Abstract
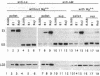
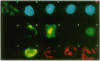
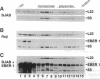
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), an oncogenic herpesvirus, encodes two small RNAs (EBERs) that are expressed at high levels during latent transformation of human B lymphocytes. Here we report that a 15-kDa cellular protein called EAP (for EBER associated protein), previously shown to bind EBER1, is in fact the ribosomal protein L22. Approximately half of the L22 in EBV-positive cells is contained within the EBER1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particle, whereas the other half residues in monoribosomes and polysomes. Immunofluorescence with anti-L22 antibodies demonstrates that L22 is localized in the cytoplasm and the nucleoli of uninfected human cells, as expected, whereas EBV-positive lymphocytes also show strong nucleoplasmic staining. In situ hybridization indicates that the EBER RNPs are predominantly nucleoplasmic, suggesting that L22 relocalization correlates with binding to EBER1 in vivo. Since incubation of uninfected cell extracts with excess EBER1 RNA does not remove L22 from preexisting ribosomes, in vivo binding of L22 by EBER1 may precede ribosome assembly. The gene encoding L22 has recently been identified as the target of a chromosomal translocation in certain patients with leukemia, suggesting that L22 levels may be a determinant in cell transformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Construction and analysis of additional adenovirus substitution mutants confirm the complementation of VAI RNA function by two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J. The small RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Feb;17(2):81–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00996215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Takasaki Y., Tan E. M. Nonhistone nuclear antigens reactive with autoantibodies. Immunofluorescence studies on distribution in synchronized cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):654–660. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. M., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Ridley A., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Willard H. F., Bieber F. R., Page D. C. Homologous ribosomal protein genes on the human X and Y chromosomes: escape from X inactivation and possible implications for Turner syndrome. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1205–1218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90416-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan K., Rajadurai P., Resnick L., Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus small nuclear RNAs are not expressed in permissively infected cells in AIDS-associated leukoplakia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harte W. E., Jr, Swaminathan S., Mansuri M. M., Martin J. C., Rosenberg I. E., Beveridge D. L. Domain communication in the dynamical structure of human immunodeficiency virus 1 protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8864–8868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Viral latency and transformation: the strategy of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaris-Karatzas A., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):544–547. doi: 10.1038/345544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The p53 protein and its interactions with the oncogene products of the small DNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90505-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Tarlé S. A., Hajra A., Claxton D. F., Marlton P., Freedman M., Siciliano M. J., Collins F. S. Fusion between transcription factor CBF beta/PEBP2 beta and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.8351518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjar J. J., Michel S., Cozzone A. J., Reboud J. P. A method to identify individual proteins in four different two-dimensional gel electrophoresis systems: application to Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):174–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Ward D. C. Nucleoplasmic organization of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in cultured human cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):715–727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Blobel G. Nopp140 shuttles on tracks between nucleolus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90539-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myer V. E., Lee S. I., Steitz J. A. Viral small nuclear ribonucleoproteins bind a protein implicated in messenger RNA destabilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Erickson P., Drabkin H. A., Rowley J. D. The 3;21 translocation in myelodysplasia results in a fusion transcript between the AML1 gene and the gene for EAP, a highly conserved protein associated with the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7784–7788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Higo K., Osawa S. Isolation of seventeen proteins and amino-terminal amino acid sequences of eight proteins from cytoplasmic ribosomes of yeast. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4545–4550. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwemmle M., Clemens M. J., Hilse K., Pfeifer K., Tröster H., Müller W. E., Bachmann M. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 in interphase and mitotic Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10292–10296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Flint J. Transcriptional and transforming activities of the adenovirus E1A proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:47–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60995-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Williams D. G., Venables P. J., Maini R. N. Monoclonal antibodies to the Sjögren's syndrome associated antigen SS-B (La). J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 28;77(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. J., Denell R. Mutations in the Drosophila gene encoding ribosomal protein S6 cause tissue overgrowth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2524–2535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S., Huneycutt B. S., Reiss C. S., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) do not modulate interferon effects in infected lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5133–5136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5133-5136.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toczyski D. P., Steitz J. A. EAP, a highly conserved cellular protein associated with Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs (EBERs). EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):459–466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toczyski D. P., Steitz J. A. The cellular RNA-binding protein EAP recognizes a conserved stem-loop in the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):703–710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Collatz E., Wool E. G., Lin A. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 60 S ribosomal subunit proteins L4, L5, L7, L9, L11, L12, L13, L21, L22, L23, L26, L27, L30, L33, L35', L37, and L39. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7940–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Zinn A. R., Page D. C., Nishimoto T. Functional equivalence of human X- and Y-encoded isoforms of ribosomal protein S4 consistent with a role in Turner syndrome. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):268–271. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Konrad K. D., Woods D. F., Bryant P. J. Drosophila homolog of the human S6 ribosomal protein is required for tumor suppression in the hematopoietic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11302–11306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Mann R. B., Epstein J. I., MacMahon E., Lee W. A., Charache P., Hayward S. D., Kurman R. J., Hayward G. S., Ambinder R. F. Abundant expression of EBER1 small nuclear RNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A morphologically distinctive target for detection of Epstein-Barr virus in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded carcinoma specimens. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1461–1469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]