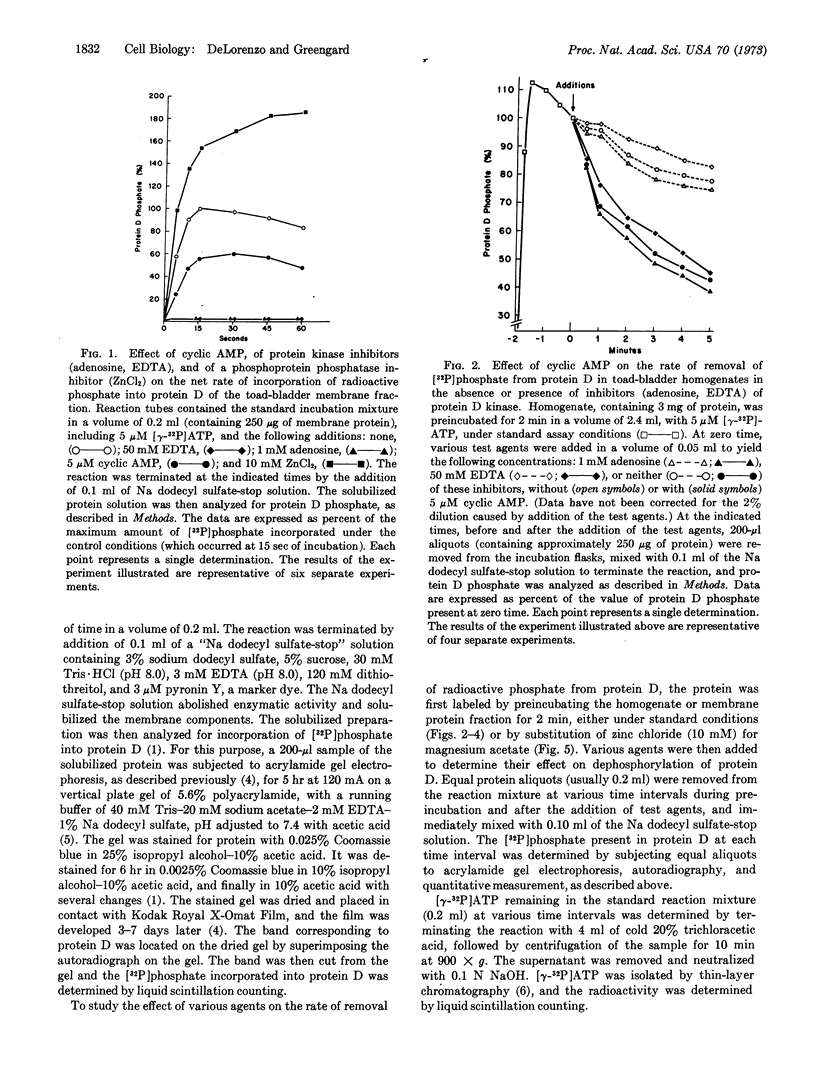
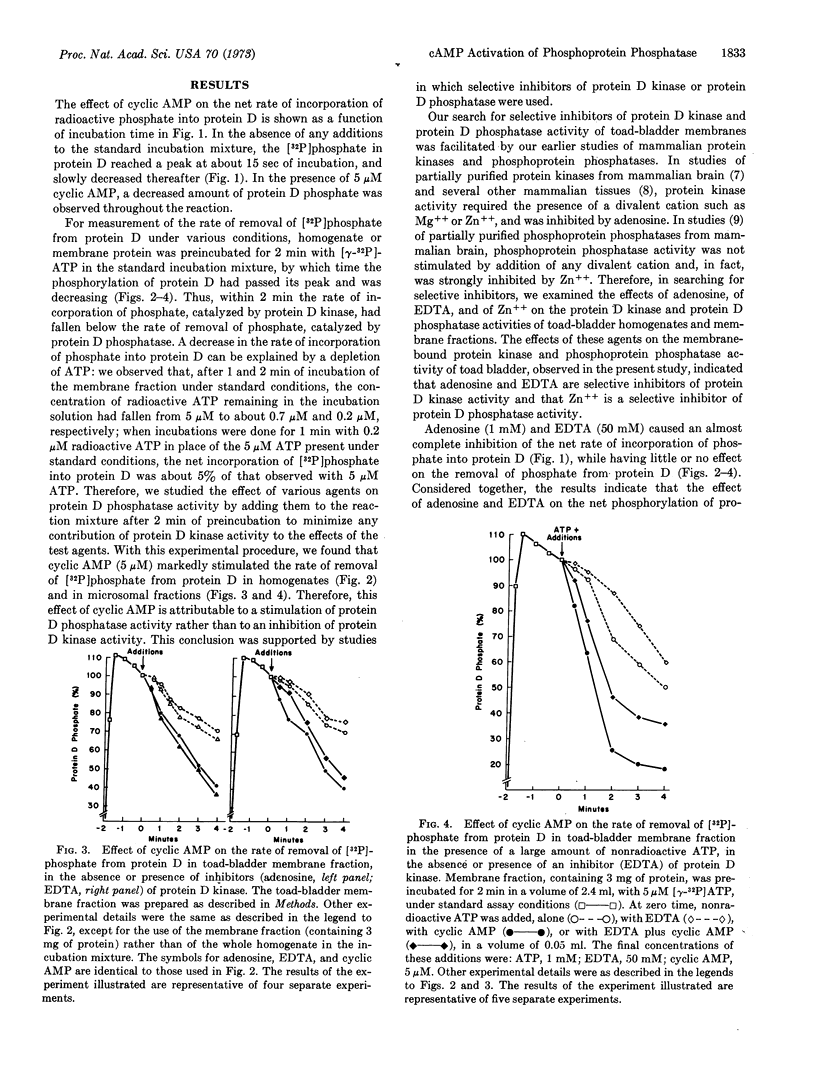
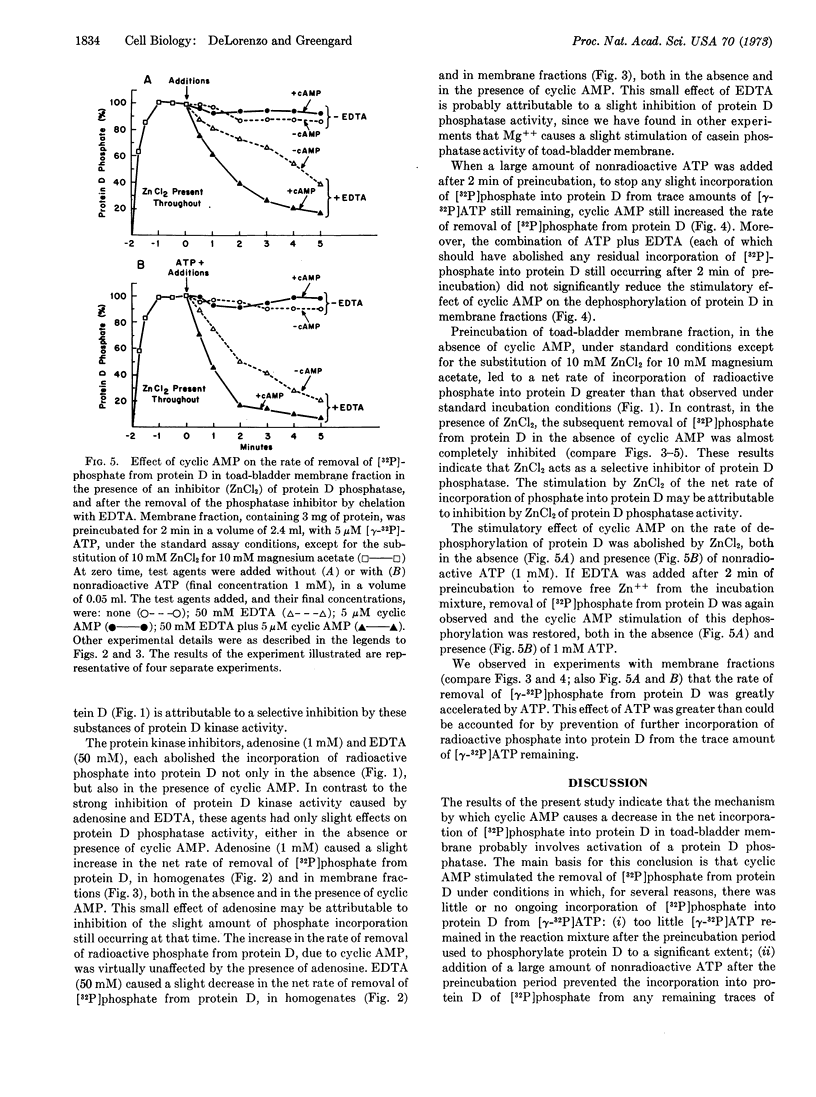
Adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) caused a decrease in the net rate of incorporation of radioactive phosphate into a specific protein (protein D) in a membrane fraction from toad bladder. Moreover, when the membrane protein was prelabeled with radioactive phosphate, cyclic AMP caused an increase in the net rate of removal of radioactive phosphate from this specific protein. Certain agents were shown to be selective inhibitors of membrane-bound protein D kinase or protein D phosphatase. With the help of these agents, it was concluded that cyclic AMP caused the activation of membrane-bound protein D phosphatase. The present data, together with earlier studies, are compatible with the possibility that the cyclic AMP-induced activation of a membrane-bound phosphoprotein phosphatase in toad bladder, with the consequent dephosphorylation of protein D, may be responsible for the physiological effects of antidiuretic hormone on sodium and/or water transport in this tissue.
Keywords: cyclic AMP, protein D, antidiuretic hormone
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chelala C. A., Torres H. N. Regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase phosphatase activity. II. Interconversions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):504–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J., Walton K. G., Curran P. F., Greengard P. Regulation of phosphorylation of a specific protein in toad-bladder membrane by antidiuretic hormone and cyclic AMP, and its possible relationship to membrane permeability changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman H. I., Agrawal K. C., Sartorelli A. C. Localization in Escherichia coli B of two enzymatic sites of action by 1-formylisoquinoline thiosemicarbazone (IQ-1) on ribonucleic acid biosynthetic pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Dec 15;21(24):3223–3233. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Ueda T., Maeno H., Greengard P. Adenosine 3',5-monophosphate-dependent phosphorylation of a specific protein in synaptic membrane fractions from rat cerebrum. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5650–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Krueger B. K., Sanes J. R., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. V. Preparation and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from various bovine tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 15;212(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno H., Greengard P. Phosphoprotein phosphatases from rat cerebral cortex. Subcellular distribution and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3269–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno H., Johnson E. M., Greengard P. Subcellular distribution of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Riley G. A. The activation and inactivation of phosphorylase phosphatase from bovine adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3517–3524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. 3. Purification and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6395–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


