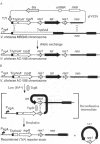
Abstract
An understanding of the patterns of gene expression in response to specific environmental signals can yield insight into a variety of complex biological systems such as microbial-host interactions, developmental cycles, cellular differentiation, ontogeny, etc. To extend the utility of the reporter gene fusion approach to such studies, we have constructed a gene expression reporter cassette that permits the generation of transcriptional fusions to tnpR encoding resolvase, a site-specific recombinase of the transposable element gamma delta. Induction of the transcriptional fusions results in production of resolvase, which in turn, catalyzes excision of a linked tetracycline-resistance reporter gene flanked by direct repeats of res, the DNA sequences at which resolvase functions. The loss of tetracycline resistance in descendant bacteria serves as a permanent and heritable marker of prior gene expression. This gene fusion approach will allow us to assay the induction of gene expression in as few as one cell. Additionally, gene expression can be assayed at a later time and/or different place from the inducing environment facilitating the study of gene expression in complex environments such as animal tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin H. W., Matzuk M. M., Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Recombination site selection by Tn3 resolvase: topological tests of a tracking mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. E., Barton J. C. Factors affecting iron balance. Am J Hematol. 1981;10(2):199–225. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830100212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Sciortino C. V., McIntosh M. A. Role of iron in microbe-host interactions. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S759–S777. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
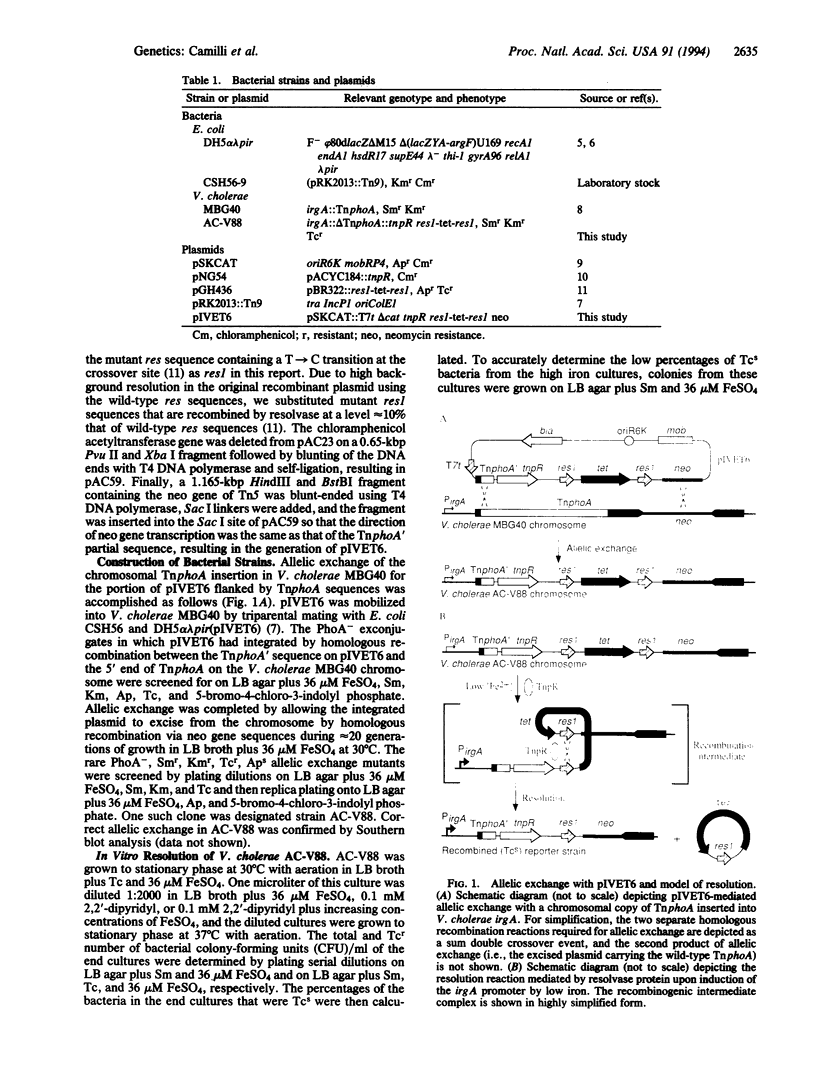
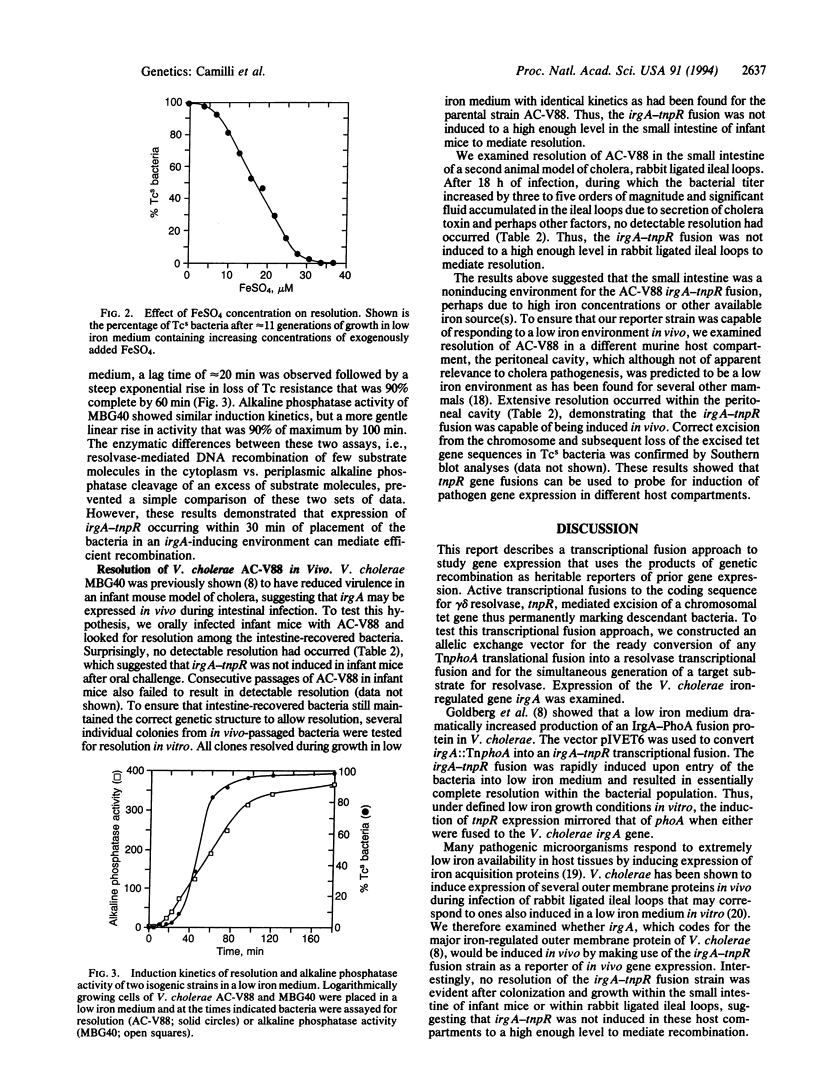
- Goldberg M. B., DiRita V. J., Calderwood S. B. Identification of an iron-regulated virulence determinant in Vibrio cholerae, using TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.55-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Humphreys J., Leach A., Scanlon L. Alterations in the tRNA's of Escherichia coli recovered from lethally infected animals. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):312–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.312-317.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Trans-complementation-dependent replication of a low molecular weight origin fragment from plasmid R6K. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan M. J., Slauch J. M., Mekalanos J. J. Selection of bacterial virulence genes that are specifically induced in host tissues. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.8430319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B. J., Grindley N. D. Mutants of the gamma delta resolvase: a genetic analysis of the recombination function. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90501-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Shibuya G. I., Steitz J. A. Nucleotide sequence of gamma delta resolvase gene and demonstration that its gene product acts as a repressor of transcription. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):381–383. doi: 10.1038/300381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. Roles of motility and flagellar structure in pathogenicity of Vibrio cholerae: analysis of motility mutants in three animal models. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2727–2736. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2727-2736.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciortino C. V., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae expresses iron-regulated outer membrane proteins in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.990-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slauch J. M., Silhavy T. J. Genetic fusions as experimental tools. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:213–248. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. M., Grindley N. D., Hatfull G. F., Boocock M. R. Resolvase-catalysed reactions between res sites differing in the central dinucleotide of subsite I. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3541–3548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojiljkovic I., Cobeljic M., Hantke K. Escherichia coli K-12 ferrous iron uptake mutants are impaired in their ability to colonize the mouse intestine. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Mar 15;108(1):111–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]