Abstract
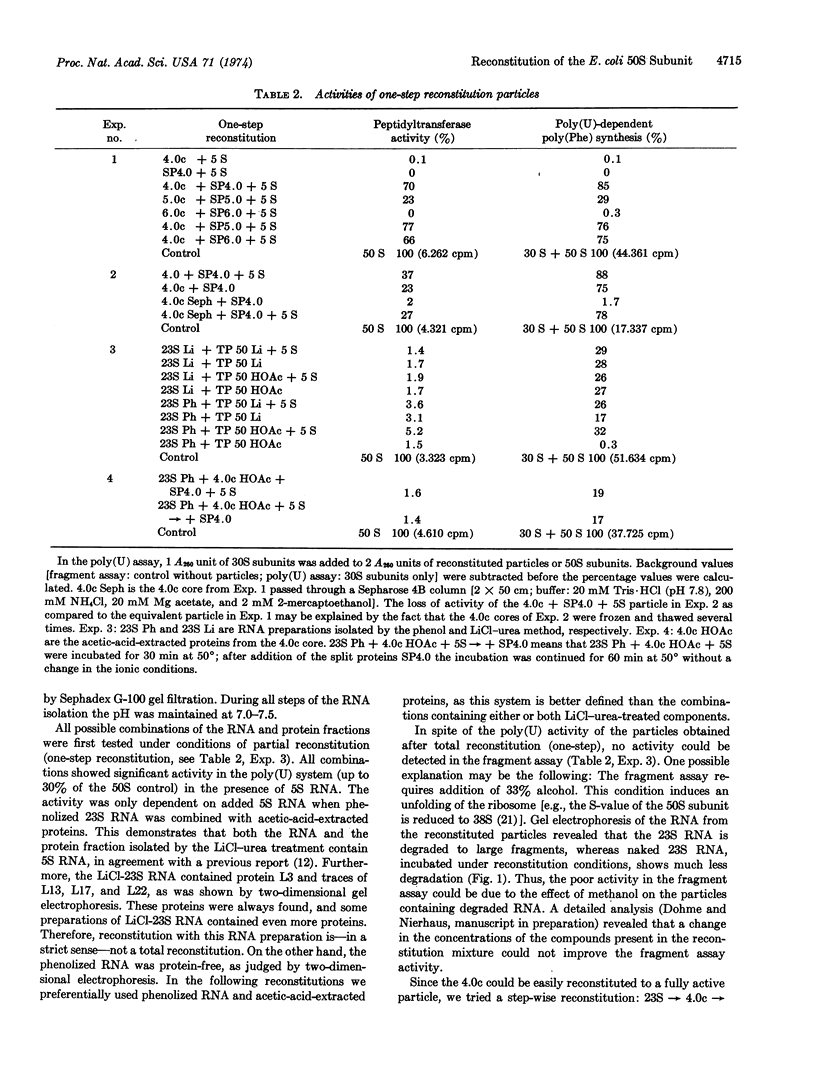
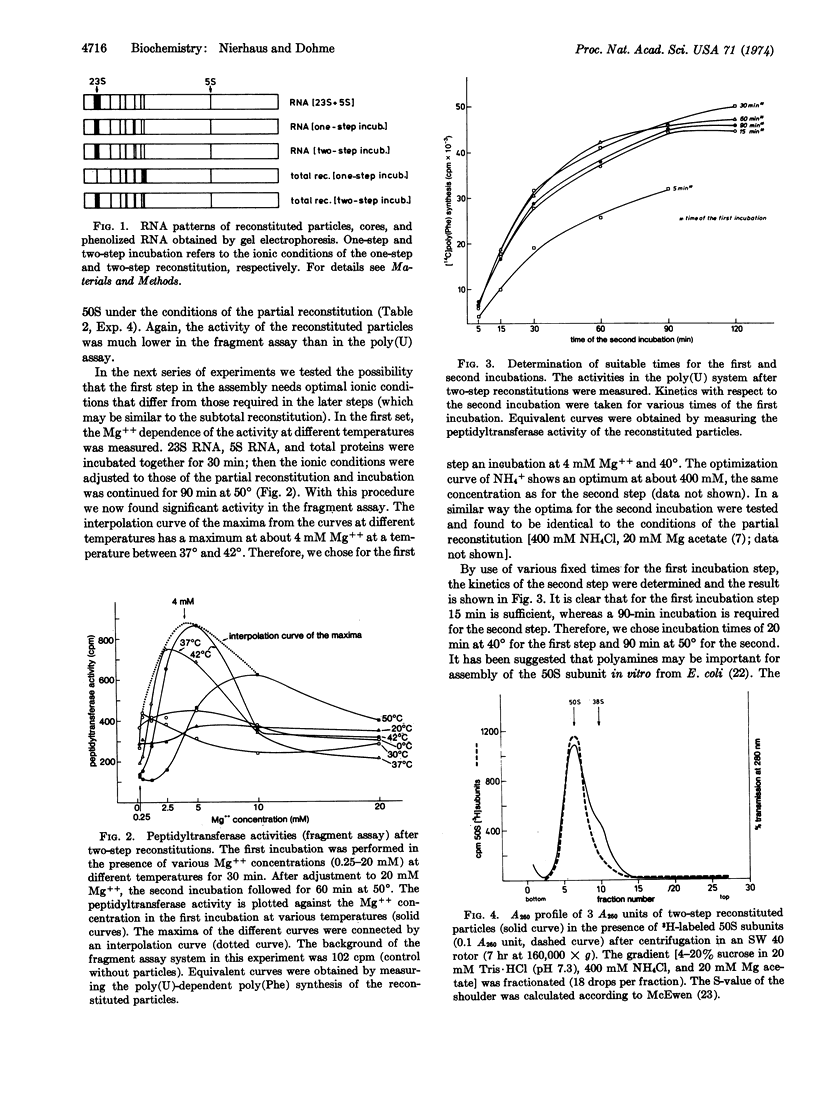
Total reconstitution of 50S subunits from E. coli was achieved by a two-step incubation procedure. In the first step, 23S RNA, 5S RNA, and the total proteins from 50S subunits were incubated for 20 min at 40° in the presence of 4 mM Mg++ and 400 mM NH4Cl. In the second step, the Mg++ concentration was raised to 20 mM and the incubation was performed for 90 min at 50°. No requirement for 30S subunits or other components (e.g., polyamine) was found. The reconstituted particle has the same sedimentation coefficient as the native 50S subunit and is highly active in protein synthesis with natural (R17 RNA) and artificial [poly(U)] messengers as well as in tests for peptidyltransferase (fragment assay) and for binding of antibiotics (chloramphenicol).
Keywords: peptidyltransferase, poly(U) system, natural messenger, chloramphenicol binding, “subtotal” reconstitution
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ceri H., Maeba P. Y. Association of a ribonuclease with the 50-S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli MRE 600. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 23;312(2):337–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maeba P. Y. Physical reconstitution of 23 S RNA-50 S protein complexes from Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):129–139. doi: 10.1139/o73-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Nierhaus K., Wittmann-Liebold B. Ribosomal proteins. XXII. Studies on the altered protein S5 from a spectinomycin-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Koka M., Nakamoto T. Requirement of an Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal protein component for effective interaction of the ribosome with T and G factors and with guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Mora G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2897–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann H. E., Nierhaus K. H. Ribosomal proteins. Protein compositions of biosynthetic precursors and artifical subparticles from ribosomal subunits in Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 28;20(2):249–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa K., Fujimura R. K., Nomura M. Reconstitution of functionally active ribosomes from inactive subparticles and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):198–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa K., Kiho Y., Migita L. K. Assembly of Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomes from ribonucleic acid and protein components. I. Chemical and physical factors affecting the conformation of assembled particles. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4135–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischa K., Möller W., Stöffler G. Reconstitution of a GTPase activity by a 50S ribosomal protein and E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio233062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcot-Queiroz J., Monier R. Les ribosomes d'Escherichia coli. II. Préparation de particules 18S et 25S par traitement des ribosomes au chlorure de lithium. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1967;49(5):477–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Tsuchiya T., Mizuno D. In vitro reassembly of functionally active 50 s ribosomal particles from ribosomal proteins and RNA's of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus D., Nierhaus K. H. Identification of the chloramphenicol-binding protein in Escherichia coli ribosomes by partial reconstitution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2224–2228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Bordasch K., Homann H. E. Ribosomal proteins. 43. In vivo assembly of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Montejo V. A protein involved in the peptidyltransferase activity of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1931–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Assembly of bacterial ribosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):864–873. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Erdmann V. A. Reconstitution of 50S ribosomal subunits from dissociated molecular components. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):744–748. doi: 10.1038/228744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Maglott D. M., Monro R. E. On the catalytic center of peptidyl transfer: a part of the 50 S ribosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:39–48. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Meselson M. In vitro recovery o ribosomes and of synthetic activity from synthetically inactive ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of E. coli ribosomes. V. Reconstitution of functionally active 30S ribosomal particles from RNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):777–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt J., Parmeggiani A. Action of methanol on the assocation of ribosomal subunits and its effect on the GTPase activity of elongation factor G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. S., Wittmann H. G. The structural basis for functional inactivity of reconstituted 50-S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 7;319(3):388–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]