Abstract
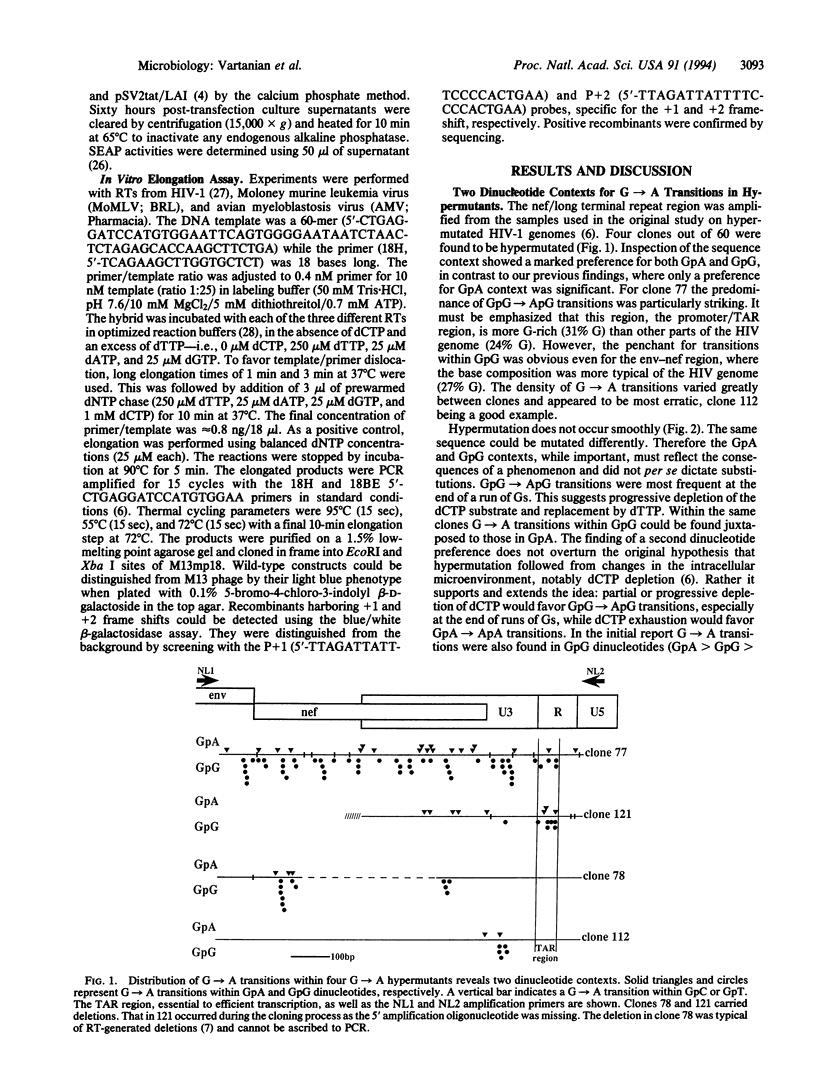
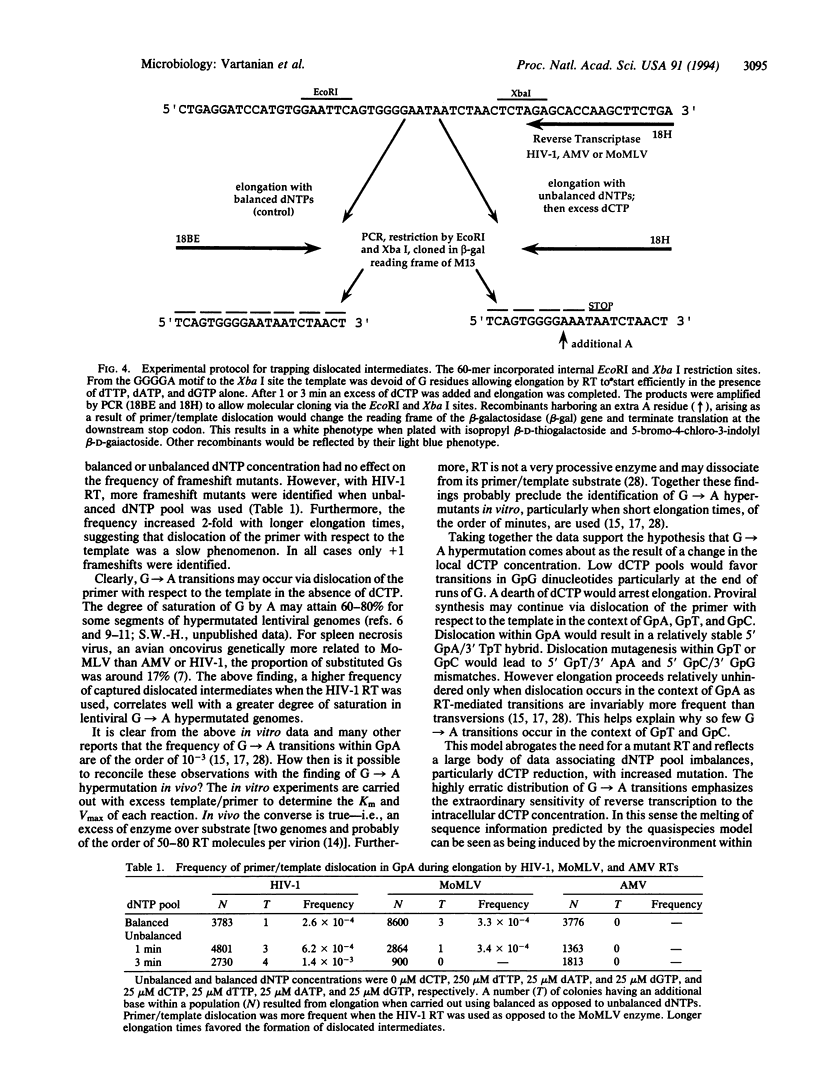
The quasispecies model for RNA viruses predicts the existence of a replication error threshold beyond which there is a melting or total loss of sequence information. Retroviral G-->A hypermutation is probably an example. Here it is shown that G-->A transitions may occur in both GpG and GpA dinucleotide contexts. Transitions in GpG preferentially occur via base mispairing at the ends of runs of G residues, whereas G-->A transitions within GpA may result from temporary dislocation of the primer and template strands by a single base. The two circumstances may be related by the local dCTP substrate concentration. An in vitro elongation assay shows that primer/template dislocation is more frequent for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase than for murine or avian retroviral enzymes. Taken together these data suggest that G-->A hypermutation is an example of induced mutation whereby the viral reverse transcriptase is forced into making errors by imbalances in the intracellular dCTP concentration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H., Cattaneo R., Billeter M. A. Biased hypermutation of viral RNA genomes could be due to unwinding/modification of double-stranded RNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):331–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Roberts J. D., Kunkel T. A. The effects of dNTP pool imbalances on frameshift fidelity during DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3589–3596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Eschle D., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Billeter M. A. Biased hypermutation and other genetic changes in defective measles viruses in human brain infections. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90048-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delassus S., Cheynier R., Wain-Hobson S. Evolution of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef and long terminal repeat sequences over 4 years in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):225–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.225-231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Yue L., White A. T., Pappas P. G., Barchue J., Hanson A. P., Greene B. M., Sharp P. M., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Human infection by genetically diverse SIVSM-related HIV-2 in west Africa. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):495–499. doi: 10.1038/358495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M., Huet T., Saurin W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Wain-Hobson S. HIV-1 isolates are rapidly evolving quasispecies: evidence for viral mixtures and preferred nucleotide substitutions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Hamm T. E., Goldstein S., Kitov S., Hirsch V. M. The genetic fate of molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus in experimentally infected macaques. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Alexander P. S. The base substitution fidelity of eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Mispairing frequencies, site preferences, insertion preferences, and base substitution by dislocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Biological asymmetries and the fidelity of eukaryotic DNA replication. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):303–308. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz B. A., Kohalmi S. E. Modulation of mutagenesis by deoxyribonucleotide levels. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:339–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Merges M. J., Dembo M., Spouge J. L., Conley S. R., Moore J. P., Raina J. L., Renz H., Gelderblom H. R., Nara P. L. Factors underlying spontaneous inactivation and susceptibility to neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):695–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90593-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K., Ji J. DNA precursor asymmetries, replication fidelity, and variable genome evolution. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):295–301. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M. The molecular basis of mutations induced by deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pool imbalances in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Cheynier R., Albert J., Seth M., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Temporal fluctuations in HIV quasispecies in vivo are not reflected by sequential HIV isolations. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Vartanian J. P., Hultgren C., Plikat U., Karlsson A., Wang L., Eriksson S., Wain-Hobson S. Restriction and enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by modulation of intracellular deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):535–540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.535-540.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara P. J., Nichol S. T., Horodyski F. M., Holland J. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particles can contain extensive genomic sequence rearrangements and base substitutions. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: deletions and deletions with insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6024–6028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. T., Flaherty M. T., Kelley M. J., Clabough D. L., Tronick S. R., Coggins L., Whetter L., Lengel C. R., Fuller F. The surface envelope protein gene region of equine infectious anemia virus is not an important determinant of tropism in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4085–4097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4085-4097.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phear G., Nalbantoglu J., Meuth M. Next-nucleotide effects in mutations driven by DNA precursor pool imbalances at the aprt locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4450–4454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Poiesz B. J., Loeb L. A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.2460924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricchetti M., Buc H. Reverse transcriptases and genomic variability: the accuracy of DNA replication is enzyme specific and sequence dependent. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1583–1593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Howell M. L., Wang Y., Mathews C. K. Deoxyadenosine reverses hydroxyurea inhibition of vaccinia virus growth. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2290–2298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2290-2298.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian J. P., Meyerhans A., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Selection, recombination, and G----A hypermutation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1779–1788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1779-1788.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 quasispecies in vivo and ex vivo. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;176:181–193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77011-1_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



