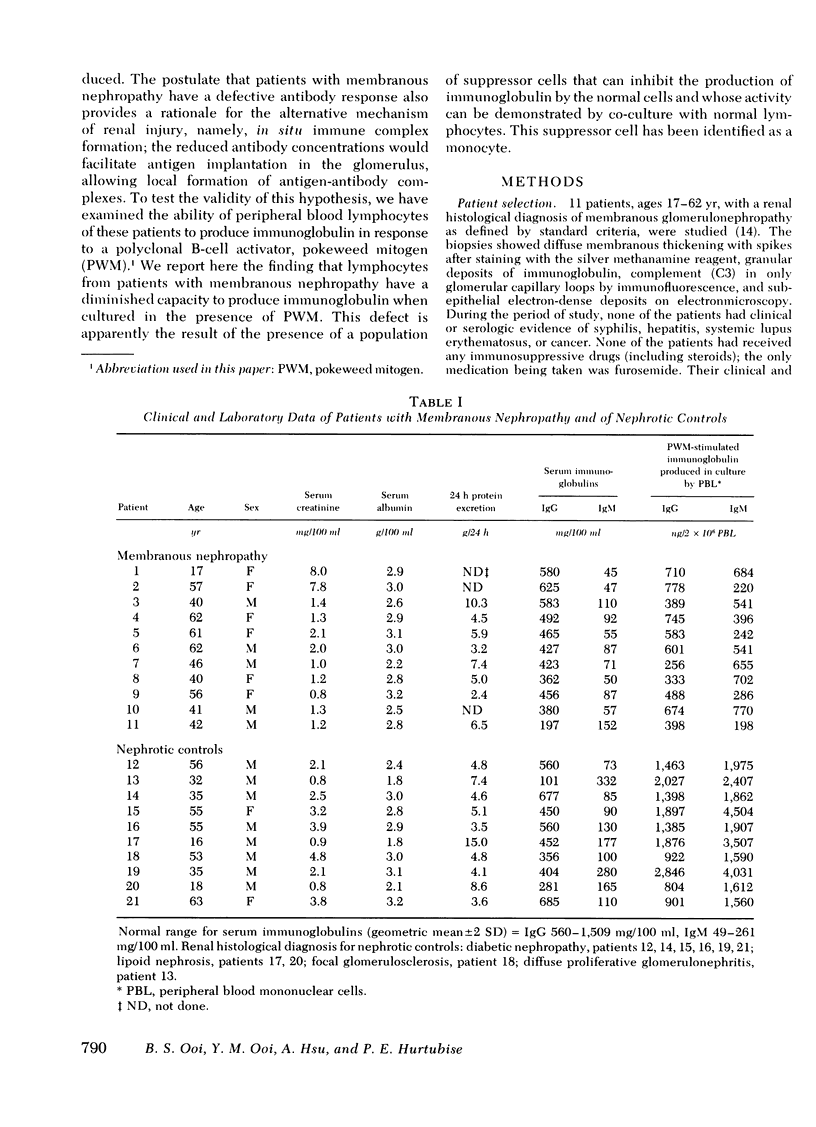
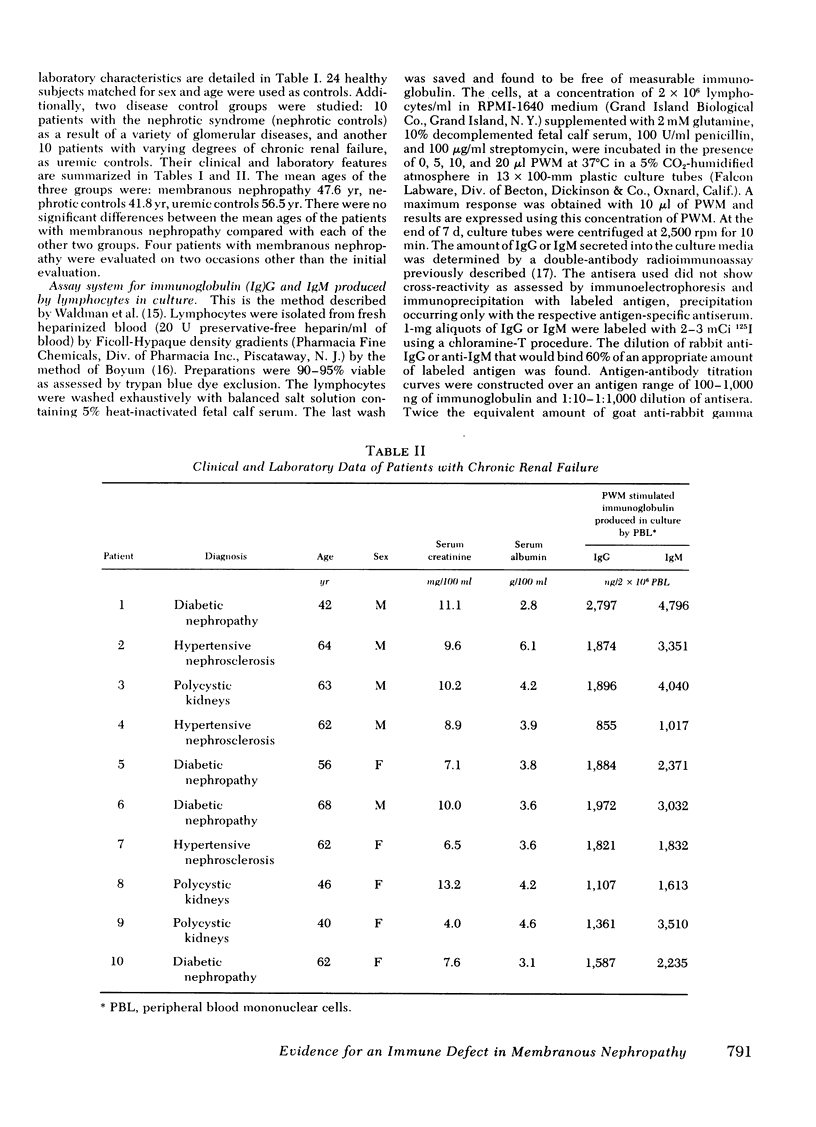
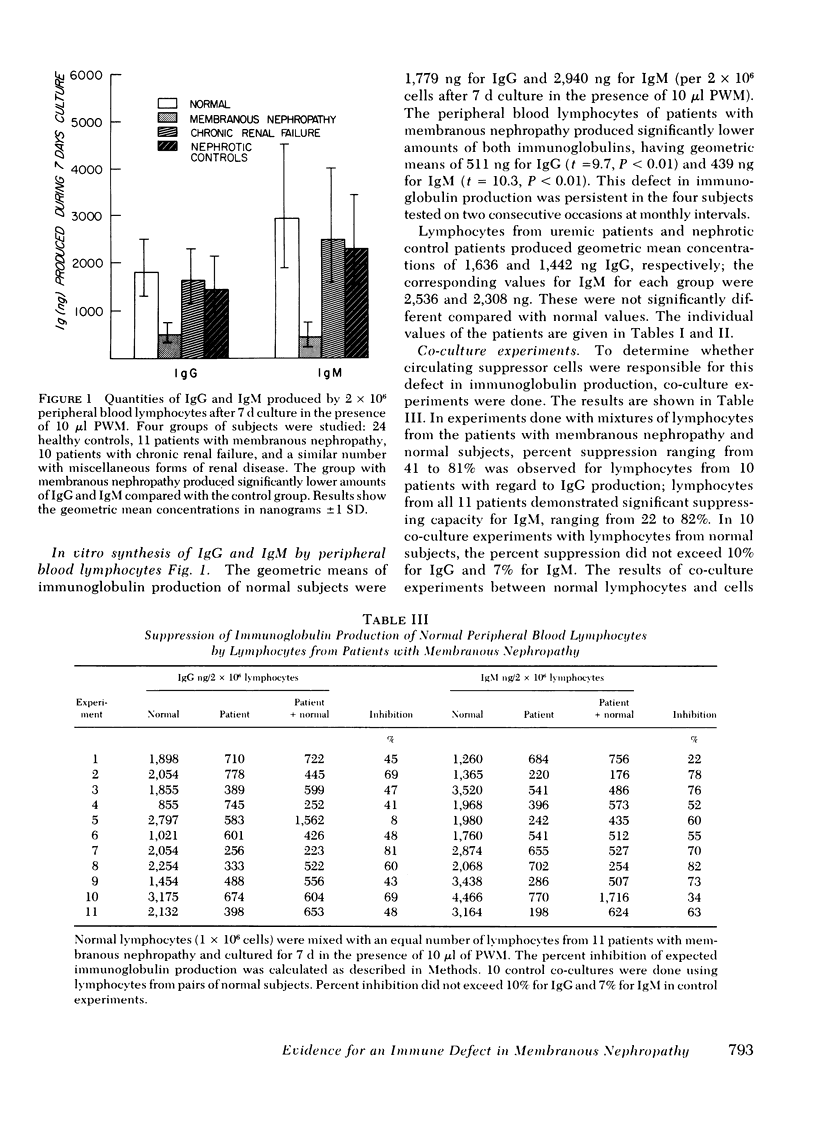
Abstract
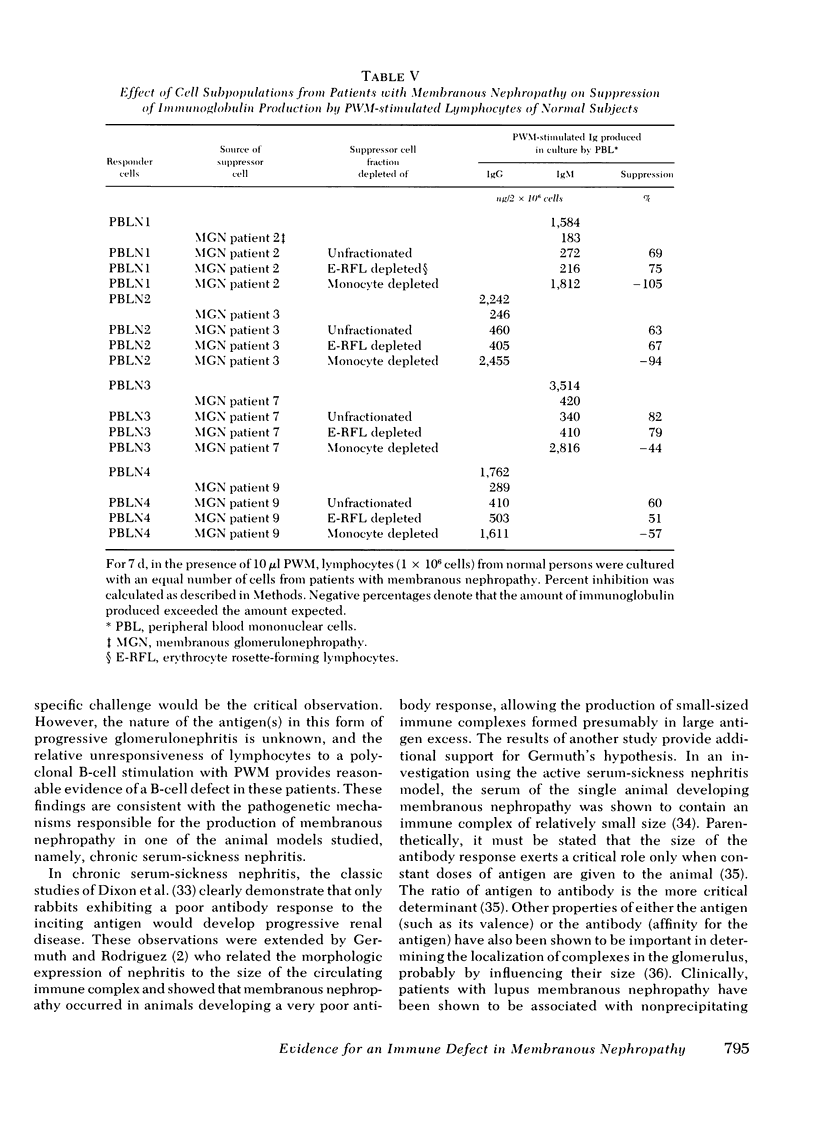
Some studies of animal models of serum-sickness nephritis have shown that the lesions of membranous nephropathy develop in animals exhibiting a poor antibody response to the administered antigen (if given in constant amounts). It is postulated that patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy may share a similar characteristic, namely, a diminished capacity to produce sufficient amounts of antibody. To test this hypothesis, we examined the ability of lymphocytes isolated from 11 patients with this disorder to produce immunoglobulin (Ig)G and IgM on stimulation with a polyclonal B-cell activator, pokeweed mitogen. The peripheral blood lymphocytes (2 x 10(6) cells) from 24 normal individuals had geometric mean production rates of 1,779 ng for IgG, and 2,940 ng for IgM after 7 d of culture in the presence of pokeweed mitogen. By contrast, under identical conditions, lymphocytes from the 11 patients with membranous nephropathy produced significantly lower quantities of both immunoglobulins, with geometric mean concentrations of 511 ng for IgG and 439 ng for IgM. When lymphocytes from patients with membranous nephropathy were co-cultured with normal lymphocytes, the production of immunoglobulin by normal lymphocytes was depressed by 22-82%, suggesting that a population of suppressor cells was responsible for this disturbance in B-cell function. By co-culturing normal lymphocytes with patient lymphocytes depleted of either T cells or monocytes, the suppressor cell was identified as a monocyte.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Mechanisms by which activated macrophages inhibit lymphocyte responses. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:3–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Koffler D. Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):185–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. S., Kim Y., Michael A. F., Donadio J. V. Pathogenesis of membranous nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible role of nonprecipitating DNA antibody. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 1;1(6052):25–25. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6052.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. S., Michael A. F. Hypothesis: immunologic rationale for the therapy of membranous lupus nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 May;10(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrod H. G., Buckley R. H. Use of a human plaque-forming cell assay to study peripheral blood bursa-equivalent cell activation and excessive suppressor cell activity in humoral immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):868–876. doi: 10.1172/JCI109386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Fournié G. J., Türler H., Miescher P. A. Features of systemic lupus erythematosus in mice injected with bacterial lipopolysaccharides: identificantion of circulating DNA and renal localization of DNA-anti-DNA complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1115–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for a local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):428–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Fauci A. S. Inhibition of polyclonal B-cell activation by suppressor monocytes in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jun;32(3):554–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama A., Niwa Y., Shigematsu H., Taniguchi M., Tada T. Studies on passive serum sickness. II. Factors determining the localization of antigen-antibody complexes in the murine renal glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1978 Mar;38(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T. The value of immunofluorescence in the study of human renal disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):242s–255s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi Y. M., Ooi B. S., Pollak V. E. Relationship of levels of circulating immune complexes to histologic patterns of nephritis: a comparative study of membranous glomerulonephropathy and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Nov;90(5):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi Y. M., Ooi B. S., Vallota E. H., First M. R., Pollak V. E. Circulating immune complexes after renal transplantation. Correlation of increased 125I-Clq binding activity with acute rejection characterized by fibrin deposition in the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):611–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI108812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi Y. M., Vallota E. H., West C. D. Serum immune complexes in membranoproliferative and other glomerulonephritides. Kidney Int. 1977 Apr;11(4):275–283. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglieroni T., MacKenzie M. R. Studies on the pathogenesis of an immune defect in multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1120–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI108736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Haberkern R., Christian C. L. Experimental chronic glomerulitis. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):819–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Feldhaus J., Robins R. A. Single step separation of human T and B cells using AET treated srbc rosettes. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(3-4):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. A., Choi Y. S., Shou L., Good R. A. Modulatory effects on immunoglobulin synthesis and secretion by lymphocytes from immunodeficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1176–1187. doi: 10.1172/JCI108742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M., Good R. A. Suppression of B-cell differentiation by leukocytes from hypogammaglobulinemic patients. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):109–122. doi: 10.1172/JCI108439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., Woodroffe A. J., Ahlin T. D., Williams R. C., Jr, Wilson C. B. Application of the solid phase C1q and Raji cell radioimmune assays for the detection of circulating immune complexes in glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):61–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI109115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Foldes M., McKenzie P. E., Thompson A. J., Seymour A. E., Clarkson A. R. Serum immune complexes and disease. Aust N Z J Med. 1979 Apr;9(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1979.tb04315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. Y., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Differentiation capacity of cultured B lymphocytes from immunodeficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3180–3189. doi: 10.1172/JCI107518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


