Abstract
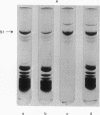
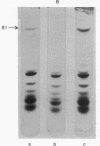
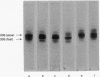
The MS2 RNA binding capacity of 30S ribosomal subunits, which is lost when protein S1 is removed, can be restored following incubation with interference factor iα and repelleting. Polyacrylamide-agarose gel electrophoresis shows that, under these conditions, a faster moving, non-RNA binding 30S species, which contains no S1, is converted to a slower moving RNA-binding one, having the same mobility as the 30S species that contains protein S1. Factor iα binds to single-stranded RNAs in a pattern that closely resembles the RNA binding pattern of initiation factor IF-3.
Keywords: gel electrophoresis, 30S ribosomes, messenger RNA
Full text
PDF
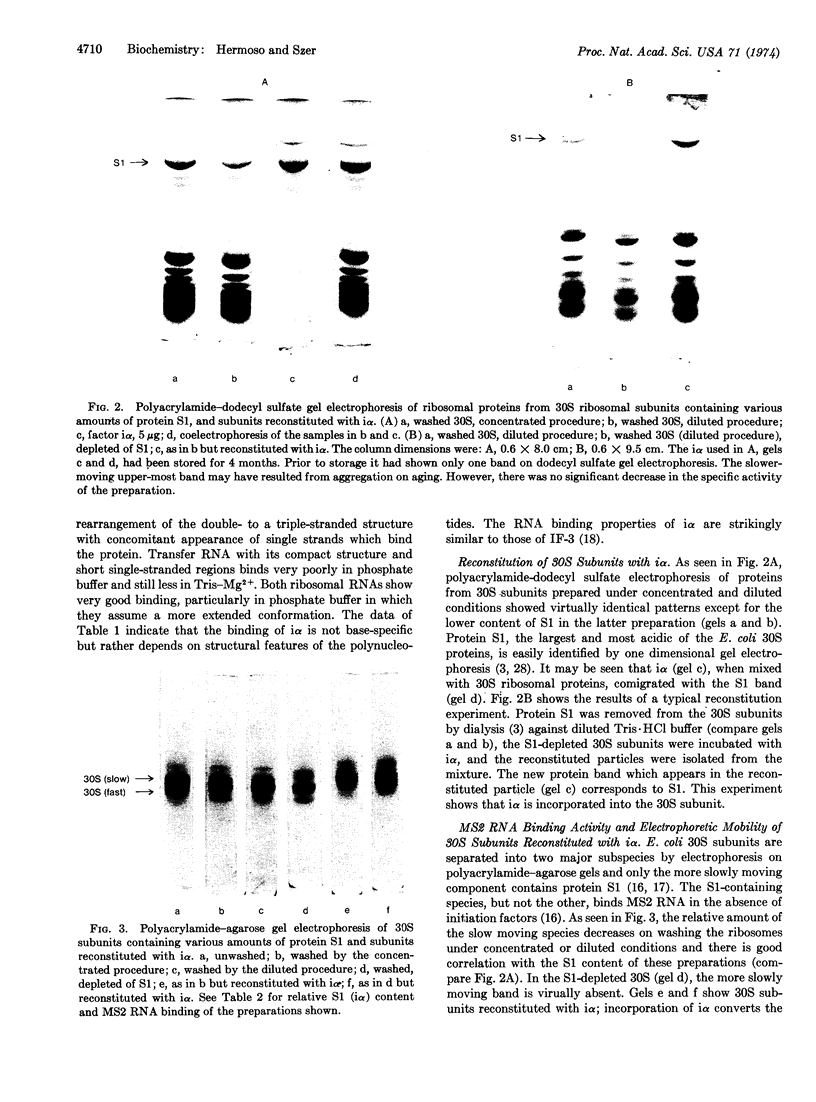


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bickle T. A., Traut R. R. Differences in size and number of 80 S and 70 S ribosomal proteins by dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6828–6834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Chemical and physical characterization of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2906–2915. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Electrophoretic characterization of bacterial polyribosomes in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzionara M., Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 8. Molecular weights of isolated ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1909–1913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner Y., Pollack Y., Berissi H., Revel M. Cistron specific translation control protein in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):16–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio239016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner Y., Scheps R., Kamen R., Kolakofsky D., Revel M. Host subunit of Q replicase is translation control factor i. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 6;239(88):19–20. doi: 10.1038/newbio239019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Pollack Y., Petre J. Physical and functional homology between ribosomal protein S1 and interference factor i. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):109–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K., Sabol S., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. VII. Role of initiation factors in formation of the chain initiation complex with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Kaempfer R. Host interference with viral gene expression: mode of action of bacterial factor i. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 15;82(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. Characterization of the subunits of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):527–533. doi: 10.1038/228527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Kondo M., Römer W., Weissmann C. Reconstitution of Q replicase lacking subunit with protein-synthesis-interference factor i. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 21;31(1):44–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Gallerani R., Weissmann C. Subunit structure of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):525–527. doi: 10.1038/228525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Randall L., Lutter L. Physical and functional heterogeneity of E. coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Ochoa S. Purification and properties of two messenger-discriminating species of E. coli initiation factor 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):84–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Ochoa S. Specific inhibitors of MS2 and late T4 RNA translation in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90420-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Sillero M. A., Ochoa S. Isolation and properties of crystalline initiation factor F1 from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb;18(4):536–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler S., Szer W. Purification and properties of initiation factor IF-3 from Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1458–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M., Felsenfeld G. A study of polyadenylic acid at neutral pH. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):455–466. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsett M. N. EVIDENCE FOR HELICAL STRUCTURE IN POLYURIDYLIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Apr;46(4):445–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder R. Initiation factor 2-dependent ribosomal binding of N-formylmethionyl-transfer RNA without added guanosine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2770–2773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolarsky M., Tal M. Novel method for measuring polyuridylic acid binding to ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley W. M., Jr, Bock R. M. Isolation and physical properties of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1302–1311. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W. Ordered state of poly-uridylic acid above room temperature. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):585–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Aviram M., Kanarek A., Weiss A. Polyuridylic acid binding and translating by Escherichia coli ribosomes: stimulation by protein I, inhibition by aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 27;281(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C., van Alphen W., van Knippenberg P., Bosch L. Initiation factor-dependent binding of MS2 RNA to 30-S ribosomes and the recycling of IF-3. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):295–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Miller M. J., Niveleau A., Landers T. A., Carmichael G. G., Weber K., Hawley D. A., Slobin L. I. Subunit I of G beta replicase and 30 S ribosomal protein S1 of Escherichia coli. Evidence for the identity of the two proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3314–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., van Knippenberg P. H. Functional heterogeneity of the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. 3. Requirement of protein S1 for translation. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 25;84(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]