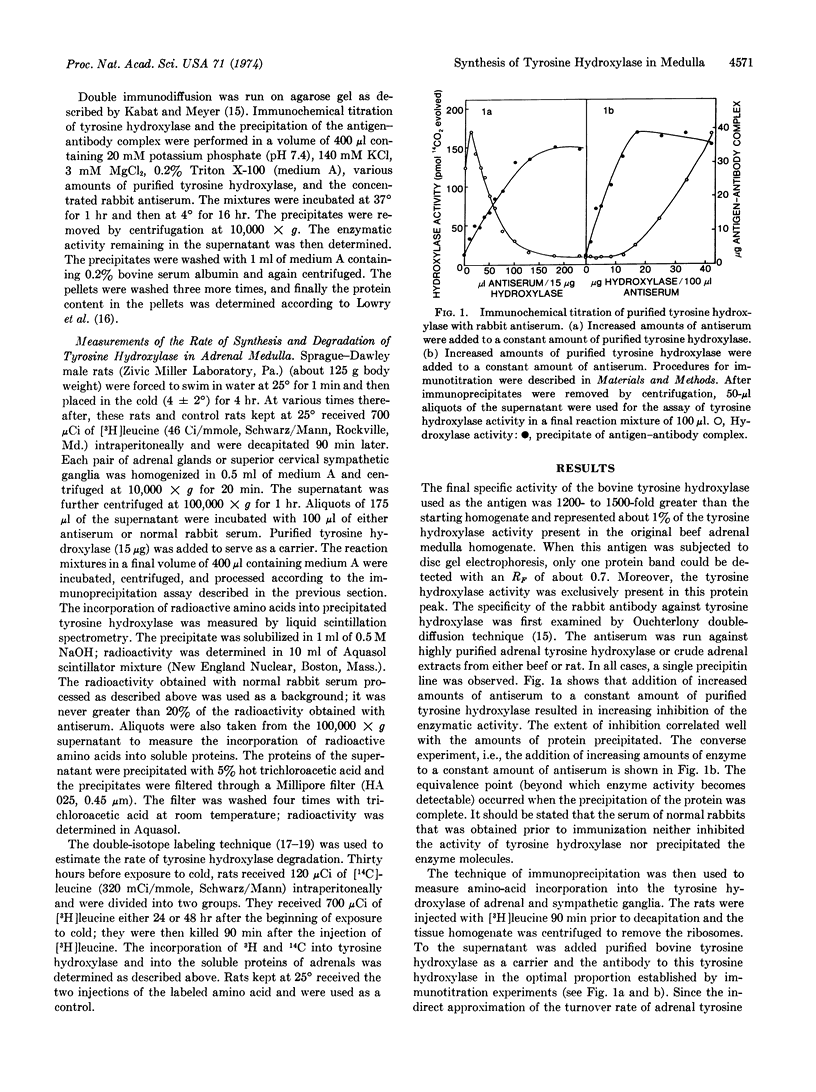
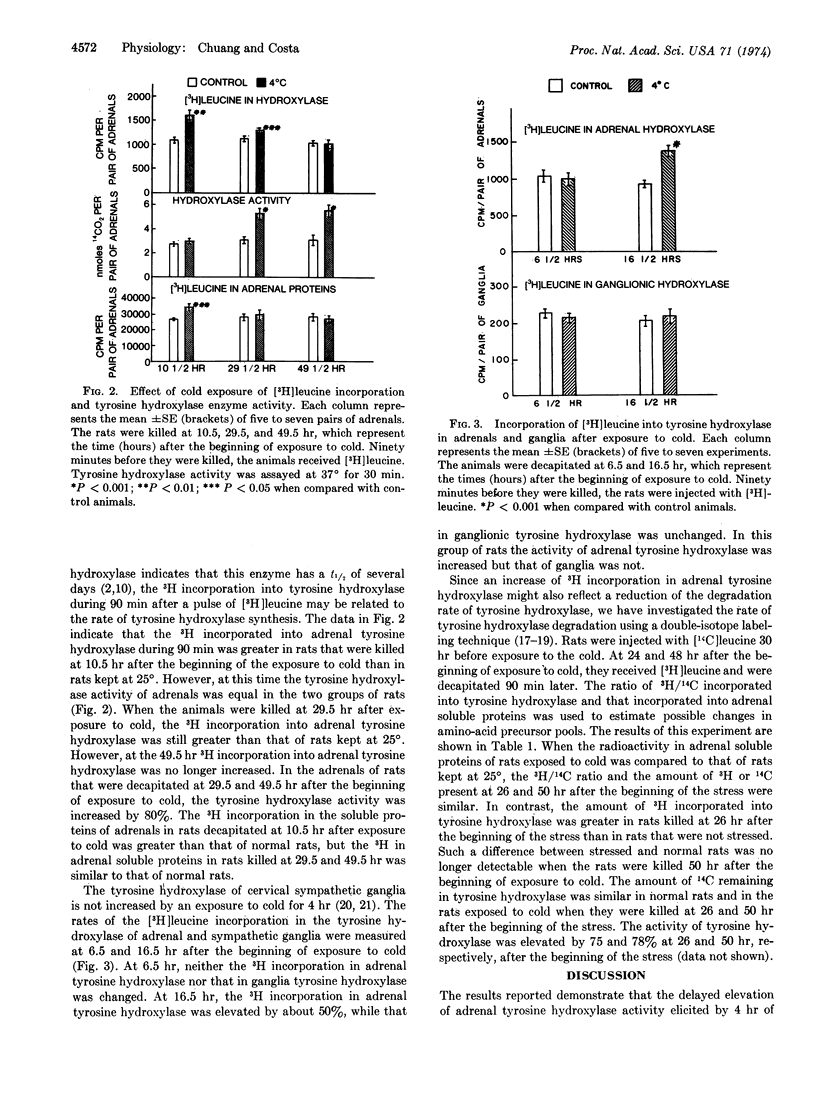
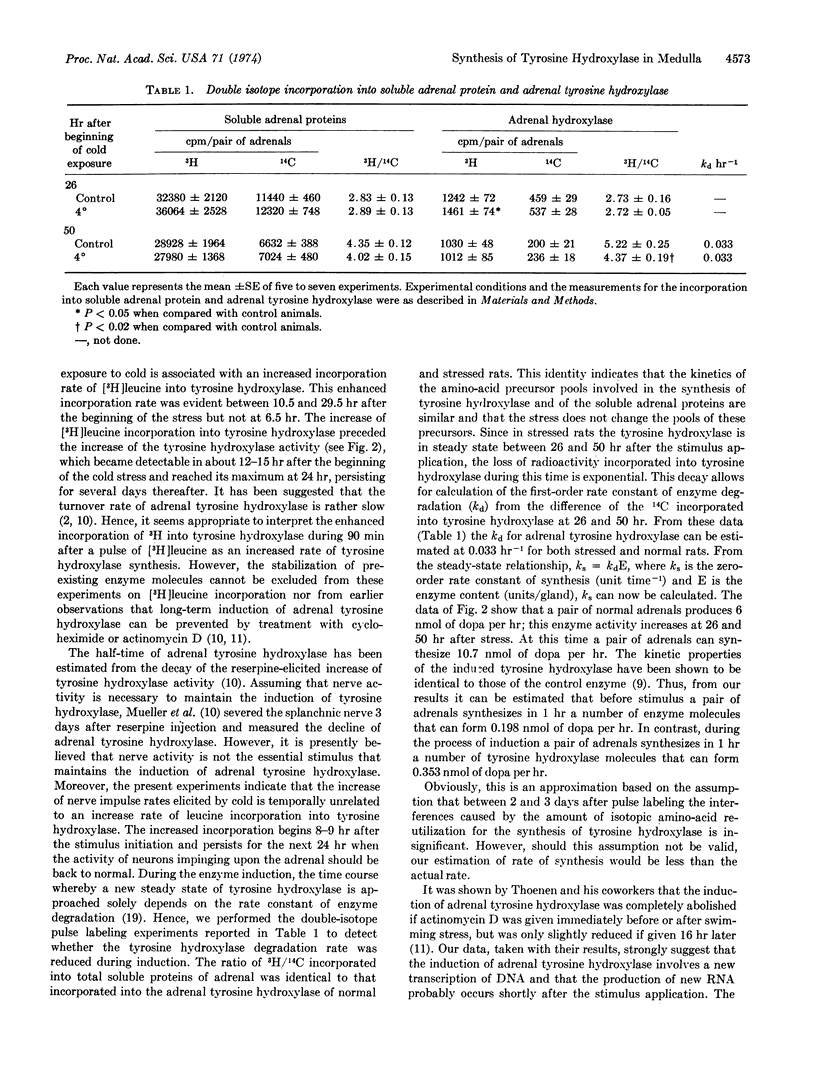
Abstract
Exposure of rats to cold increases the content of tyrosine hydroxylase [EC 1.14.16.2; L-tyrosine, tetrahydropteridine:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating)] in adrenal medulla, causing a long-lasting enhancement of the enzymatic activity. We have used an antibody specific to tyrosine hydroxylase to study the molecular mechanisms involved in the trans-synaptic induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. The rate of [3H]-leucine incorporation into adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase was measured by specific immunoprecipitation at various times after exposure to cold (4 hr). This enhanced rate of incorporation was evident between 11 and 30 hr after the beginning of exposure to cold, but not at 7 and 50 hr. The increase of 3H incorporation preceded the maximal enhancement of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase activity, which occurred about 30 hr after stimulation. Neither the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase nor the rate of 3H incorporation into tyrosine hydroxylase in cervical sympathetic ganglia was changed by 4 hr of exposure to cold. The rate of degradation of tyrosine hydroxylase was estimated at 26 and 50 hr after the beginning of cold stress, as determined by the technique of double-isotope labeling. The data indicate that the tyrosine hydroxylase degradation rate was not reduced by exposure to cold. Thus, the induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase appears to be due to an increased rate of its synthesis.
Keywords: radioimmunoassay, tyrosine hydroxylase degradation, sympathetic ganglia
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias I. M., Doyle D., Schimke R. T. Studies on the synthesis and degradation of proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3303–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Hanbauer I. Do cyclic nucleotides promote the trans-synaptic induction of tyrosine hydroxylase? Life Sci. 1974 Apr 1;14(7):1169–1188. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganschow R. E., Schimke R. T. Independent genetic control of the catalytic activity and the rate of degradation of catalase in mice. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4649–4658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Costa E. Involvement of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the activation of tyrosine hydroxylase elicited by drugs. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):902–904. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Zivkovic B., Pfeiffer R., Costa E. Involvement of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the increase of tyrosine hydroxylase activity elicited by cold exposure. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;278(2):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00500650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Kopin I. J. Mechanisms involved in the trans-synaptic increase of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in sympathetic ganglia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;280(1):39–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00505353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeldtke R., Lloyd T., Kaufman S. An immunochemical study of the induction of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat adrenal glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90802-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Geghman C., Reis D. Immunochemical demonstration of increased accumulation of tyrosine hydroxylase protein in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla elicited by reserpine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2767–2771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvetnansky R., Weise V. K., Kopin I. J. Elevation of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase by repeated immobilization of rats. Endocrinology. 1970 Oct;87(4):744–749. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvetnanský R., Gewirtz G. P., Weise V. K., Kopin I. J. Catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes in the rat adrenal gland during exposure to cold. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):928–931. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd T., Kaufman S. Production of antibodies to bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase: cross-reactivity studies with other pterin-dependent hydroxylases. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. A., Thoenen H., Axelrod J. Increase in tyrosine hydroxylase activity after reserpine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. A., Thoenen H., Axelrod J. Inhibition of trans-synaptically increased tyrosine hydroxylase activity by cycloheximide and actinomycin D. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;5(5):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Doyle D. Control of enzyme levels in animal tissues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:929–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. Induction of tyrosine hydroxylase in peripheral and central adrenergic neurones by cold-exposure of rats. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):861–862. doi: 10.1038/228861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Mueller R. A., Axelrod J. Trans-synaptic induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Oct;169(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Bjur R., Weiner N. Assay of tyrosine hydroxylase by coupled decarboxylation of DOPA formed from 1- 14 C-L-tyrosine. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):588–600. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


