Abstract
Alkylureas (methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, and butyl-) can inhibit both the gelation of deoxyhemoglobin S and red cell sickling without denaturation of the hemoglobin or intrinsic alteration of its oxygen affinity. This effect is directly proportional to the length of the alkyl chain and substantiates the importance of hydrophobic interactions in the polymerization of hemoglobin S. In addition, it opens the possibility that further systematic investigations with these compounds will help quantitate the role of hydrophobic interactions in this system so as to further our understanding of the polymerization of deoxyhemoglobin S.
Keywords: protein chemistry, sickling, gelation, hydrophobic interactions, sickle cell anemia
Full text
PDF
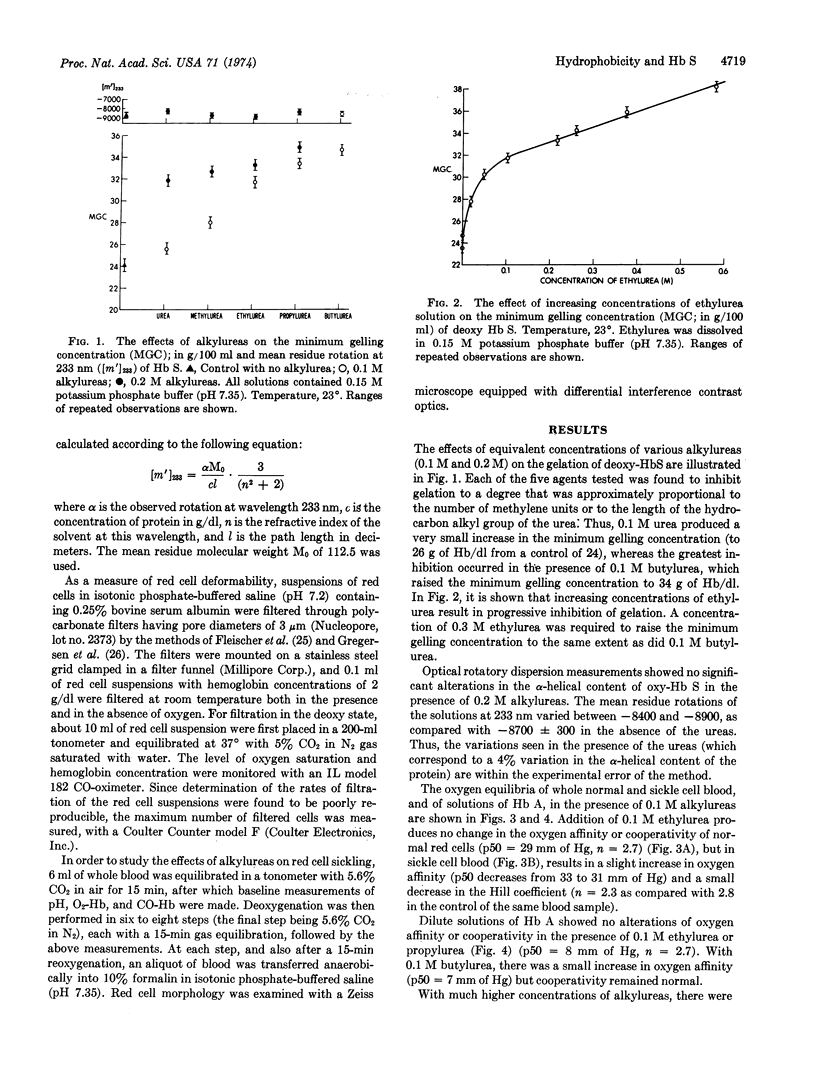
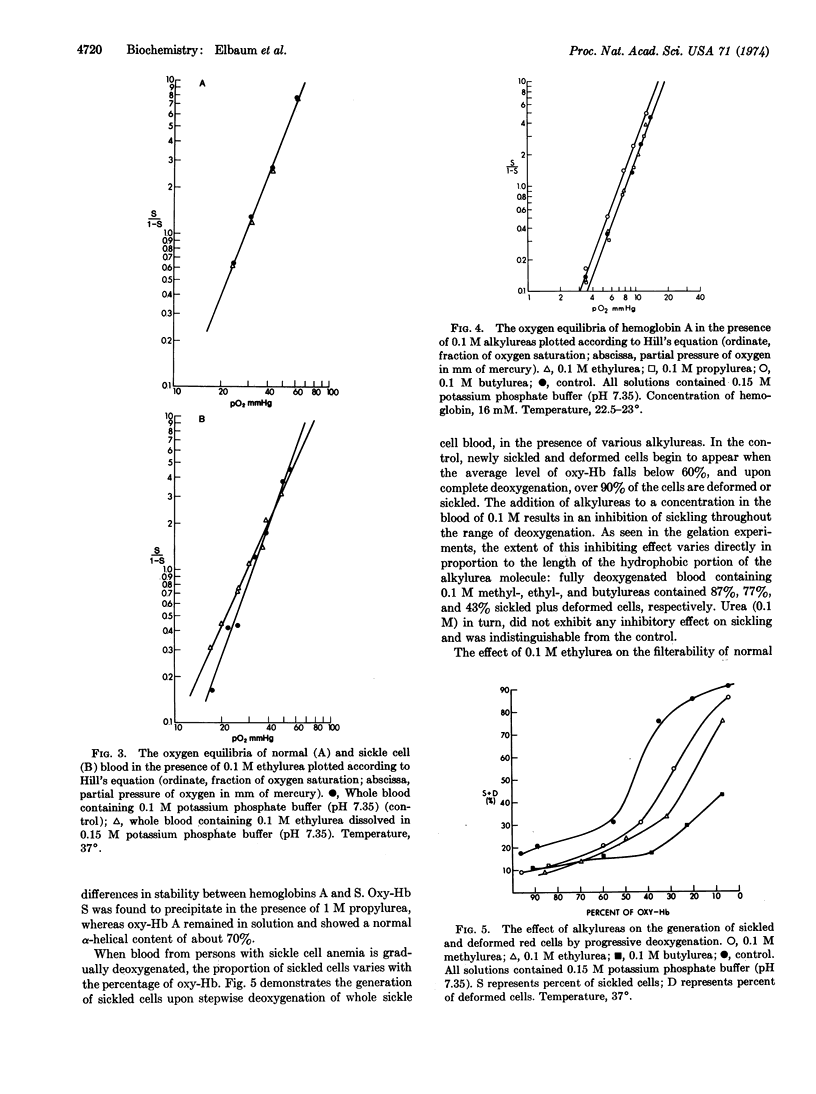


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN D. W., GUTHE K. F., WYMAN J., Jr Further studies on the oxygen equilibrium of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):393–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLEN D. W., WYMAN J., Jr Equilibre de l'hémoglobine de drépanocytose avec l'oxygène. Rev Hematol. 1954;9(2):155–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R., MACDUFF G., BENESCH R. E. DETERMINATION OF OXYGEN EQUILIBRIA WITH A VERSATILE NEW TONOMETER. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:81–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSIS M., NOMARSKI G., THIERY J. P., BRETON-GORIUS J. Etude sur la falciformation des globules rouges au microscope polarisant et au microscope électronique. II. L'intérieru du globule; comparaison avec les cristaux intra-globulaires. Rev Hematol. 1958 Apr-Jun;13(2):249–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcroft J., Hill A. V. The nature of oxyhaemoglobin, with a note on its molecular weight. J Physiol. 1910 Mar 8;39(6):411–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell R. Q., Oemijati S., Pribadi W., Weng M. I., Liu C. S. Hemoglobin G Makassar: beta-6 Glu leads to Ala. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):396–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Nagel R. L., Ranney H. M. The effect of beta 73 Asn on the interactions of sickling hemoglobins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 17;221(2):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briehl R. W., Ewert S. Effects of pH, 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and salts on gelation of sickle cell deoxyhemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 5;80(3):445–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Manning J. M. Potassium cyanate as an inhibitor of the sickling of erythrocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1180–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Luse S. A., Bryant C. A. Hemolysis during filtration through micropores: a scanning electron microscopic and hemorheologic correlation. Microvasc Res. 1971 Apr;3(2):183–203. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(71)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durocher J. R., Glader B. E., Gaines L. T., Conrad M. E. Effect of cyanate on erythrocyte deformability. Blood. 1974 Feb;43(2):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Telford J. N., Crepeau R. H. Structure of fibers of sickle cell hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaum D., Herskovits T. T. Dissociation of human hemoglobin by the ureas and amides. Osmotic pressure and light scattering studies. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 12;13(6):1268–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00703a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaum D., Pandolfelli E. R., Herskovits T. T. Denaturation of human and Glycera dibranchiata hemoglobins by the urea and amide classes of denaturants. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 12;13(6):1278–1284. doi: 10.1021/bi00703a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Perutz M. F., Bertles J. F., Döbler J. Structure of sickled erythrocytes and of sickle-cell hemoglobin fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer R. L., Price P. B., Walker R. M. Tracks of Charged Particles in Solids. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):383–393. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Weissmann G., Gorman B. D., Cunningham-Rundles W. Sickle hemoglobin gelation--inhibition by tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane and sugars. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Mar 15;22(6):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90399-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen M. I., Bryant C. A., Hammerle W. E., Usami S., Chien S. Flow Characteristics of Human Erythrocytes through Polycarbonate Sieves. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):825–827. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. W. Studies on the destruction of red blood cells. VIII. Molecular orientation in sickle cell hemoglobin solutions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Oct;75(1):197–201. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Hendricker D. G., Eaton W. A. Structure of hemoglobin S fibers: optical determination of the molecular orientation in sickled erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM V. M. A specific chemical difference between the globins of normal human and sickle-cell anaemia haemoglobin. Nature. 1956 Oct 13;178(4537):792–794. doi: 10.1038/178792a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURAYAMA M., OLSON R. A., JENNINGS W. H. MOLECULAR ORIENTATION IN HORSE HEMOGLOBIN CRYSTALS AND SICKLED ERYTHROCYTES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:194–199. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURAYAMA M. Titratable sulfhydryl groups of normal and sickle cell hemoglobins at O degrees and 38 degrees. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):231–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdoff-Fairchild B., Swerdlow P. H., Bertles J. F. Intermolecular organization of deoxygenated sickle haemoglobin determined by x-ray diffraction. Nature. 1972 Sep 22;239(5369):217–219. doi: 10.1038/239217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama M. Molecular mechanism of red cell "sickling". Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):145–149. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel R. L., Rieder R. F., Bookchin R. M., James G. W., 3rd Some functional properties of hemoglobin Leiden. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1240–1245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian R. M., Henry R. L., Barnhart M. I., Nichols B. M., Camp F. R., Jr, Wolf P. L. Sickling reversed and blocked by urea in invert sugar. Am J Pathol. 1971 Aug;64(2):405–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS A. The metamorphosis of hemoglobin in the bullfrog. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Sep;35(1):23–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI-FANELLI A., ANTONINI E. Studies on the oxygen and carbon monoxide equilibria of human myoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Oct;77(2):478–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., SINGER L. Studies on abnormal hemoglobins. VIII. The gelling phenomenon of sickle cell hemoglobin: its biologic and diagnostic significance. Blood. 1953 Nov;8(11):1008–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Feig S. A., Mentzer W. C., McCaffrey R. P., Wells R., Bunn H. F., Shohet S. B., Nathan D. G. Effects of urea and cyanate on sickling in vitro. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 13;287(2):59–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207132870201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. The fine structure of sickled hemoglobin in situ. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):561–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr Concerted formation of the gel of hemoglobin S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1506–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


