Abstract
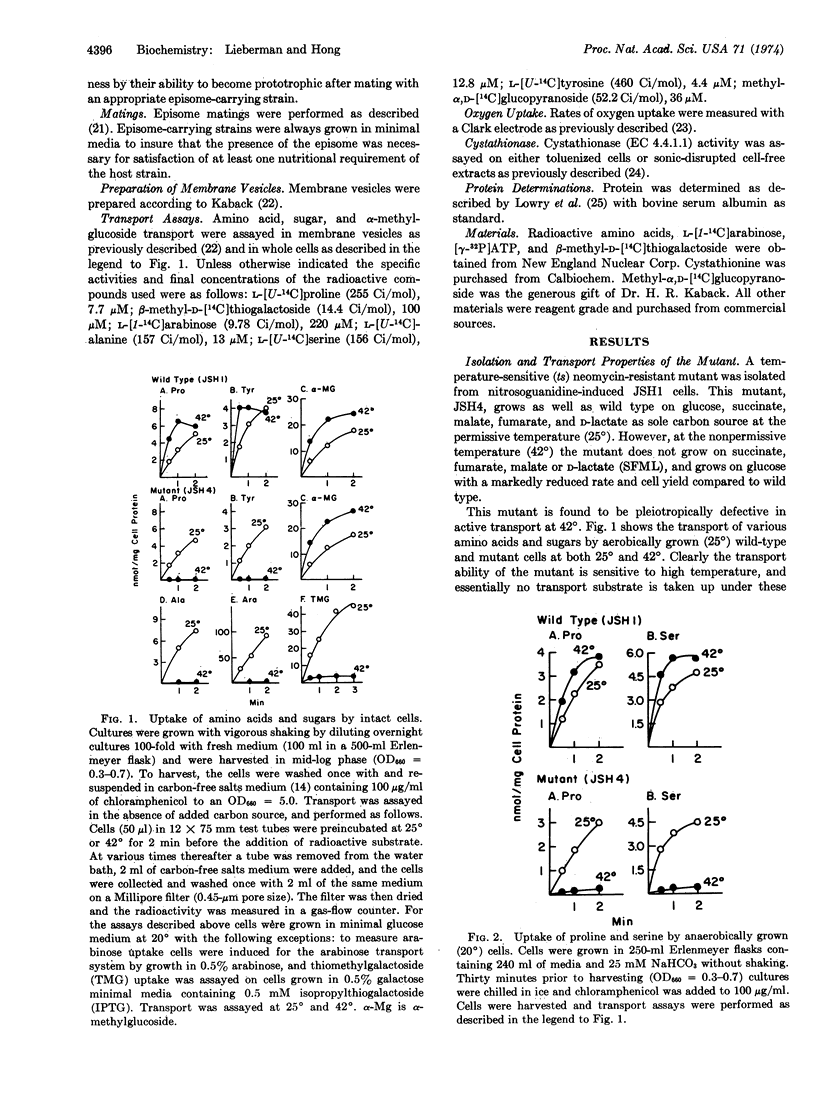
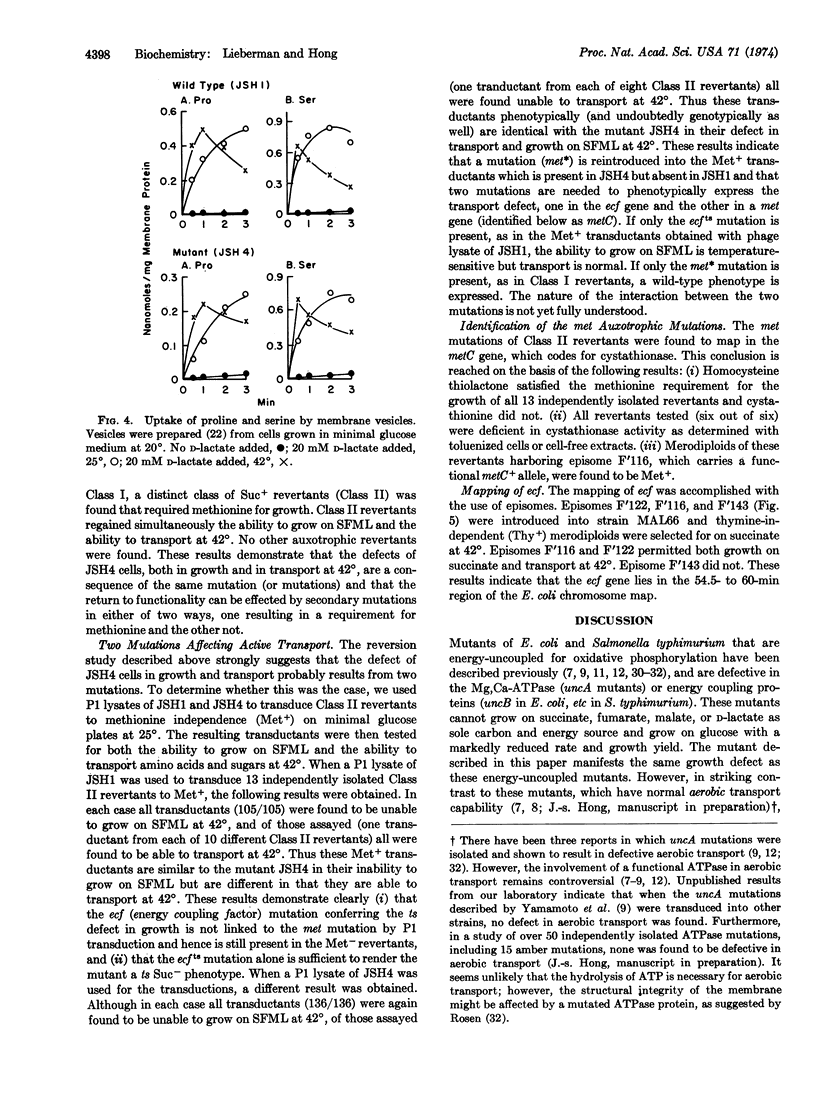
The isolation of a temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli K12 whose active transport of amino acids and sugars is not coupled to metabolic energy at 42° is described. This mutant cannot grow on succinate, fumarate, malate, or D-lactate as sole carbon source at 42° and grows on glucose at 42° with a reduced rate and yield. Efflux of accumulated substrate is also demonstrated upon heat inactivation. The defect of this mutant in both growth and transport is not due to a failure in electron transport through the respiratory chain nor the absence of Mg, Ca-ATPase activity. The mutant is thus distinct from the other energy-uncoupled mutants uncA, uncB, or etc. Analysis of spontaneous revertants indicates that the transport defect is caused by two mutations, one in the energy coupling factor gene and the other in the metC gene. The ecfts mutation has been mapped to be in the 54.5- to 60-min region of the E. coli chromosome map. Possible interactions between the metC mutation and the mutated energy coupling factor protein are discussed.
Keywords: temperature-sensitive mutant, energy coupling factor, cystathionase
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. I. The site of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5518–5522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K-12: the genetic and biochemical characterisations of a strain carrying a mutation in the uncB gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Lam K. W., Sanadi D. R. Escherichia coli nicotinamide adenine nucleotide transhydrogenase driven by aerobic oxidation and its enhancement by an energy transfer factor from rat-liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90660-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D., Calvo J. M., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.215-219.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:297–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Foulds J., Soll L., Berg P. Instability of a missense suppressor resulting from a duplication of genetic material. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):563–581. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway C. T., Greene R. C., Su C. H. Regulation of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):734–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.734-747.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Kaback H. R. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli pleiotropically defective in active transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3336–3340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka N., Nakamura S., Inuzuka M., Tomoeda M. Specific action of sodium dodecyl sulfate on the sex factor of Escherichia coli K-12 Hfr strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):827–835. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.827-835.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:561–598. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L., Boyer P. D. Energization of active transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Reeves J. P., Short S. A., Kaback H. R. Evaluation of the chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacterial membrane vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:312–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Konings W. N. Transport of lactate and succinate by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and a pseudomonas species. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):58–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Boos W. Energy coupling of the -methylgalactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4429–4435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prezioso G., Hong J. S., Kerwar G. K., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. XII. Active transport by a mutant of Escherichia coli uncoupled for oxidative phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Feb;154(2):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Hong J. S., Kaback H. R. Reconstitution of D-lactate-dependent transport in membrane vesicles from a D-lactate dehydrogenase mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1917–1921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Haddock B. A. -Galactoside accumulation in a Mg 2+ -,Ca 2+ -activated ATPase deficient mutant of E.coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):544–551. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Shallenberger M. K. Coupling of energy to active transport of amino acids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T. H., Mével-Ninio M., Valentine R. C. Essential role of membrane ATPase or coupling factor for anaerobic growth and anaerobic active transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 26;314(3):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


