Abstract
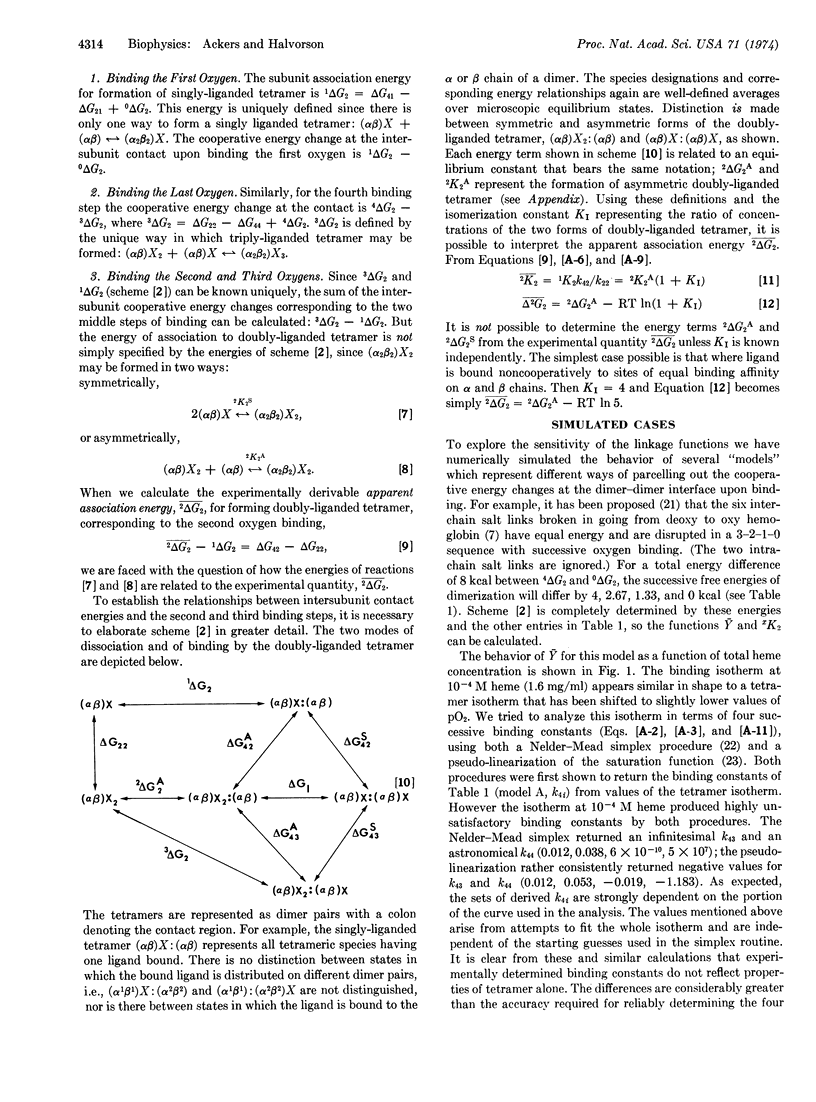
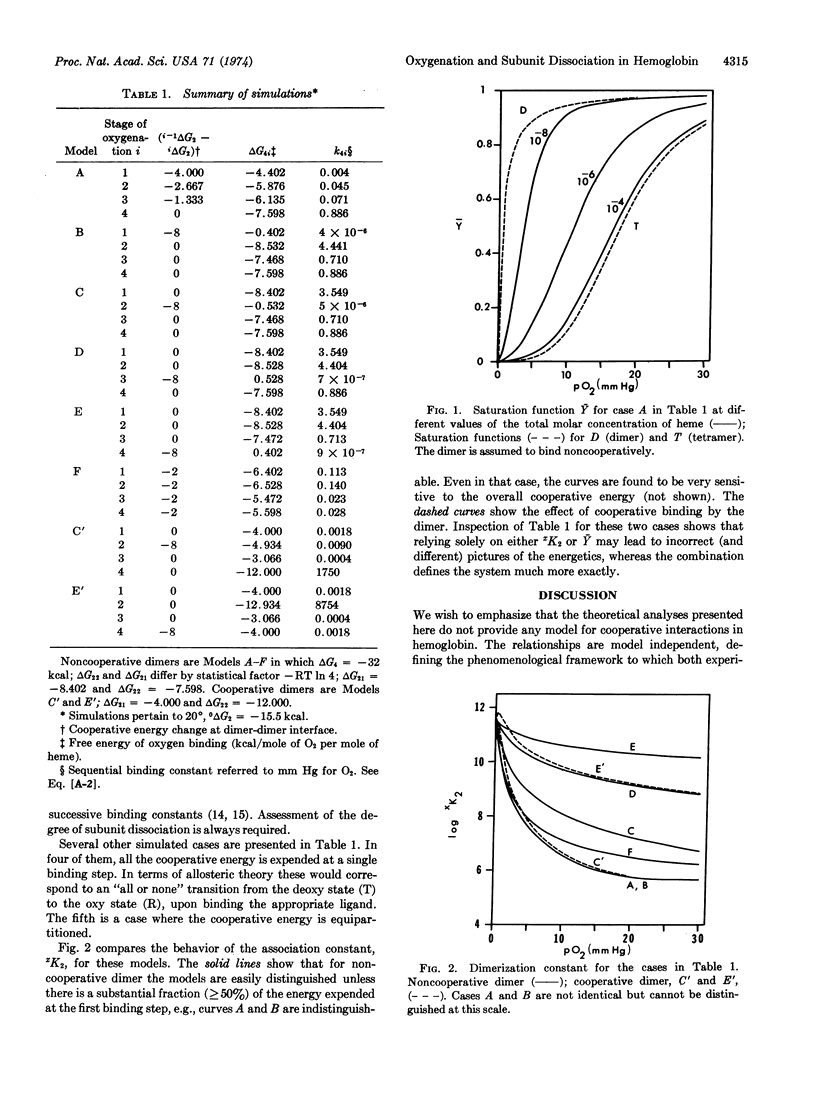
The use of subunit dissociation as a means of probing intersubunit contact energy changes which accompany cooperative ligand binding has been studied for the case of human hemoglobin. An analysis is presented delineating the information that can be obtained from the linkage relationships between ligand binding and subunit dissociation of hemoglobin tetramers into dimers. The analysis defines (a) the variation of the saturation function, Ȳ, with total protein concentration, (b) the variation of the subunit dissociation constant xK2 with ligand concentration (X) and (c) the correlations between changes in dimer-dimer contact energy and the sequential ligand binding steps. Sensitivity of the linkage function has been explored by numerical simulation. It is shown that subunit dissociation may appreciably affect oxygenation curves under usual conditions of measurement and that relying solely on either xK2 or Ȳ may lead to incorrect picutres of the energetics, whereas the combination defines the system much more exactly.
Keywords: protein association, ligand binding, thermodynamics
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K., THOMPSON T. E. DETERMINATION OF STOICHIOMETRY AND EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANTS FOR REVERSIBLY ASSOCIATING SYSTEMS BY MOLECULAR SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:342–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen M. E., Moffat J. K., Gibson Q. H. The kinetics of ligand binding and of the association-dissociation reactions of human hemoglobin. Properties of deoxyhemoglobin dimers. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2796–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. II. Human oxyhemoglobin: gel filtration studies. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal W. J. Cooperative binding of oxygen to hemoglobin: analysis of accurate equilibrium binding data. Biopolymers. 1973;12(9):2057–2073. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Rehmar M. J., Olson J. S., Gibson Q. H. Functional aspects of the subunit association-dissociation equilibria of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4372–4381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaum D., Herskovits T. T. Dissociation of human hemoglobin by the ureas and amides. Osmotic pressure and light scattering studies. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 12;13(6):1268–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00703a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Studies on the chemistry of hemoglobin. IV. The mechanism of reaction with ligands. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3704–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. A., Kilmartin J. V., Eyck L. F., Perutz M. F. Noncooperativity of the dimer in the reaction of hemoglobin with oxygen (human-dissociation-equilibrium-sulfhydryl-absorption-x-ray analysis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):203–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K. Analyses of oxygen equilibria of native and chemically modified human adult hemoglobins on the basis of Adair's stepwise oxygenation theory and the allosteric model of Monod, Wyman, and Changeux. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):798–808. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett G. L. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. Ligand-linked dissociation at neutral pH. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):401–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett G. L. Ligand-free haemoglobin dimers. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 8;234(49):189–191. doi: 10.1038/newbio234189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett G. L., Schachman H. K. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. Monomer formation and the influence of ligands. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. W. Relation between allosteric effects and changes in the energy of bonding between molecular subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):479–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):726–739. doi: 10.1038/228726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., TenEyck L. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in hemoglobin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:295–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Edelstein S. J. Observation of the dissociation of unliganded hemoglobin. II. Effect of pH, salt, and dioxane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2901–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Edelstein S. J. Observation of the dissociation of unliganded hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7870–7874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyuma I., Imai K., Shimizu K. Analysis of oxygen equilibrium of hemoglobin and control mechanism of organic phosphates. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1491–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr LINKED FUNCTIONS AND RECIPROCAL EFFECTS IN HEMOGLOBIN: A SECOND LOOK. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:223–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw H. S., Ackers G. K. Molecular sieve studies of interacting protein systems. 8. Critical evaluation of the equilibrium saturation technique using stacked gel columns. Anal Biochem. 1971 Aug;42(2):405–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G. Ligand binding and internal equilibria in proteins. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):864–878. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


