Abstract
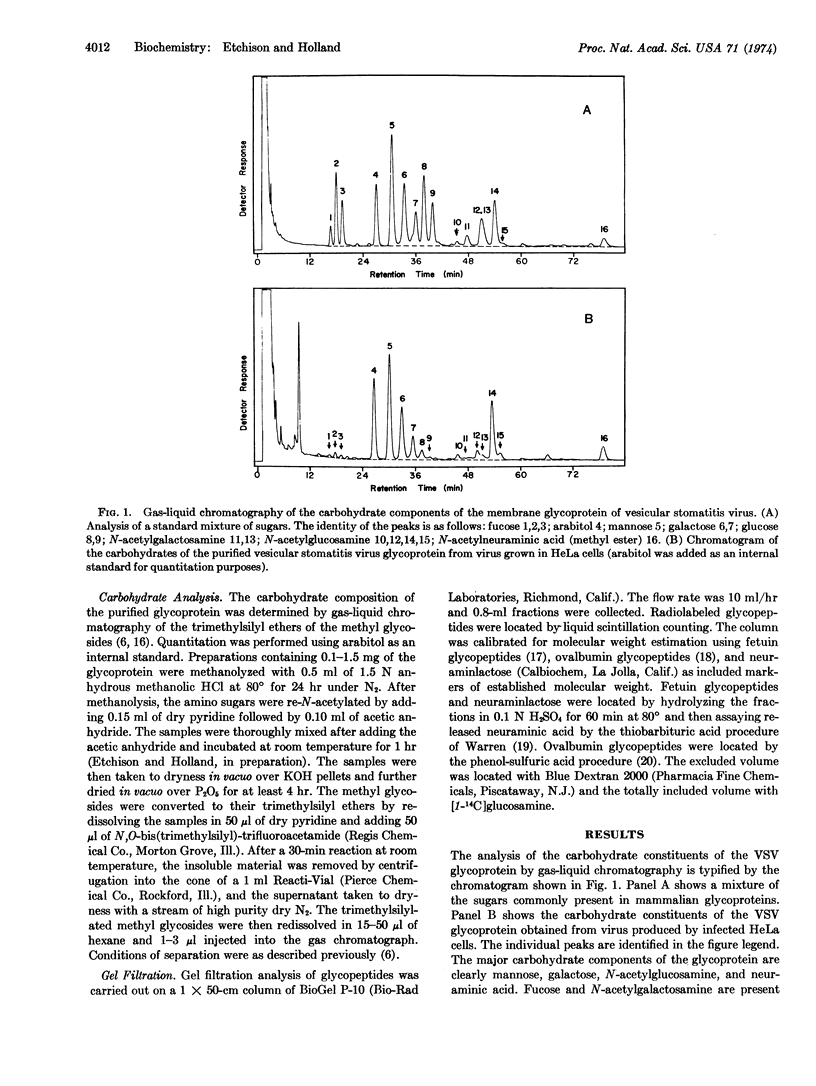
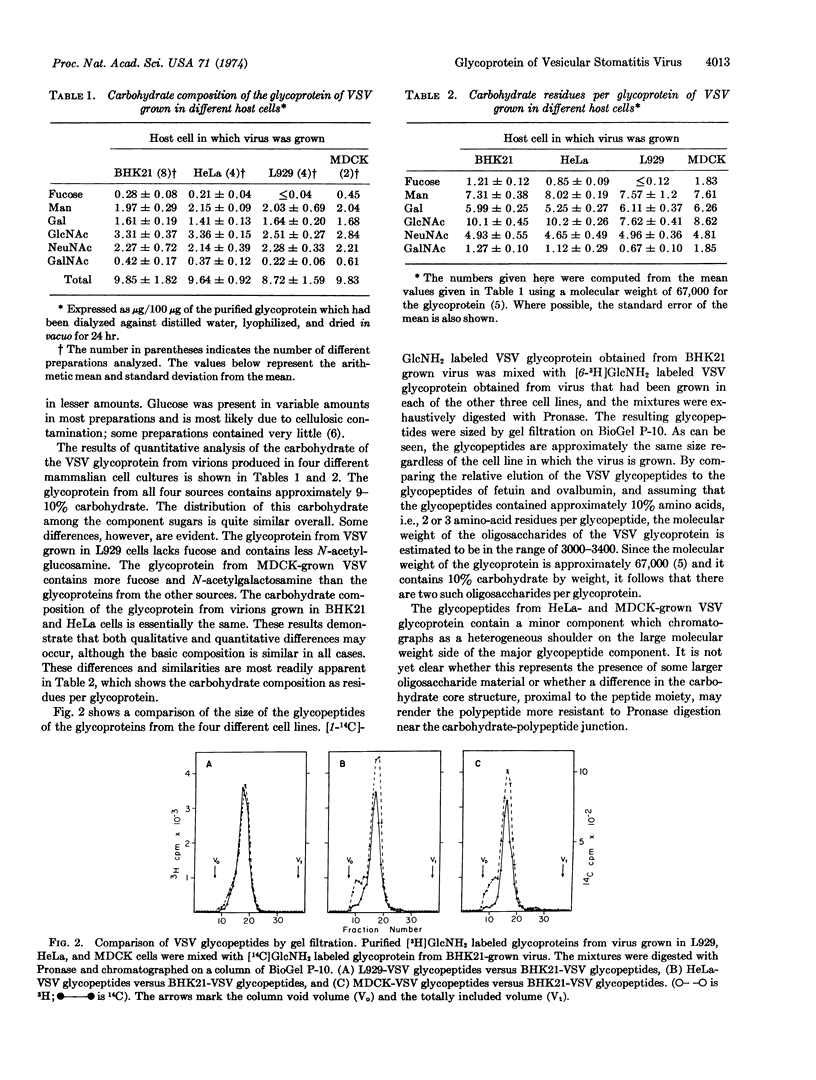
The carbohydrate composition of the membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus has been determined for virus grown in four different mammalian cell lines. The glycoprotein contains mannose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, and neuraminic acid as the major carbohydrate components, whereas N-acetyl-galactosamine and fucose are present in lesser amounts. The glycoprotein contains approximately 9-10% carbohydrate regardless of the host cell in which it is synthesized. Small quantitative differences are evident in the composition of the component sugars of the glycoprotein when the virus is grown in different host cells, and the glycoprotein of virus grown in a mouse fibroblast line (L cells) lacks fucose. The major oligosaccharide moieties of the virus glycoprotein from all cells are approximately the same size (3000-3400 daltons). The data presented here, in conjunction with previous data, indicate that the viral glycoprotein contains two major oligosaccharide constituents regardless of the host cell in which it is synthesized.
Keywords: enveloped RNA viruses, glycopeptides, glycoprotein glycosylation
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burge B. W., Huang A. S. Comparison of membrane protein glycopeptides of Sindbis virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):176–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.176-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Bhatti T., Chambers R. E. The determination of carbohydrate in biological materials by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:229–344. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison J. R., Holland J. J. Carbohydrate composition of the membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWATSON A. F., WHITMORE G. F. The development and structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1962 Apr;16:466–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian A., Westall F. C., Whitehead J. S., Eylar E. H. Glycosylation of the A1 protein from myelin by a polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. Identification of the receptor sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2519–2523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycolipid content of vesicular stomatitis virus grown in baby hamster kidney cells. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):416–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.416-417.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Keller J., Baenziger J., Kornfeld S. The structure of the glycopeptide of human gamma G myeloma proteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3259–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Carbohydrate composition of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):412–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.412-415.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Summers D. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein alterations induced by host cell transformation. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO R. G. Studies on fetuin, a glycoprotein of fetal serum. II. Nature of the carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:382–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox H. C., Jr, Hood L. Attachment of carbohydrate to the variable region of myeloma immunoglobulin light chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):975–982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Abel C. A., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Localization of the carbohydrate within the variable region of light and heavy chains of human gamma g myeloma proteins. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 13;9(21):4217–4223. doi: 10.1021/bi00823a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. A., Snyder R. M. Structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):395–403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.395-403.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zee Y. C., Hackett A. J., Talens L. Vesicular stomatitis virus maturation sites in six different host cells. J Gen Virol. 1970;7(2):95–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-7-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


