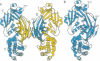Abstract
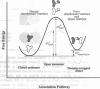
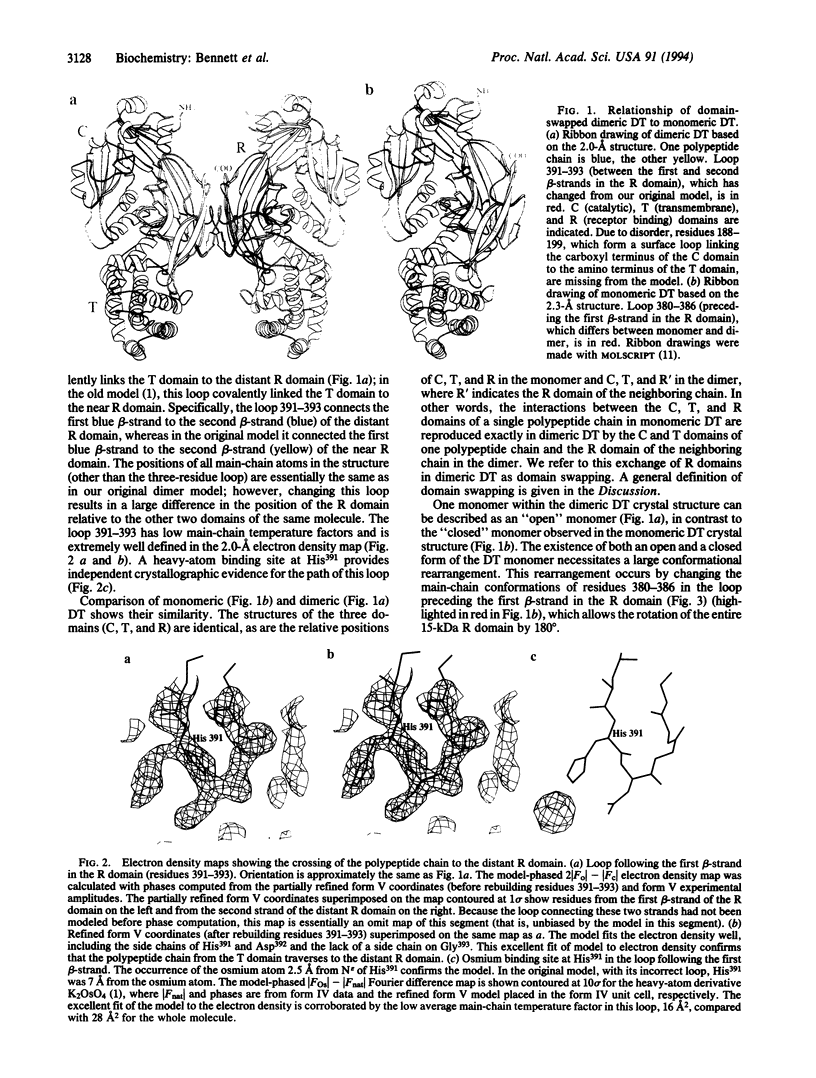
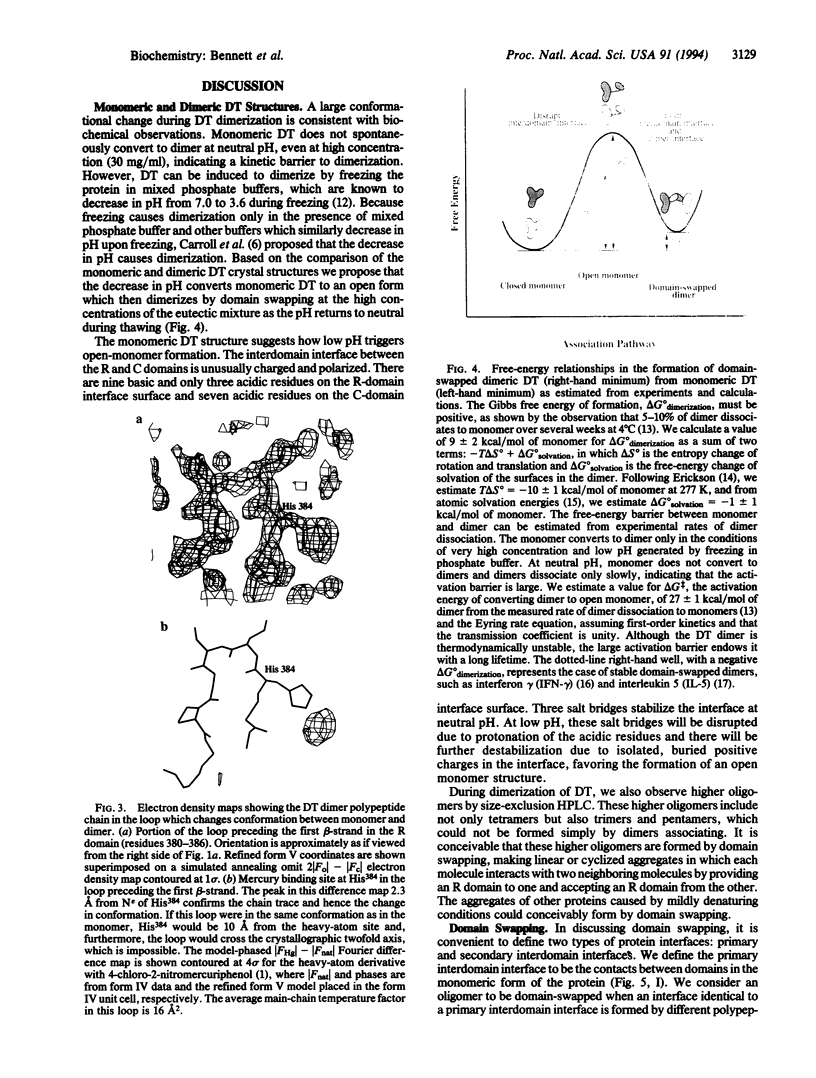
The comparison of monomeric and dimeric diphtheria toxin (DT) reveals a mode for protein association which we call domain swapping. The structure of dimeric DT has been extensively refined against data to 2.0-A resolution and a three-residue loop has been corrected as compared with our published 2.5-A-resolution structure. The monomeric DT structure has also been determined, at 2.3-A resolution. Monomeric DT is a Y-shaped molecule with three domains: catalytic (C), transmembrane (T), and receptor binding (R). Upon freezing in phosphate buffer, DT forms a long-lived, metastable dimer. The protein chain tracing discloses that upon dimerization an unprecedented conformational rearrangement occurs: the entire R domain from each molecule of the dimer is exchanged for the R domain from the other. This involves breaking the noncovalent interactions between the R domain and the C and T domains, rotating the R domain by 180 degrees with atomic movements up to 65 A, and re-forming the same noncovalent interactions between the R domain and the C and T domains of the other chain of the dimer. This conformational transition explains the long life and metastability of the DT dimer. Several other intertwined, dimeric protein structures satisfy our definition of domain swapping and suggest that domain swapping may be the molecular mechanism for evolution of these oligomers and possibly of oligomeric proteins in general.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almassy R. J., Janson C. A., Hamlin R., Xuong N. H., Eisenberg D. Novel subunit-subunit interactions in the structure of glutamine synthetase. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):304–309. doi: 10.1038/323304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Krukowski A., Erickson J. W. Slow-cooling protocols for crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing. Acta Crystallogr A. 1990 Jul 1;46(Pt 7):585–593. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390002355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. On the aggregation of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Barbieri J. T., Collier R. J. Dimeric form of diphtheria toxin: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2425–2430. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Barbieri J. T., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: purification and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:68–76. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe S., Bennett M. J., Fujii G., Curmi P. M., Kantardjieff K. A., Collier R. J., Eisenberg D. The crystal structure of diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):216–222. doi: 10.1038/357216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Westbrook E. M., McKay D. B., Eisenberg D. X-ray grade crystals of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5283–5285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curmi P. M., Cascio D., Sweet R. M., Eisenberg D., Schreuder H. Crystal structure of the unactivated form of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from tobacco refined at 2.0-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16980–16989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederichs K., Boone T., Karplus P. A. Novel fold and putative receptor binding site of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1779–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1837174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealick S. E., Cook W. J., Vijay-Kumar S., Carson M., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P., Bugg C. E. Three-dimensional structure of recombinant human interferon-gamma. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):698–702. doi: 10.1126/science.1902591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., McLachlan A. D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):199–203. doi: 10.1038/319199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. Co-operativity in protein-protein association. The structure and stability of the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fita I., Rossmann M. G. The active center of catalase. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):21–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Crestfield A. M. On the structure of ribonuclease dimer. Isolation and identification of monomers derived from inactive carboxymethyl dimers. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3875–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii G., Choe S. H., Bennett M. J., Eisenberg D. Crystallization of diphtheria toxin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 20;222(4):861–864. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90577-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Miller S., Chothia C. Surface, subunit interfaces and interior of oligomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus P. A., Schulz G. E. Refined structure of glutathione reductase at 1.54 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):701–729. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapatto R., Nalini V., Bax B., Driessen H., Lindley P. F., Blundell T. L., Slingsby C. High resolution structure of an oligomeric eye lens beta-crystallin. Loops, arches, linkers and interfaces in beta B2 dimer compared to a monomeric gamma-crystallin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 20;222(4):1067–1083. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90594-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella L., Capasso S., Demasi D., Di Lorenzo G., Mattia C. A., Zagari A. Bovine seminal ribonuclease: structure at 1.9 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Jul 1;49(Pt 4):389–402. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Hassell A. M., Lambert M. H., Jordan S. R., Proudfoot A. E., Graber P., Wells T. N. A novel dimer configuration revealed by the crystal structure at 2.4 A resolution of human interleukin-5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):172–176. doi: 10.1038/363172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. The structure of interfaces between subunits of dimeric and tetrameric proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 Nov;3(2):77–83. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.2.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morize I., Surcouf E., Vaney M. C., Epelboin Y., Buehner M., Fridlansky F., Milgrom E., Mornon J. P. Refinement of the C222(1) crystal form of oxidized uteroglobin at 1.34 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):725–739. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Gerstein A. S., Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated entry of diphtheria toxin into monkey kidney (Vero) cells: electron microscopic evaluation. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):721–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.721-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Metherall J. E., Russell D. W., Eidels L. Expression cloning of a diphtheria toxin receptor: identity with a heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor precursor. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90623-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli R., Tamburrini M., Piccialli G., Di Donato A., Parente A., D'Alessio G. The dual-mode quaternary structure of seminal RNase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1870–1874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Sigler P. B. The three-dimensional structure of trp repressor. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):782–786. doi: 10.1038/317782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider G., Lindqvist Y., Brändén C. I., Lorimer G. Three-dimensional structure of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum at 2.9 A resolution. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3409–3415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda T., Shimazu T., Matsuda S., Kawano G., Shimizu H., Nakamura K. T., Mitsui Y. Three-dimensional crystal structure of recombinant murine interferon-beta. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3193–3201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. J., Muirhead H. The active site of glucose phosphate isomerase. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 15;65(1):50–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80619-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DEN BERG L., ROSE D. Effect of freezing on the pH and composition of sodium and potassium phosphate solutions; the reciprocal system KH2PO4-Na2-HPO4-H2O. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Apr;81(2):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valegård K., Liljas L., Fridborg K., Unge T. The three-dimensional structure of the bacterial virus MS2. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):36–41. doi: 10.1038/345036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Bott R., Sjölin L. The refined crystal structure of ribonuclease A at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1325–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]